Phases Changes
advertisement
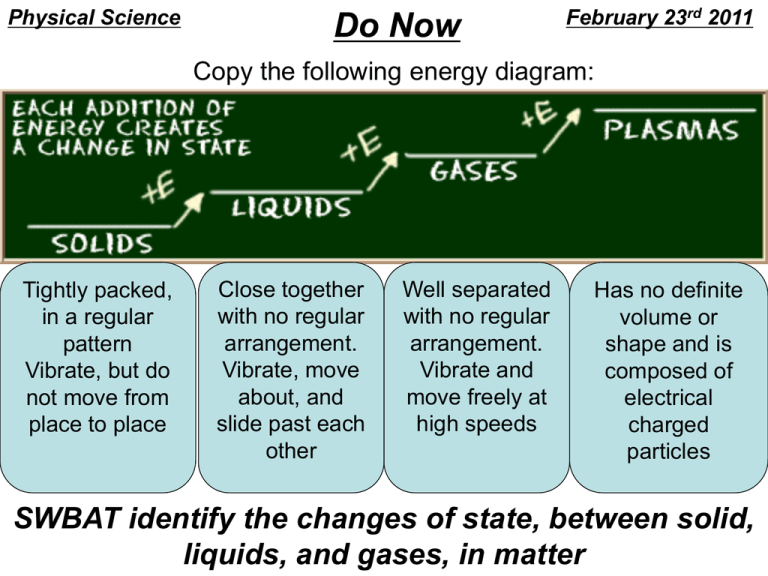
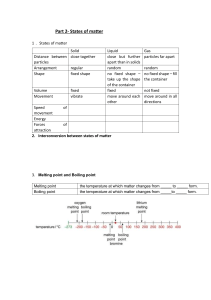
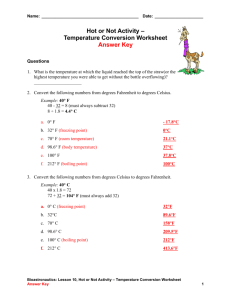
Physical Science Do Now February 23rd 2011 Copy the following energy diagram: Tightly packed, in a regular pattern Vibrate, but do not move from place to place Close together with no regular arrangement. Vibrate, move about, and slide past each other Well separated with no regular arrangement. Vibrate and move freely at high speeds Has no definite volume or shape and is composed of electrical charged particles SWBAT identify the changes of state, between solid, liquids, and gases, in matter Elements Draw this chart! Pure Substances Compounds Matter Homogeneous Mixtures Heterogeneous Phases Changes • Phase changes require that a substance absorb energy or release energy to occur. • There is NO Change in Temperature associated with a phase change! • Different words are used to denote direction when dealing with a phase change. PHASE CHANGES Description of Phase Change Solid to liquid Term for Phase Change Melting Liquid to Freezing solid Heat Movement During Phase Change Heat goes into the solid as it melts. Heat leaves the liquid as it freezes. PHASE CHANGES Description of Phase Change Liquid to gas Term for Phase Change Vaporization, which includes Heat goes into the boiling and liquid as it vaporizes. evaporation Gas to liquid Condensation Solid to gas Heat Movement During Phase Change Sublimation Heat leaves the gas as it condenses. Heat goes into the solid as it sublimates. *Boiling & freezing points depend on the pressure. Phase Diagram WaterSteam 120 Steam 100 Water Ice - Water 0 -5 Ice Alta Physics What are properties? • Matter has observable and measurable qualities. • We can use general properties to identify substances. • Two basic types of properties of matter: Physical properties and Chemical properties: Physical Properties • Physical properties are used to identify, describe and classify matter. – Characteristic of a substance that can be observed (using your senses) without changing the substance into something else. Hardness Texture Color Odor Taste Temperature More EXAMPLES Physical • size, shape, freezing point, boiling point, melting point, magnetism, viscosity, density, luster and many more. – Viscosity - The resistance of a liquid to flowing. – Examples: – Low viscosity-water, rubbing alcohol – High viscosity-honey Chemical Properties • Chemical properties are characteristics involved when a substance interacts with another substance to change its chemical make-up. Flammability Rusting Creating a Reactivity with new chemical water product Creating gas bubbles pH Classwork & Homework • Complete ‘Phase Changes’ worksheet • Copy all definitions and summary from Chapter 2 Section 2 – Pages 45 – 52 – Summary on page 52 • Homework – Complete ‘Concept Review’ worksheet (both sides)