PowerPoint Presentation - 13 Colonies
advertisement

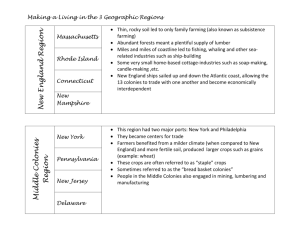
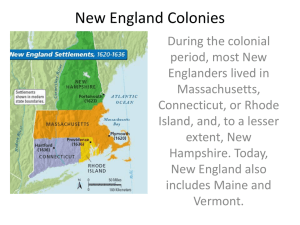
The 13 Colonies and Colonial Life The New England Colonies *Can you find Boston and the Erie Canal on your map? Massachusetts (Maine) New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies Video Climate Summers were warm, but short Winters were long and frigidly cold Very short growing season Soil and weather made farming very difficult Land Features o hilly terrain with mountains and valleys o thin and rocky soil o jagged coastlines Resources Forests with an abundance of wood Used wood to create ships and buildings Access to fish and whales-used for food and other products Shipped fish and lumber to Africa and Europe Received spices and tea for imports Formed a triangular trade Middle Colonies NY PA NJ DE The Middle colonies included: New York (NY) , New Jersey (NJ) , Delaware (DE), and Pennsylvania (PA). * Can you find New York City and Philadelphia on your map? Middle Colonies Video Climate More balanced summers and winters Longer growing season Soil was very fertile Sunny days and plenty of rainy days to feed crops Land Features o Rolling hills and valleys o Wide rivers like the Delaware and the Hudson were perfect to transport crops and receive farm supplies Resources Forests rich with wildlife Many hunted and trapped deer and beaver Perfectly fertile soil for growing MD VA Southern Colonies NC SC GA The Southern Colonies included: Maryland (MD), Virginia (VA), North Carolina (NC), South Carolina (SC), and Georgia (GA). Southern Colonies Video Climate Rich land, plenty of rain, and a long growing season Warm weather for much of the year Land Features • Coastal plains, swamps, forests, and harbors • Many rivers, bays, and wetlands • Tidewater- the water levels rise and fall everyday with the ocean tide Resources Forests in the backcountry Due to rich and fertile soil, many cash crops are grown Colonial Life Large Landowners A plantation is a large farm on which crops are raised by workers who live on the farm Landowners gained wealth by selling cash crops Needed help from indentured servants and slaves to keep the farm running Colonial Farms Video Farmers Struggled in New England Colonies-more prosperous in Middle and Southern colonies Raised livestock such as cattle and pigs Grew vegetables, fruit, and grains Artisans Were skilled at making something by hand such as silver spoons or wooden chairs Either owned their own store or worked from home Examples of artisans include blacksmiths, carpenters, and jewelers Women Roles depended on where they lived Had tough lives full of spinning, sewing, food preservation, cooking, cleaning, and caring for their families Indentured Servants Wanted a better life in America, but did not have the money to pay for their passage Got their passage paid for along with room and board in exchange for promising labor for 4-7 years Had few rights without the permission Most worked on large plantations working long, hard days Slaves and Indentured Servants Slaves Got here through the triangular trade Worked on Southern plantations as field laborers or servants Slowly replaced indentured slave labor Bought and sold like pieces of propertyoftentimes families are split apart Struggles of Slaves Were given poor shelter, food, and clothing-many died early Often punished by overseers Created a community of support Lived under harsh punishment and laws Some ran away or resisted in other ways Native Americans At first, colonists and Native Americans had a good relationship Native Americans taught colonists how to grow crops and survive the winter They traded with one another Once colonies were established, Indians were pushed West