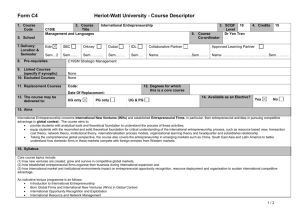
Intrapreneurship - entrepreneurship within large organizations
advertisement

TRENDS IN RESEARCH AND EDUCATION Intrapreneurship - entrepreneurship within large organizations Gazelle - a business establishment with at least 20% sales growth every year (for five years), starting with a base of at least $100,000. o Gazelles produce twice as many product innovations per employee as do larger firms. o The common myth is that 85% of all firms fail in the first year. o The more accurate statement is that about half of all start-ups last between 5 and 7 years. INTERNET Smaller ventures use the Internet for a variety of operations: o customer-based identification o advertising o consumer sales o business-to-business transactions o e-mail o private internal networks for employees. Stickiness – how long a website can keep someone looking at it #1 use is for company information EVOLUTION OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP Entreprendre – French for to undertake: where entrepreneurship is derived from. The Corridor Principle - With every venture launched, new and unintended opportunities often arise. (Post it notes) Entrepreneurial Schools-of-Thought Approach The Macro View (External locus of control) o The Environmental School of Thought o The Financial/Capital School of Thought o The Displacement School of Thought 1. Political Displacement 2. Cultural Displacement 3. Economic Displacement The Micro View (Internal locus of control) o The Entrepreneurial Trait School of Thought o The Venture Opportunity School of Thought o The Strategic Formulation School of Thought Strategic Formulation as a Leveraging of Unique Elements - Unique Markets: mountain gap strategies - Unique People: great chef strategies - Unique Products: better widget strategies - Unique Resources: water well strategies 3M’s Innovation Rules o Don’t kill a project o Tolerate failure o Keep divisions small o Motivate the champions o Stay close to the customer o Share the wealth Corporate Entrepreneurship Assessment Instrument (CEAI) (measured key entrepreneurial climate factors) o Management Support o Autonomy/Work Discretion o Rewards/Reinforcement o Time Availability o Organizational Boundary Venture Team - composed of two or more people who formally create and share the ownership of a new organization. o The leader is called a “product champion” or an “intrapreneur”. The Top Ten Characteristics Today’s Entrepreneurs Share: o Recognize and take advantage of opportunities o Resourceful o Creative o Visionary o Independent thinker o Hard worker o Optimistic o Innovator o Risk taker o Leader The Dark Side of Entrepreneurship o Confrontation with Risk 1. Financial Risk 2. Career Risk 3. Family and Social Risk 4. Psychic Risk o Stress o Ego 1. Extreme Sense of Distrust 2. Overbearing Need for Control 3. Overriding Desire for Success 4. Unrealistic Optimism Creativity - the generation of ideas that result in the improved efficiency or effectiveness of a system. Innovation - The process by which entrepreneurs convert opportunities into marketable ideas. More than just a good idea. 1. Types of Innovation o Invention o Extension o Duplication o Synthesis 2. Sources of Innovation 1. Unexpected Occurrences 2. Incongruities 3. Process Needs 4. Industry and Market Changes 5. Demographic Changes 6. Perceptual Changes 7. Knowledge-Based Concepts ETHICS The four rationalizations are believing…. 1. that the activity is not “really” illegal or immoral; 2. that it is in the individual’s or the corporation’s best interest; 3. that it will never be found out; and 4. that because it helps the company, the company will condone it. Types of morally questionable acts: Non-role: Against the firm. Expense Account cheating Role Failure: Against the firm. Superficial Performance Appraisal Role Distortion: For the firm. Bribery Role Assertion: For the firm. Not withdrawing product line until sold enough Code of conduct - is a statement of ethical practices or guidelines to which an enterprise adheres. Approaches to Managerial Ethics: -Immoral Management: Managerial decisions, actions and behavior imply a positive and active oppositions to what is moral (ethical). Decisions are discordant with accepted ethical principles. An active negation of what is moral is implied. -Amoral Management: Management is neither moral nor immoral, but decisions lie outside the sphere to which moral judgments apply. Managerial activity is outside or beyond the moral order of a particular code. A lack of ethical perception and moral awareness may be implied. -Moral Management: Managerial activity conforms to a standard of ethical, or right, behavior. Managers conform to accepted professional standards of conduct. Ethical Leadership is common- place on the part of management. A Holistic Approach Principle 1: Hire the