Click Here for the answer key
advertisement

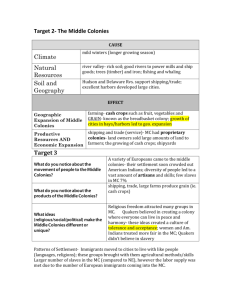
Middle Colonies Region New England Region Making a Living in the 3 Geographic Regions Massachusetts Rhode Island Connecticut Thin, rocky soil led to only family farming (also known as subsistence farming) Abundant forests meant a plentiful supply of lumber Miles and miles of coastline led to fishing, whaling and other searelated industries such as ship-building Some very small home-based cottage-industries such as soap-making, candle-making ,etc. New England ships sailed up and down the Atlantic coast, allowing the 13 colonies to trade with one another and become economically interdependent New Hampshire New York Pennsylvania New Jersey Delaware This region had two major ports: New York and Philadelphia They became centers for trade Farmers benefited from a milder climate (when compared to New England) and more fertile soil, produced larger crops such as grains (example: wheat) These crops are often referred to as “staple” crops Sometimes referred to as the “bread basket colonies” People in the Middle Colonies also engaged in mining, lumbering and manufacturing Southern Colonies Region Virginia Maryland South Carolina Georgia Had the richest soil and warmest climate of all 3 regions Most settlers made their living from farming Large property owners made their living from selling cash crops such as tobacco In the low-lying areas along the coast planting rice was profitable This region became dependent on slave labor and hired “overseers” to supervise the slaves and enforce strict “slave codes” The economies of the southern colonies grew faster than any other region because of cash crops and abundant, free slave labor. New England Colonies Middle Colonies General Geography and Climate Types of Farming Other types of economic activities Main Religion Types of Government Southern Colonies