New England Colonies
advertisement
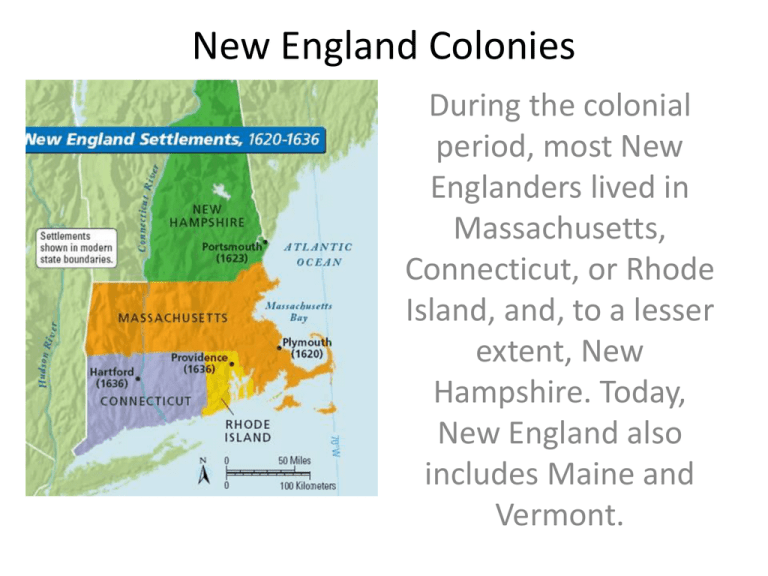
New England Colonies During the colonial period, most New Englanders lived in Massachusetts, Connecticut, or Rhode Island, and, to a lesser extent, New Hampshire. Today, New England also includes Maine and Vermont. Economy of New England Most New Englanders were farmers, but soils were rocky and the growing seasons were short. They grew mostly subsistence and staple crops to eat or trade locally. More than any other region, New England profited from the sea by fishing, whaling, and trading. Abundant timber helped make New England an important shipbuilding center. The Great Migration John Winthrop thought the Massachusetts Bay Colony would be a “city on a hill” that would serve as a shining example of purity. Between 1629 and 1640 more than 40,000 English Puritans came to New England. The Mayflower compact is the earliest example of self-government in the English colonies. Squanto and Samoset taught the Pilgrims how to farm in New England. Religion, Community, Education The town meeting was a cherished part of New England’s government. Ministers like Cotton Mather and Jonathan Edwards (above) were the most influential figures in New England New Englanders were the first to support public education because they felt all Christians had an obligation to read the Bible for themselves. Town meetings are still important in New England today. Dissenters Anne Hutchinson Although women and particularly widows had more rights in New England than in other regions, Puritan ministers were unwilling to accept Anne Hutchinson’s assertion that ordinary people, even women, could interpret the Holy Scriptures without the aid of Ministers. They banished her. Roger Williams was also banned by the Puritan ministers for advocating separation of church and state, religious tolerance, and fair treatment of Native Americans. He founded his own colony in Rhode Island. Middle Colonies New York, New Jersey, Delaware and Pennsylvania were the Middle Colonies The Middle Colonies produced staple crops and traded with each other as well as with New England and the Southern Colonies. Staple Crops In the Middle colonies farmers grew staple crops such as corn, wheat, barley, and oats, and raised cows, chickens, and pigs. Staple crops are crops that can be used to make staples of our diet like bread. Flour, butter, eggs, milk, etc. are considered staples. Staple crops would be consumed by the farmer and his family and traded locally. Diversity in the Middle Colonies The Middle Colonies were more ethnically and religiously diverse than the New England Colonies. From the Dutch in New York we get such American traditions as the Coffee Klatch, Santa Claus, Doughnuts, cookies, Ragamuffin Parades, and words like cookie, boss, and yacht. Philadelphia Freedom Pennsylvania was founded by William Penn and the Quakers (a.k.a. the society of Friends) who treated the Native Americans fairly, were pacifists, tolerated other faiths and even believed in equal rights for women. Southern Colonies The Southern Colonies of Maryland, Virginia, the Carolinas, and Georgia were where cash crops were grown using slave labor. Most southerners, however were small farmers who grew subsistence crops. Cash Crops Indigoused to make blue dye. Cotton was not grown in the South until later, but it eventually became an important cash crop. Rice was grown in the Carolinas. Tobacco, brought from the West Indies to Virginia by John Rolfe, helped save the colony. John Rolfe with his wife, Pocahontas Slavery Although there were a small number of slaves in New England and a larger number in the Middle Colonies, most imported African slaves worked on plantations in the South where they tended and harvested cash crops. Most plantations were in the South, but even in the South, most farms were small and most farmers could not afford slaves. First Colony The First English colony in the New World was Jamestown in Virginia. The colonists were saved from the ravages of the “starving time” by Pocahontas and her father, Chief Powhatan. An earlier colony at Roanoke disappeared mysteriously. The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly The first African slaves were brought to Virginia, also in 1619 In 1619 the House of Burgesses became the earliest example of representative government in the colonies. In 1676, a mob led by Nathaniel Bacon attacked friendly American Indians, stole their land and burned the capital. The uprising, known as Bacon’s Rebellion was later quashed. Gimme Shelter Maryland’s Religious Toleration Act of 1649 James Oglethorpe founded Georgia as a haven for debtors, who had been imprisoned in England for failing to repay the money they owed their creditors. Georgia served as a buffer between the English colonies and Spanish Florida. George Calvert, Lord Baltimore, founded Maryland as a refuge for English Catholics. England had been a Catholic country for 1,000 years, but, after the Reformation, Catholics were often persecuted, prompting some of them to seek religious freedom in Maryland.











