Key Terms - Russian Revolution
advertisement

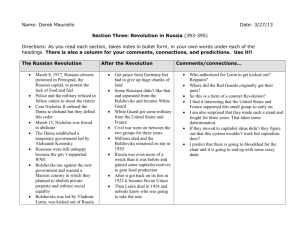
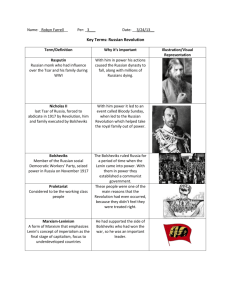
Name: _Christine Le___________ Per: _3___ Date: __3/24/13__ Key Terms: Russian Revolution Term/Definition Why it’s important Rasputin: A Russian monk who had influence over the Tsar and his family during World War I He led to the fall of the Russian Dynasty and was the cause of the death of millions Nicholas II: The last Tsar of Russia, forced to abdicate in 1917 by Revolution, him and his family executed by Bolsheviks He was hated by the Russian people, therefore he was a main cause of the Russian Revolution and the rebellions that started it Bolsheviks: Members of the Russian social Democratic Workers’ Party, seized power in Russia Nov. 1917 The Bolsheviks won the revolution and came into power in Russia afterward Illustration/Visual Representation Proletariat: Working class people The grievances of the Proletariat was one of the main causes of the revolution Marxism-Leninism: Expanded form of Marxism that emphasizes Lenin’s concept of imperialism as the final stage of capitalism, shifts focus to underdeveloped countries He led Russia during the Revolution and ruled the Bolsheviks who essentially won the revolution and then took control of Russia afterwards New Economic Policy: Proposed by Lenin after the Revolution when the economy began to fail, allowed some aspects of capitalism This policy did allow peasants to sell their goods, which is against communism Duma: Legislative body in the ruling assembly of Russia The Duma eventually were the ones who asked Tsar to step down Red Guard: Transitional military force from the imperial Russian army, base of Bolsheviks The Red Guard was made up of the Bolsheviks, who won the war and were procommunist The Whites: Confederation of Anti-Communist forces who fought the Bolsheviks during the civil war The Whites consisted of wealthy landowners and they generally didn’t support communism