Name: Email
advertisement

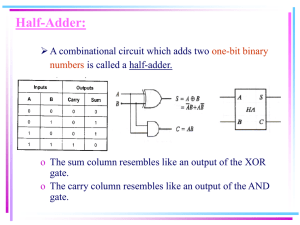
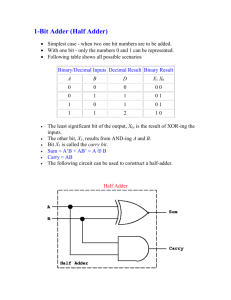
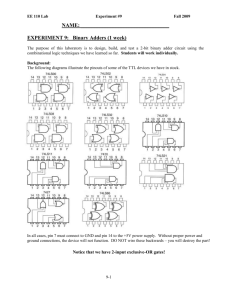
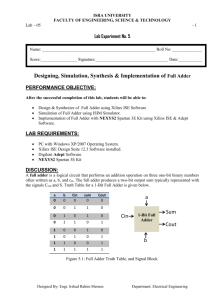
Computer Engineering: CMPE110 Spring11 Name: _____________________ Email:_____________________ HW 2 1. Amdahl’s Law: Assume that an architect is thinking about adding a vector functional unit (FU). When an instruction stream is executed using this FU, it runs 16 times faster than when the same instruction stream is executed in scalar mode. For the purpose of this question, the percentage of vectorization is defined to be the percentage of time that could be spent using vector mode in a given program. What percentage of vectorization is needed to achieve a speedup of 3? (10 points) 2. The Boolean equation for a full adder is • SUM = A XOR B XOR C • Cout = (A *B) + (A*Cin) + (B*Cin) a. Draw the gate level representation of the Cout function using NAND gates and show resulting equation. (2 points) 1|Page Computer Engineering: CMPE110 Spring11 3. Below is a functional view of a 4-bit ripple-carry adder. A0 B0 A1 FA C0 B1 FA C1 S0 A2 B2 FA C2 S1 A3 B3 FA C3 S2 Cout S3 a. Draw a gate level representation using AND, OR, , and XOR gates (2 points) A TMC foundry just issued their latest specification for their new TMC45(nm) technology in the table below. Propagation Delay Table Inputs AND 2-input 10 ps 3-input 12 ps 4-input 15 ps 5-input 20 ps for Technology TMC-45 OR XOR 15 ps 25 ps 18 ps 30 ps 20 ps 35 ps 25 ps 40 ps b. Given the propagation delays for TMC-45, draw a line through the critical path of the 4-bit ripple-carry adder. What is the delay associated with the critical path? (4 points) 2|Page Computer Engineering: CMPE110 c. Spring11 Assume the input to the ripple-carry adder is A=3, B=14 and Cin=0. Draw a timing diagram for all outputs (extend diagram as required). Indicate on each Sum signal its actual propagation delay time. Assume calculation of delay starts on the positive edge of the clock. (10 points) CLK C0 A0 B0 C1 A1 B1 C2 A2 B2 C3 A3 B3 S0 S1 S2 S3 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 3|Page Computer Engineering: CMPE110 Spring11 4. The carry lookahead adder decreases propagation delay by implementing a lookahead network. The Boolean representation for one such network is provided in the equations below. C1 = C2 = C3 = C4 = G0 + G1 + G2 + G3 + P0C0 P1C1 = G1 + P1(G0 + P0C0) = G1 + P1G0 + P1P0C0 P2C2 = G2 + P2G1 + P2P1G0 + P2P1P0C0 P3C3 = G3 + P3G2 + P3P2G1 + P3P2P1G0 + P3P2P1P0C0 The carry lookhead adder below is implemented using this lookahead network: P[3] G[2] P[3] C[out ] P [3] P [2] G[1] A[3] P [3] B[3] G[3] C[4] P [3] P [2] P [1] G[0] P [3] P [2] P[ 1] P [0] C[0] G[3] P[2] G[1] P[2] P[1] G[0] P[2] A[2] C[3] P[2] P[1] P[0] B[2] C[0] G[2] G[2] Sum [1] P[1] P[1] A[1] B[1] G[1] G[0] C[2] P[1] P[0] C[0] G[1] P[0] B[0] Sum [ 0] P[0] C[1] C[0] B[0] G[0] G[0] C[in] PG Generator Carry Generator Sum Generator . a. Given that A =3 and B = 14 and Cin=0, define the value for each of the signals in the carry lookahead adder equations. Signals Adder[0] (i=0) Adder[1] (i=1) Adder[2] (i=2) Adder[3] (i=3) P[i] G[i] C[i] Sum[i] 4|Page Computer Engineering: CMPE110 Spring11 b. Given the delays for the TMC-45 logic, what is the worse-case propagation delay from valid inputs (available at the same clock edge) to stable state for each sum output bit and the Cout value. Signals Worse-case propagation delays Adder[0] Adder[1] Adder[2] Adder[3] (i=0) (i=1) (i=2) (i=3) Cout Sum[i] 5|Page