America as a World Power
advertisement
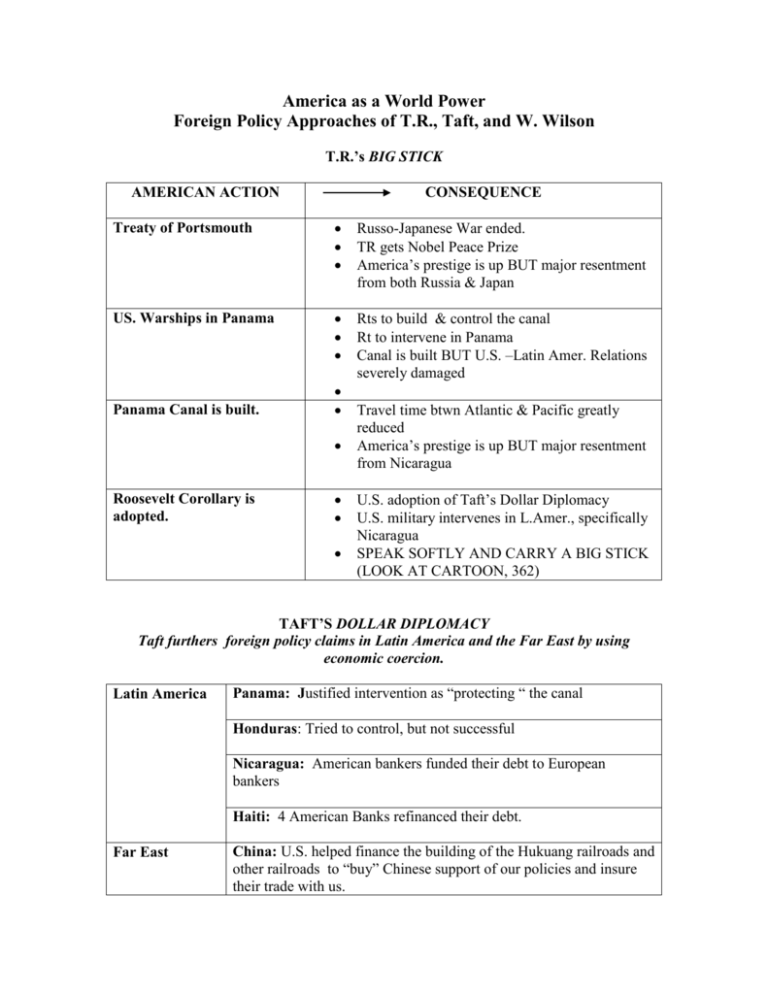
America as a World Power Foreign Policy Approaches of T.R., Taft, and W. Wilson T.R.’s BIG STICK AMERICAN ACTION CONSEQUENCE Treaty of Portsmouth Russo-Japanese War ended. TR gets Nobel Peace Prize America’s prestige is up BUT major resentment from both Russia & Japan US. Warships in Panama Rts to build & control the canal Rt to intervene in Panama Canal is built BUT U.S. –Latin Amer. Relations severely damaged Panama Canal is built. Roosevelt Corollary is adopted. Travel time btwn Atlantic & Pacific greatly reduced America’s prestige is up BUT major resentment from Nicaragua U.S. adoption of Taft’s Dollar Diplomacy U.S. military intervenes in L.Amer., specifically Nicaragua SPEAK SOFTLY AND CARRY A BIG STICK (LOOK AT CARTOON, 362) TAFT’S DOLLAR DIPLOMACY Taft furthers foreign policy claims in Latin America and the Far East by using economic coercion. Latin America Panama: Justified intervention as “protecting “ the canal Honduras: Tried to control, but not successful Nicaragua: American bankers funded their debt to European bankers Haiti: 4 American Banks refinanced their debt. Far East China: U.S. helped finance the building of the Hukuang railroads and other railroads to “buy” Chinese support of our policies and insure their trade with us. WILSON’S MORAL DIPLOMACY AMERICAN ACTION CONSEQUENCES Wilson uses an incident with Mexico to occupy Vera Cruz Death of 200 Mexicans/ 19 Americans U.S. & Mexico are close to War (1914-1915) ABC negotiations: Argentina, Brazil, & Chile negotiate a peace between Mexico & U.S. Wilson recognizes Carranza’s government U.S. comes in conflict with Zapata and Pancho Villa Wilson refuses Carranza’s demand to withdraw U.S. troops sent into Mexico to capture Villa Growing Anti-American feeling Mex. nationalizes oil and mineral resources Mex. adopts strict regulations on foreign investors Gen. Pershing pursues Villa, but cannot capture him and is recalled to U.S.











