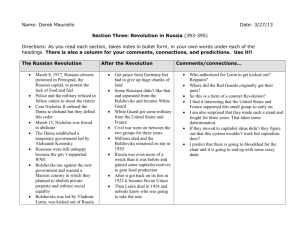
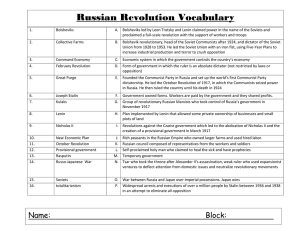
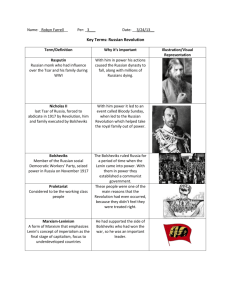
The Russian Revolution
advertisement

MP/Lecture 7/27 September/Russian Revolution/Overheads What is a revolution? Why do people revolt? Why Russia? Why did the war and revolution in Russia in 1904-5 not lead to the collapse of the tsars? Why did the Provisional Government fail to gain mass support in Russia? Why and how did the Bolsheviks succeed in gaining support in Russia? Why were communists so unsuccessful everywhere else? 1. What is a revolution? Transformation Political AND social Overthrow of old regime Violent? Contrast English and American revolutions with French and Russian Marx Lenin Role of coup d’état 2. Why do people revolt? Persecution War Famine Direction Education Political Consciousness – what does this mean? World view of pre-revolutionary revolutionary workers/peasants When do people revolt: de Tocqueville and 3. Why Russia? Changes leading up to 1905 o Declining power o Rapid industrialisation o Failure to modernise o Abrogation of new freedoms o Defeat in Russo-Japanese war 4. Why did the tsardom not collapse? Incoherent opposition Sufficient concessions by Tsar Tsar kept means of coercion 3 again: changes leading up to 1917 Not enough for: o Peasants o Workers o Political system But significant changes in: o Trade unions and political parties o Media o ? Notion of a Russian ‘state’ o War experience 5. Why did the Provisional Government not gain support? Authority Imperial inheritance Renunciation of means of coercion Existence of an alternative 6. Why were the Bolsheviks successful? Lenin Willingness to use any means 7. Why were communists so unsuccessful elsewhere? Britain France Italy Germany Hungary