Key to Cell Worksheet PPT
advertisement

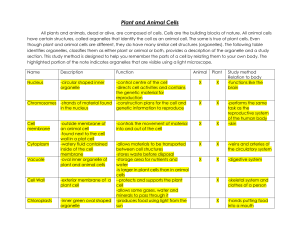
KEY TO CELL WORKSHEET BIO 137 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Dr. Mary Cat Flath Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath Directions: Label the cell parts in the diagram on the next slide., and then fill-inthe-blanks regarding the structure and function of each labeled part on the pages that follow. A key will be posted next week. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 2d. ______________ 1. _______ 2a. _________________ 2c.________ 9.________________ l l l 2b. ___________________ 10. ___________________ 3. _______________ 4. ____________ 11. ____________ 12. __________ 5. ____________ 13. __________ 6. _______________ 7. _____________________ Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 8. ______________________ 2d. chromatin 1. flagellum____________ 2c.nucleolus 2a. nuclear envelope______ l l l 2b. nucleus_________________ l 3. centrioles/ centrosome 4. mitochondrion__ 9.ribosomes 10. cell membrane 11. rough endoplasmic reticulum 12. smooth endoplasmic reticulum 5. microvilli_____ 13. cilia 6. Golgi Apparatus__ 7. microtubule_____________ Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 8. lysosomes____________ 1. Name the long tail-like extension. FLAGELLUM • The function of this extension is TO PROVIDE LOCOMOTION FOR THE CELL. • Name the only human cell that possesses this organelle. SPERM Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 2a. Name the cell part. NUCLEAR ENVELOPE • The membrane surrounding # 2b below, is similar to the cell membrane, however it fuses at some points to form NUCLEAR PORES. • Name two things that readily pass through these pores. – RIBOSOMES – MESSENGER RNA Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 2b. Name cell part. NUCLEUS • This central core of the cell functions to control all cellular activities. It contains DNA (and proteins), which directs protein synthesis in the cell. • The most important function of the proteins synthesized by the cell is that some serve as biological catalysts called ENZYMES. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 2c. Name the organelle. NUCLEOLUS • This dense-staining, spherical organelle within the nucleus is composed of what two macromolecules? RNA and PROTEIN. • It functions in the synthesis of what other organelle? RIBOSOMES • FYI: Cells may possess more than one of this organelle. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 2d. Name the organelle. CHROMATIN • During the majority of a cell’s life, it’s DNA is loosely coiled with nuclear protein and is referred to as CHROMATIN. • If the cell were preparing to divide, how would its DNA (and protein) appear? CHROMOSOMES Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 3. Name the cell part. Pair of CENTRIOLES (or CENTROSOME) • This pair of cylinders composed of microtubules is always located near the cell nucleus, and at right angles to one another. • This structure (or structures) aid in the migration of CHROMOSOMES during cell division (or mitosis). Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 4. Name the cell part. MITOCHONDRION • The inner membrane of this kidneyshaped organelle is folded into shelflike partitions called CRISTAE. • The function of this organelle is to release ENERGY/ATP from nutrients we eat in a process called CELLULAR RESPIRATION. • Consequently, this organelle is commonly called the POWER-HOUSE of the cell. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 5. Name these extensions of the cell membrane. MICROVILLI • Name the function of these extensions. TO INCREASE THE SURFACE AREA OF THE MEMBRANE • Name the human organ whose lining possesses these. SMALL INTESTINE Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 6. Name the cellular organelle. GOLGI APPARATUS • This “stack of pancakes” functions to MODIFY, PACKAGE, and TRANSPORT newly made proteins in the cell. • Each “pancake” is called a CISTERNAE, and possesses necessary enzymes to perform the function above. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 7. Name this protein filament. MICROTUBULE • These protein filaments along with microfilaments and intermediate filaments compose the CYTOSKELETON of the cell. • These function to support the cell and are sometimes called the “BONES and MUSCLES” of the cell. • These protein filaments also allow for INTRACELLULAR TRANSPORT. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 8. Name these organelles. LYSOSOMES • These membranous sacs contain DIGESTIVE enzymes that destroy worn cell parts and foreign debris. • Because they function in this manner they are sometimes called the SUICIDE SACS of the cell. • Special white blood cells called PHAGOCYTES have many of these organelles, and function to eat and destroy bacteria and prevent disease. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 9. Name the organelles. RIBOSOMES • These small organelles are composed of what two macromolecules? RNA and PROTEINS • In what organelle were these organelles synthesized? NUCLEOLUS • Name the function of these organelles. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • These organelles can be free in the cytoplasm or studded on the membranes of ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 9. continued • Besides enzymes, list five other functions of proteins. – STRUCTURE – TRANSPORT – CHEMICAL MESSENGERS – MOVEMENT – DEFENSE Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 10. Name the organelle. CELL MEMBRANE • This outer boundary of the cell is composed of a bilayer of (a) PHOSPHOLIPIDS and (b) PROTEINS. • 10a. are positioned so that their PHOSPHATE- heads (which are polar) form the surfaces of the membrane. Therefore the membrane surfaces are hydrophilic. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 10. continued • The FATTY-ACID tails (which are non- polar portion of 10a) form the internal portion of the membrane. Therefore the membrane is essentially hydrophobic. • This membrane is selectively permeable, which means it CONTROLS WHAT ENTERS and LEAVES the cell (I.E. MEMBRANE TRANSPORT) • In general, small, FAT-soluble substances pass through this membrane more readily than WATER-soluble substances. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 11. Name the organelle. ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • This maze of membranous channels is studded with what other organelles? ROBOSOMES • This organelle functions to synthesize PROTEINS for the cell. • Once synthesized, these structures must pass to the GOLGI APPARATUS to be modified, packaged, and transported. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 12. Name the organelle. SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • This maze of membranous channels functions to synthesize LIPIDS and CHOLESTEROL for the cell. • Name the functions of the macromolecule made at this organelle. – ENERGY STORE – CHEMICAL MESSENGERS (HORMONES) – CELL MEMBRANE COMPONENTS Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 13. Name the cellular extensions. CILIA • Name the function of these eyelash-like extensions. TO BEAT AND PUSH SUBSTANCES THROUGH PASSAGEWAYS • Name the human organ whose lining possesses these. TRACHEA Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath All of the organelles discussed above are suspended in a jellylike fluid called CYTOPLASM. Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 2d. chromatin 1. flagellum____________ 2c.nucleolus 2a. nuclear envelope______ l l l 2b. nucleus_________________ l 3. centrioles/ centrosome 4. mitochondrion__ 9.ribosomes 10. cell membrane 11. rough endoplasmic reticulum 12. smooth endoplasmic reticulum 5. microvilli_____ 13. cilia 6. Golgi Apparatus__ 7. microtubule_____________ Copyright 2012 Dr. Mary Cat Flath 8. lysosomes____________