Calculations with Chemical Formulas & Equations
advertisement

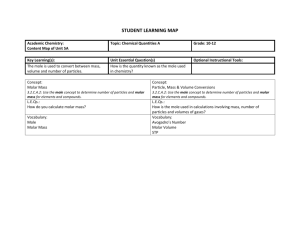
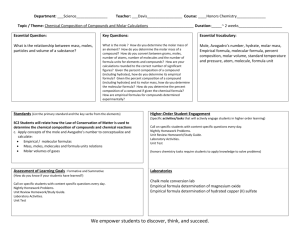
Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas & Equations Benchmarks MOLAR MASS What is molar mass and how is it calculated? MOLE TOWN Sketch a mini Mole Town MASS PERCENT How is mass percent calculated? EMPIRICAL AND MOLECULAR FORMULAS What is the difference between empirical and molecular formulas? How are these formulas determined? LIMITING REAGENTS Describe what a limiting reagent is. Remember making s’mores? PERCENT YIELD How is percent yield calculated? What is a good percent yield? 1 Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas & Equations MOLAR MASS Molecular weight: molar mass of a molecule (2 nonmetals) (p90) Formula weight: molar mass of a formula unit (metal & nonmetal) p90 Molar Mass: the mass of one mole of a substance – GENERIC TERM (p92) A mole is 6.02*1023 “items” either atoms, ions, MC or FU. This is Avogadro’s number. (p91) Questions 21-24 p.120 relate to molar mass MOLE TOWN Sketch mole town and review how to use it for with the mole.(p93-95 &107-110) Questions 25 – 40, 71 – 82 p.120-123 relate to mole town MASS PERCENT Mass Percentage: mass of A in the whole X 100% mass of the whole (p96) Questions 41 – 54 p.121 relate to mass % Calculating % from combustion (p98) - determine masses through stoichiometry - all C goes to CO2 - all H goes to H2O - subtract to find mass or % of O Questions 55 – 56 use stoichiometry with mass % EMPIRICAL AND MOLECULAR FORMULAS Empirical formula: simplest, most reduced ratio of atoms (p99) - finding EF o divide each mass by its respective atomic mass o divide by the smallest number of moles = subscripts may have to multiply by 2 to get rid of decimal Questions 57 – 64 p. 122 relate to EF Molecular formula: is some multiple, n of the EF. (p 103) Method 1 1. find EF 2. divide molar mass of MF by molar mass of EF to find multiple, then multiply all subscripts by n. Method 2 1. multiply molar mass of MF by each % of elements, then divide by respective atomic mass = subscript in MF. Questions 65 – 68 p 122 relate to MF 2 Chapter 3 Go to p 107 to see how to interpret an equation in terms of representative particles, moles or mass. Write a description for yourself or a visual to help you remember. Questions 69 – 70 p 122 relate to interpreting equations. LIMITING REAGENT Limiting Reactant: the reactant that runs out first limiting the amount of product produced. (p 111) - take both starting reagents to the same product, smallest is the answer. Questions 83 – 88 p123 – 124 relate to LR PERCENT YIELD Theoretical Yield: the maximum amount that could be produced – found by doing stoichiometry. (p114) Actual Yield is the amount actually produced in the lab. Percentage Yield = actual yield Theoretical yield X 100% Questions 89 – 90 relate to% yield Be sure to read through the “A Chemist Looks At” segments at the end of the chapter. The information in these profiles is considered common knowledge on the AP Test! Homework. Label as Chapter 3. Page 120 – 124 Questions: 21 – 90 odds. Show FULL thought process/work shown, so that you will remember how to do it in the future. Check your answers to the odds with the back of the book A-28. Look through review questions p 119 Q: 1- 14, omitting 9, and 11. 3