Soft Skills WBT - Learning, Design and Technology
advertisement

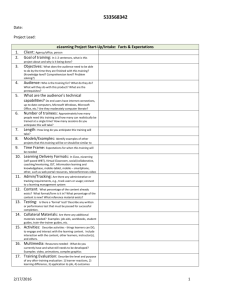
Soft Skills WBT A How-to for Human Resources Development Professionals Janette Cullinan Learning, Design, and Technology Stanford University School of Education June 2000 Curriculum in Brief Below is a brief description of the content in each module, including the key messages of the module, any tools associated with the module, and the basic activity of the module. The writing style matches that of the WBT program, informal and direct. Introduction: This Course Is … Key Messages The course is targeted to experienced HRD professionals who are new to WBT. Although content is applicable to all kinds of WBT, the course focuses on selecting and implementing a packaged soft skills WBT. In order to successfully implement WBT for soft skills topics, this class will define learning as creating change in the community of practice. At the end of the class, you should be able to consider issues specific to WBT in order to implement a program as one piece of an overall strategy for creating change in the community of practice. Introduction: Tour of Course Features Key Messages Knowing the features offered by the course will help you choose what you find most useful. Defining Learning: An Introduction to Communities of Practice Key Messages You “learn” a lasting skill by developing it on the job in your community of practice, rather than by acquiring it in class. Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 2 Learning is more about creating change within the community of practice than changing the behavior of an individual. Given this perspective on learning, WBT can be a good beginning to that learning process if you use it as part of an overall strategy. Activity Considering a training you have recently attended, you note what in your workplace community of practice supported the application of your new skill and what did not. Self-Critique Did you consider these factors? Incentive or recognition programs Workgroup norms Your manager's practices Co-workers' expectations What people joke about in your office Senior management behavior Needs Assessment: Overview Key Messages Even more than for your instructor-led classes, conduct a thorough assessment of cultural readiness for the content. Will learners return to their community of practice only to be discouraged from applying their new skill? It’s important for you to understand the state of your technology infrastructure before you decide that WBT is a part of your strategy. Tools The Needs Assessment Analysis Tool can be found at www.stnford.edu/~janettec/master/needs.doc. Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 3 Activity Consider a content area you are considering delivering via the web. Go through the Needs Assessment Analysis Tool and quickly jot down answers to the questions. If you don’t know, guess. Self-Critique Now review the form you’ve filled out and consider these questions. Which questions were new considerations for you? Surprised you? Who could you ask about the questions where you guessed? Given the answers you’ve documented, what might you want to do within the organization before embarking on implementing a WBT strategy? Choosing a WBT Program: Overview Key Messages As with ILT programs, there is no right answer. This course will try to provide you with a solid process and a set of criteria to consider. You are probably used to choosing programs on your own and then conducting a pilot for feedback. Since WBT has no live instructor to mediate course content for users, it’s important that the program itself be usable and appeal to a variety of users. Use an evaluation team to help you choose the right program to pilot. Choosing a WBT Program: Getting Familiar with What’s out There Key Messages Before you involve a team, be sure you understand what vendors are providing the kind of content Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 4 you’re looking for. You’ll understand the work ahead better and make your process more efficient. Tools You can find the Program Evaluation Form at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/eval.doc. Activity Check out different vendor course libraries to see if they provide the kind of content you’re interested in. Using the Program Evaluation Form, look at their advertising material and start to think about ways you’ll differentiate between vendors and products. Choosing a WBT Program: Choosing an Evaluation Team Key Messages Follow basic team effectiveness guidelines. Include a variety of functional areas along with a diversity of background and style. Activity Include IS from the beginning. Considering a content area you are looking to implement in the near future, choose an evaluation team. Self-Critique Critique your list with the following questions: Is the team a manageable size? Have you included some WBT skeptics to help push the team to be thorough and consider alternatives? Are there groups of users in your target audience whose concerns won’t be represented by this team? Is the IS person you’ve chosen an influential advocate? Are they knowledgeable about WBTrelated infrastructure issues? Who needs to buy-in to the team representatives? Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 5 Who could provide advice on the composition of the team? Choosing a WBT Program: Defining and Prioritizing Criteria Key Messages Consider a broad set of criteria, but prioritize so you can make trade-offs. Define what you and your team think you’ll need to be successful in your organization. Tools Find the Program Evaluation Form at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/eval.doc. Find the Sample Criteria and Definitions at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/samples.doc. Activity Take a quick run at defining the criteria outlined on the Program Evaluation Form. Even if you’re not familiar with a particular set of criteria, take a guess at what might be important. Self-Critique Use the Sample Criteria and Definitions document to look back over your first try at defining and prioritizing criteria. Do you see some definitions that you didn’t think of which might be critical to your organization? Might you now change your definition of your needs? How will that impact the priority you’ve given to different criteria? What questions do you now have that need to be answered before you can help your evaluation team define and prioritize criteria? Choosing a WBT Program: Previewing Programs Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 6 Key Messages The more programs you review, the more ideas you will have about what you want for your implementation. Use all resources available to you, but the best way to review programs is to actually take and complete the class. Have more than one team member look at each program, so you get different perspectives. You’re not likely to find the one and only program that works for everyone. Focus on finding the one that meets as many needs as your team can articulate and evaluate. Tools Find the Program Evaluation Form at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/eval.doc. Activity Go back to the vendors and programs you reviewed in “Getting Familiar with What’s out There.” Using any materials readily available to you, try to rate each program against your current draft of criteria on the Program Evaluation Form. Self-Critique How does the quality of readily available materials impact your ability to evaluate whether a particular program will meet your needs? What materials will you plan to have available to your evaluation team? Could you formulate a set of questions to ask every vendor about their products? What criteria are you finding hardest to evaluate? How might you prepare your team to better consider these tough issues? Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 7 Choosing a WBT Program: Piloting Programs Key Messages A pilot is absolutely essential to a successful soft skills WBT implementation. Try to make the pilot conditions match as closely as possible with those for your actual implementation. Be open to any feedback, but be sure the evaluation team has identified some specific questions to be answered in the pilot. Tools Find the Pilot Evaluation Form at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/eval.doc. Activity Given the work you’ve done so far in defining criteria and previewing programs, do a quick customization of the Pilot Evaluation Form to be sure you’ll get the feedback you need for a successful implementation in your organization. Self-Critique Did you include questions that related to your top five criteria? Did you ask for feedback on how successful the course would be in the learner’s community of practice given the current climate and company initiatives? Look at the form and visualize the way you would present this data to argue that the implementation will be successful. Might you need different demographic information? Questions worded slightly differently? Planning Implementation: Overview – Focusing on the User Experience Key Messages Go ahead and build the elements of your Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 8 implementation plan according to your usual process, but make sure you consider that plan from the perspective of the target audience – employees from different parts of the organization. Planning Implementation: Building Your Plan – Creating Change in the Community of Practice Key Messages Make sure you have done your best to eliminate barriers to the development of the new skill within the community of practice. Because soft skills WBT is often an individual experience, your implementation plan must include ways of having the workgroup collaboratively deal with the content. Tools Find the Needs Assessment Analysis at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/needs.doc. Activity Go back to the Needs Assessment document and flag the questions in the Cultural Readiness for Content section that might be a barrier to employees developing a new skill in this content area within the community of practice. Jot down some ideas about what your implementation plan should include to help remove or overcome these barriers. Self-Critique Are you feeling discouraged? Whose help might you need to enlist to start working on these tough issues? Have you considered possible organizational incentives for developing this skill? Who has a vested interest in creating this change in the community of practice and might be an ally Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 9 to you in this effort? What kind of help can they offer you? How could you easily get some information from your target audience about how they view the current practices and the possibility for change? Planning Implementation: Considering Motivation Key Messages You should know why employees would be motivated to take and complete the WBT program. Your implementation plan should include elements that will create a “pull” for this content. WBT is a very easy way for employees to access content if they are motivated to learn it. Tools Find the Implementation Plan Review at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/tool.doc. Activity Considering the content area you are looking to implement, go through the Motivation section of the Implementation Plan Review and answer those questions. Be sure to think about the questions from the perspective of employees from different parts of the target audience. Self-Critique Given your answers to these questions, how likely are employees to take this class? Of the problems highlighted by this set of questions, which is easiest to change quickly? How would you start? Are there other motivation questions to consider in your particular workplace? Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 10 Planning Implementation: Building Buy-in and Accountability Key Messages If you’re worried about people finishing a WBT program, make sure you build in accountability to their manager or co-workers. This strategy only works if managers or coworkers have bought into the importance of the content and have a mechanism for monitoring progress. Team events and agreements are one of the best ways to build in a reason for finishing by a certain deadline. Tools Find the Implementation Plan Review Tool at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/tool.doc. Activity For your WBT implementation Plan, answer the questions in the Accountability section of the Implementation Plan Review Tool. Self-Critique If you don’t have concrete answers to the questions, brainstorm some ideas on how your implementation plan might build in these mechanisms for accountability. How could these questions be answered if the implementation plans focused on the team and changing as a community of practice rather than a set of individuals being required to finish a specific class? Does your implementation plan include an opportunity for interaction with peers around the content? Planning Implementation: Supporting Desktop Learning Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 11 Key Messages The devil is in the details for a successful desktop learning implementation. Be sure you’ve thought through and tested the details. Try to anticipate and avert technical problems, but be sure users have somewhere to turn when they need help. Consider the realities of employees’ desks and find creative ways to help them make time for learning. Tools Find the Implementation Plan Review Tool at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/tool.doc. Activity Answer the questions in the Supporting Desktop Learning Section of the Implementation Plan Review Tool. Self-Critique Have you considered these questions for the variety of functional areas within the target audience? Does your implementation plan provide a resource for employees to get quick, easy answers to these questions? If you don’t know the answers to some of these questions, who can you ask? Planning Implementation: Applying Learning – The User Experience Key Messages Think through how the WBT program you’ve selected and your implementation plan will support learners in applying their new knowledge or skill. Tools Find the Implementation Plan Review Tool at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/tool.doc. Activity Try answering the questions in the Applying Learning Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 12 section of the Implementation Plan Review Tool for your upcoming implementation. Self-Critique Given your answers, how hard will it be for an individual to start applying their new knowledge or skill on the job? Are there some easy ways for you to augment your implementation plan to improve their chances? How will these answers differ for employees from different organizations or functions within the target audience? Do you need more information about the user’s perspective on this before you can improve your plan? Planning Implementation: Developing a Strategy for Continuous Evaluation Key Messages Define success up front and be sure you can get the data you need to evaluate whether you are attaining it. One of the great benefits of WBT programs is that you get real-time data on how people are using (or not using) the system. Be sure you’ve defined how this data will contribute to your definition of a successful implementation. Some of it may not be important to you. Watch your measurements regularly so you can intervene. The real value of real-time data is that you can make corrections before it’s too late. Tools Find the Implementation Plan Review Tool at www.stanford.edu/~janettec/master/tool.doc. Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 13 Activity Make a quick draft of a set of objectives for an upcoming implementation and note down the measurements you would use to monitor successfully meeting those objectives. Self-Critique What data could your WBT system provide to help you monitor progress toward meeting your objectives? Who should see this data and how often? Think about what would happen if these measures were showing poor progress. Would you be able to intervene quickly? Wrap-up Activity: Design Your Own Reference Page This module would provide the user with one page containing all the resources or text they selected during the course. The user could then organize these elements into a coherent document for future use. Soft Skills WBT: A How To for HRD Professionals Page 14