right people Principle 2: Set standards more than rules Principle 3: Don’t let yourself get isolated Principle 4: The most important principle is to let your ethical example at all times be absolutely impeccable The Social Responsibility Challenge - Social Obligation: Some firms simply react to social issues through obedience to the laws – Social Responsibility: others respond more actively; accepting responsibility for various programs - Social Responsiveness: still others are highly proactive and are even willing to be evaluated by the public for various activities NEW VENTURES Pitfalls in Selecting New Ventures o Lack of Objective Evaluation o No Real Insight into the Market o Inadequate Understanding of Technical Requirements o Poor Financial Understanding o Lack of Venture Uniqueness o Ignorance of Legal Issues Critical Factors for New-Venture Development o Uniqueness o Investment o Sales Growth o Lifestyle ventures o Small profitable ventures o High-growth ventures o Product Availability o Customer Availability Why New Ventures Fail o Product/Market Problems o Financial Difficulties o Managerial Problems Types and Classes of First-Year Problems 1. Obtaining external financing 2. Internal financial management 3. Sales/marketing 4. Product development 5. Production/operations management 6. General management 7. Human resource management 8. Economic environment 9. Regulatory environment MARKETING Business incubator - is a facility with adaptable space that small businesses can lease on flexible terms and at reduced rents. Types of Incubators 1. Publicly Sponsored 2. Nonprofit-sponsored 3. University-related 4. Privately sponsored Market - a group of consumers (potential customers) who have purchasing power and unsatisfied needs. A new venture will survive only if a market exists for its product or service. Market segmentation - is the process of identifying a specific set of characteristics that differentiate one group of consumers from the rest (market niche). Consumer Behavior Five Major Classifications: 1. Convenience goods: gum at the register, milk. 2. Shopping goods: things you shop for, car, house, college 3. Specialty goods: hard to find, price doesn’t matter, souvenirs 4. Unsought goods: insurance, cemetery plot, they find you 5. New products: Unknown, new invention Pricing for the Product Life Cycle - Unique product: Skimming-deliberately setting a high price to maximize short-term profits - Non-unique product: Penetration-setting prices at such a low level that products are sold at a loss - Growth Stage: Consumer Pricing- combining penetration and competitive pricing to gain market share; depends on consumer’s perceived value of product - Maturity Stage: Demand oriented pricing- a flexible strategy that bases pricing decisions on the demand level for the product - Decline Stage: Loss Leader Pricing- pricing the product below cost in an attempt to attract customers to other products Geographic Pricing: depending on where you live FINANCIAL The Balance Sheet – (also called a snapshot) Represents the financial condition of a company at a certain date. It details the items the company owns (assets) and the amount the company owes (liabilities). It also shows the net worth of the company and its liquidity. Assets = Liability + Owners Equity The Income Statement - Commonly referred to as the P & L (profit and loss) statement, which provides the owner/manager with the results of operations. Statement of Cash Flow - An analysis of the cash availability and cash needs of the business. Preparing Financial Statements - The Operating Budget - Typically, the first step in creating an operating budget is the preparation of the sales forecast. An entrepreneur can prepare the sales forecast in several ways. One way is to implement a statistical forecasting technique such as simple linear regression. - The Cash-Flow Budget - The first step in the preparation of the cash-flow budget is the identification and timing of the cash inflows. For the typical business, cash inflows will come from three sources: (1) cash sales, (2) cash payments received on account, and (3) load proceeds. - Capital Budgeting - The first step in capital budgeting is to identify the cash flows and their timing. The inflows, or returns as they are commonly called, are equal to net operating income before deduction of payments to the financing sources but after the deduction of applicable taxes and with depreciation added back. Pro Forma Statements - Pro forma statements are projections of a firm’s financial position over a future period (pro forma income statement) or on a future date (pro forma balance sheet). Payback Method - In this method the length of time required to “pay back” the original investment is the determining criterion. Net Present Value (NPV method) - The concept works on the premise