Salivary amylase question Graph for student A should have dilutions
advertisement
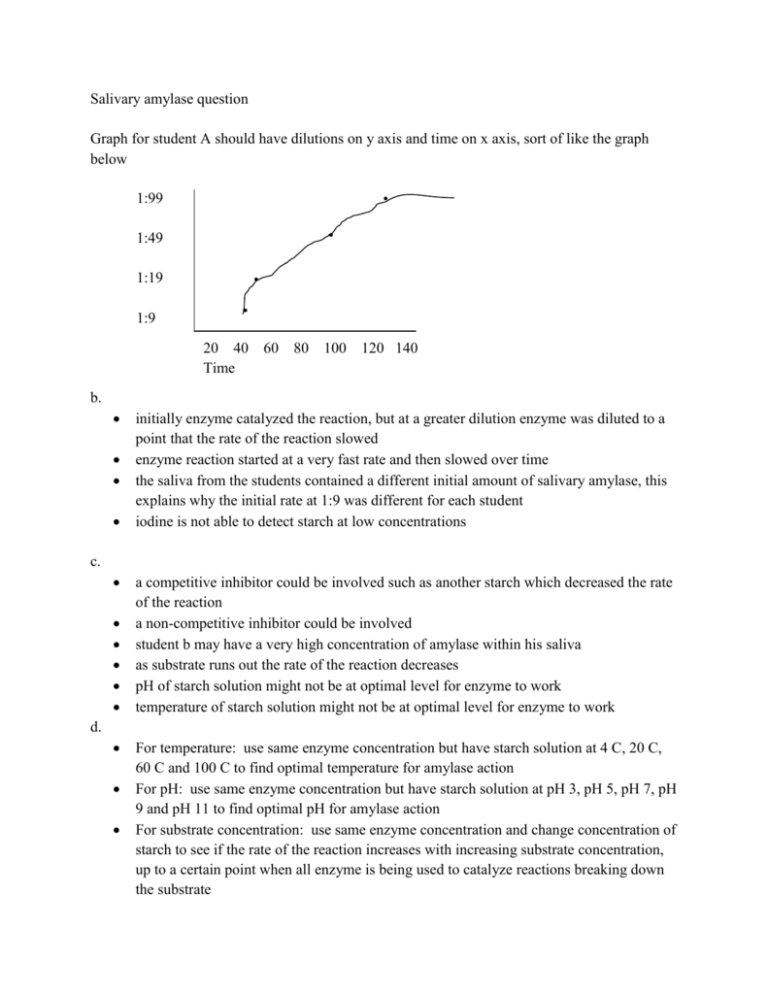
Salivary amylase question Graph for student A should have dilutions on y axis and time on x axis, sort of like the graph below 1:99 1:49 1:19 1:9 20 40 Time 60 80 100 120 140 b. initially enzyme catalyzed the reaction, but at a greater dilution enzyme was diluted to a point that the rate of the reaction slowed enzyme reaction started at a very fast rate and then slowed over time the saliva from the students contained a different initial amount of salivary amylase, this explains why the initial rate at 1:9 was different for each student iodine is not able to detect starch at low concentrations c. a competitive inhibitor could be involved such as another starch which decreased the rate of the reaction a non-competitive inhibitor could be involved student b may have a very high concentration of amylase within his saliva as substrate runs out the rate of the reaction decreases pH of starch solution might not be at optimal level for enzyme to work temperature of starch solution might not be at optimal level for enzyme to work d. For temperature: use same enzyme concentration but have starch solution at 4 C, 20 C, 60 C and 100 C to find optimal temperature for amylase action For pH: use same enzyme concentration but have starch solution at pH 3, pH 5, pH 7, pH 9 and pH 11 to find optimal pH for amylase action For substrate concentration: use same enzyme concentration and change concentration of starch to see if the rate of the reaction increases with increasing substrate concentration, up to a certain point when all enzyme is being used to catalyze reactions breaking down the substrate For competitive inhibitors: remove inhibitors but also test with different inhibitors present such as another starch solution, monosaccharide solution, disaccharide solution For non-competitive inhibitors: remove non-competitive inhibitor if possible and test again with starch solutions and different concentrations of enzyme For each experiment you would want to collect data pertaining to the time it takes for a reaction and have a way to test for the amount of substrate or enzyme remaining