The 13 Colonies: The Details
advertisement

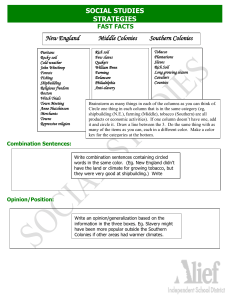
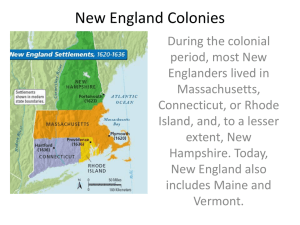
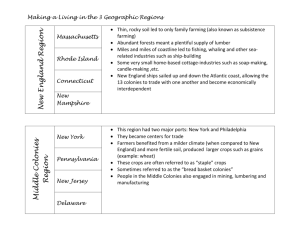
The 13 Colonies: The Details (Read pgs. 72 – 89) Section 1: Southern Colonies John Rolfe- Colonist John Rolfe introduced a new type of tobacco to the colonists of Jamestown, which they could see to England and make a profit. Pocahontas- The daughter of the Powhatan leader, married to John Rolfe. This marriage helped the colonists to have peaceful relations with the Powhatan Indians. Headright System- Plantations that were formed under the London Company. When a colonist paid his way to Virginia, he would receive 50 acres of land. If you paid for others, you would earn another 50 acres for each additional person. Indentured Servants- People who signed contracts to work for 4-7 years for the person or company that paid their journey. Bacon’s Rebellion- Group in 1676, who attacked and burned Jamestown due to Colonial high taxes and policies towards Indians. They wanted to take Indian land and to not be friendly with the Indians. Toleration Act of 1649- A bill to the colonial assembly that made it a crime to restrict the religious rights of Christians. Economy of the Southern Colonies: Cash crops- Crops that are sold for profit. Names of American cash crops- Cash crops were tobacco, rice, and indigo (plant used for making blue dye). Why slaves?- A large work force was needed to grow these crops. Slave Codes- These were laws to control slaves. Section 2: New England Colonies Separatists- People who wanted to separate from the Church of England. They wanted their own churches and to cut all ties with the Church of England. Puritans – A Protestant group of people who wanted to purify or reform the Anglican Church. Pilgrims- A Separatist group that left England in the early 1600s to escape persecution. Immigrants- People who have left the country of their birth to live in another country. Mayflower Compact- A legal contract in 2hich the Pilgrims agreed to gave four laws to protect the general good. Squanto- An Indian who had once lived in England and spoke English well. He helped the Pilgrims learn about crops and helped with Indian relationships. 3 ways women had more legal rights in America: Pilgrim women had the right to sign contracts and bring some cases before local courts. Widows could own property. The Great Migration – when and why: The time between 1629 and 1640, where many thousands of English men and families left England for economical, political, and religious reasons. The people had faced high taxes, unpopular King Charles I, and religious disagreements. New England Economy: 4 people groups important to New England’s Economy: 1. Merchants – People who traded and sold goods, such as furs, pickled beef, and pork. They grew in wealth and power. 2. Fishing – People who lived along the coastlines, and worked in catching and selling fish. Whaling was also a large industry. 3. Shipbuilding – The forests of New England provided the materials for shipbuilding. Shipbuilding among the coastal towns was a growing business for fishing, exporting, and cargo goods. 4. Skilled Craftspeople – People who did trades, such as blacksmithing, weaving, shipbuilding, and printing. Young boys learned these as apprentices. Education in the Colonies: Why Educate? Parents wanted their children to be able to read the Bible. Public Education – Communities established town schools. The General Court of Massachusetts ordered that a school be built around every 50 families. School children used the New England Primer and the Bible stories to learn to read. Some children had private tutors. Education was usually stopped after elementary grades. Then many went away to work or worked on family farms. Higher Education- In 1636, John Harvard founded Harvard College. It first taught ministers. Later other colonists pursued higher education. By 1700, 70% of men and 45% of women could read and write. Section 3: Middle Colonies Quakers- Also called the Society of Friends, were a large religious group in New Jersey and Pennsylvania. They believed in a plain life, equality of men and women, nonviolence, and religious tolerance. Middle Colony Economy: Staple Crops- Crops that were always needed. Names of Staple crops- Staple crops were wheat, barley, and oats. Where else did slaves work- New England slaves worked as skilled labors like blacksmiths and carpenters. They also worked on farms, ship building, and on ships. Who else helped the labor needs- Indentured servants. What was important to this economy?- Trade was very important to the economy. Merchants exported goods back to Britain and the West Indies. What did these women do?- They sometimes ran farms and businesses, practiced medicine, and worked as nurses and midwives. Most worked primarily in the home. They might earn more money for the family by selling garden or crafted items, or providing everyday services. History and Geography Chart page (88 & 89) A Wall of Mountains – The 1500 mile long Appalachian Mountain range, which formed a natural barrier on the west side. Natural Harbors- Large cities grew where the best natural ports were located, such as Philadelphia, New York, and Boston. Ships were important to fishing, industry, trade, and bringing in more settlers. Flood of People – The population of the colonies doubled between 1750 and 1770. Half of the people were immigrants, and half were slaves.