that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. The cost of capital is the rate used to adjust future cash flows to determine their value in present period terms. This procedure is referred to as discounting the future cash flows, and the discounted cash value is determined by the present value of the cash flow. Internal Rate of Return (IRR method) - This method is similar to the net present value method in that the future cash flows are discounted. However, they are discounted at a rate that makes the net present value of the project equal to zero. BUSNISESS PLANNING Pitfalls to Avoid in Planning Pitfall 1: No Realistic Goals Pitfall 2: Failure to Anticipate Roadblocks Pitfall 3: No Commitment or Dedication Pitfall 4: Lack of Demonstrated Experience (Business or Technical) Pitfall 5: No Market Niche (Segment) Business Plan: no more than 40 pages and summary no more that 2 pages. LEGAL STRUCTURES FOR NEW BUSINESS VENTURES Sole Proprietorship – (most common) a business that is owned and operated by one person. The enterprise has no existence apart from its owner. Partnership – an association of two or more persons acting as co-owners of a business for profit Corporation – and artificial being, invisible, intangible, and existing only in contemplation of the law; a separate legal entity apart from the individuals who own it. (Limited liability) Limited Partnership (LP) – permits capital investment without responsibility for management and without liability for losses beyond the initial investment. Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) – relatively new, that allows professionals the tax benefits of a partnership while avoiding personal liability for the malpractice of other partners. S Corporations – a business can seek to avoid the imposition of income taxes at the corporate level yet retain some of the benefits of a corporate form. Commonly known as Tax Option Corporation, an S Corp is taxed similarly to a partnership. Limited Liability Companies (LLC) – a hybrid form of business enterprise that offers the limited liability of a corporation but the tax advantages of a partnership. Statutes differ from state to state so multi-state operations may face difficulty. Close Corporation – (gov. spending) can’t have more than 30 shareholders. Franchising – any arrangement in which the owner of a trademark, trade name, or copyright has licensed others to use it in selling goods or services. Franchisee – (a purchaser of a franchise) generally legally independent but economically dependant on the integrated business system of the franchisor. Franchisor – the seller of the franchise Governed by the UFOC (Uniform Franchise Offering Circular) STRATEGIC PLANNING and EMERGING VENTURES Strategic Planning – the formulation of long-range plans for the effective management of environmental light of a venture’s strengths and weaknesses. Lack of Strategic Planning 1. Time Scarcity 2. Lack of knowledge 3. Lack of skills 4. Lack of trust and openness 5. Perception of high cost Benefits of LONG RANGE 1. Cost Savings 2. More efficient resource allocation 3. Improved competitive position 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. More timely information More accurate forecasts Reduced feelings of uncertainty Faster decision making Fewer cash flow problems Strategic Planning Levels - Structured Strategic Plans – (SSP) intense detail, very carefully planned - Structured Operational Plans – (SOP) a how to guide - Intuitive Plans – (IP) plan for thinking structured thought - Unstructured Plans – (UP) Framework without details filled in 4 Key Factors During the Growth stage of the Bathtub Curve 1. Control 2. Responsibility 3. Tolerance of failure 4. Change – adapting to your environment #1 question in Due Diligence: Why is the business being sold? P/E Ratio (Price/Earnings Ratio) – multiple of earnings method LBO (Leveraged Buyout) – allows the entrepreneur to finance the transaction by borrowing on the target company’s assets. E-LBO (Entrepreneurial Leveraged Buyout) – characterized as having: At least 2/3 of the purchase price generated from borrowed funds More than 50% of the stock acquisition owned by single individuals or their family The majority of investors devote themselves to the active management of the company after acquisition ABREVIATIONS: NPV – Net Present Value IRR – Internal Rate of Return LP – Limited Partnership LLP – Limited Liability Partnership LLC – Limited Liability Companies UFOC – Uniform Franchise Offering Circular SSP – Structured Strategic Plans SOP – Structured Operational Plans IP – Intuitive Plans UP – Unstructured Plans LOC – Line of Credit IPO – Initial Public Offering LBO – Leveraged Buyout E-LBO – Entrepreneurial Leveraged Buyout CEAI – Corporate Entrepreneurship Assessment Instrument ESOP – Employee Stock Option Plan P/E Ratio – Price/Earnings