review for biology test over proteins and nucleic acids
advertisement

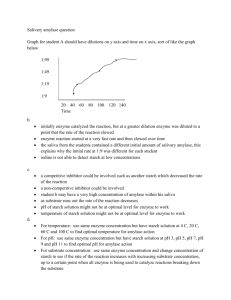
REVIEW FOR BIOLOGY TEST OVER PROTEINS AND NUCLEIC ACIDS 1. A chain of amino acids is a(n 2. What 2 functional groups are in an amino acid? How much of your dry weight is protein? 3. What is a: A) Polypeptide? B) Peptide bond? 4. How many different: A) amino acids exist in proteins? B) Proteins in the human body? Compound elements Building blocks Use in the body Carbohydrate Fat Protein 5. 6. 7. 8. List 7 functions of proteins in your body (be specific) What does: A) hemoglobin do? B) Maltase do? C) amylase do? What reaction with amino acids involves biosynthesis? The splitting of maltose into _________ and ___________ involves the enzyme________. Water (H2O) reacts in a splitting process called ________? The maltose fits into a specific place on the enzyme called the _________. What is the substrate? Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the ________ of the reaction. 9. Why are enzymes needed for the body to function at normal body temperature? 10. Why can enzyme molecules be used over and over again? 11. What is the function of a cofactor? 12. What are the 2 classes of cofactor? Give an example of each 13. Give an example of an enzyme blocker. Tell what enzyme is blocked and why this could be medically important. 14. What does pepsin do? What substrate does it act upon? What cofactor is needed? 15. Describe the “lock and key” hypothesis. How is it insufficient in describing enzyme action? 16. What enzyme is found in liver or bananas or potatoes? What substrate does this enzyme act upon? 17. What are the 2 products of the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide? 18. Why is the peroxidase (or catalase) enzyme important in the body? Benedict’s result Iodine result Monosaccharide Disaccharide Polysaccharide 19. What would starch do when tested with: a) Benedict’s reagent? b) Iodine test? 26. Suppose you added salivary amylase to a starch solution, waited 5 minutes, and the amylase hydrolyzed the starch completely. What would you observe with the following tests? A) Benedict’s? B) Iodine? 27. Suppose you tested maltose with the following tests. What would you see for? a) Benedict’s? b) Iodine? 28. What are 3 differences between DNA and RNA in terms of structure? 29. Nucleic acids are polymers of which monomer? 30. What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? Which bases are complementary?