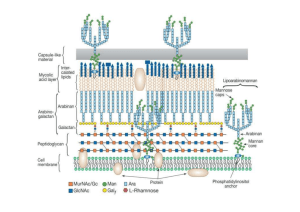
Roger`s Phat Pharm Notes II
advertisement

Autacoids uterine PGE2 + PGF2 dinoprostone (PGE2) dinoprost (PGF2) carboprost (synthetic analog) vascular PGI2 and PGE2 TXA2, LT’s airway PGF2, TXA2, LT’s PGI2, PGE2 gastric acid sec’n PGE2, PGI2 Misoprostol (Cytotec) abortifacients, evacuation of uterine contents in themanagement of missed abortion or intrauterine fetal death up to 28 weeks of gestational age. vaginal suppository intraamniotic injection i.m. Vasodilat’n vasoconstriction. LT dilate cutaneous arterioles in acute infl. bronchoconstriction bronchodilation inh. HCl sec’n. Both stim mucus and bicarb sec’n = protective effect on mucosa. p.o., analog of PGE1. Same mech as above. S.E. intestinal cramps and diarrhea. Used in conj. w/asprin and NSAID’s, to reduce gastric ulcers caused by them. platelet aggregat’n stim. Made in platelets TXA2 inh. Made in endothelium PGI2 infl/allergic rxns PGE2, PGF2a, PGD2, mediators of local pain and itching, cutaneous microvascular vasodil perm. edema. LT’s Wheal and flare rxns. Ductus arteriosus maintain patency in fetus. Asprin (COX inh) promote closure of ductus arteriosus at birth PGI2, PGE2 COX-1 and COX-2 PG synthetase-1 = constitutive, PGS-2 inducible by cytokines, inh by antiinfl. PGS-1(COX 1), glucocorticoids. NSAID’s block both PGS-1 and PGS-2. PGS-2 (COX 2) Vasc. Perm. and GI contr. by all. Kinins bradykinin* aprotinin (Trasylol) aspirin glucocorticosteroids sm.m, potent vasodil of arterioles and venules in skin, skeletal m., viscera, kidney and brain perm & edema, BP & reflex tachy. GI sm. m. contr & bronchoconstr. Infl. rxns prod pain, edema and stim PMN to come in kallikrein inh to tx acute pancreatitis and severe burn injury localized pain and swelling by inh COX antiinfl. Serotonin* stored w/n granules after synthesis. Mixed fxs on CV. Carcinoid enterochromaffin cells prod 5-HT fluctuations in BP, HR and CO. 5 HT4 R (from enteric neurons) stim peristalsis in esophagus and stomach. Pain & itching in infl., also perm , Arterioles dil, but postcap venules constr edema. CNS NT. Act on 5-HT3 R on CTZ area postrema antagonists Methysergide (Sansert) cyproheptadine (periactin) ritanserin Ondansetron(Zofran) 5-HT2 R antag., prophylactic tx of migraine b/c 5-HT2 R in cerebral arterial sm. m. mediate vasodil, & 5-HT1 R mediate vasoconstri. 5-HT1 agonist more effective than 5HT2 R antag. Therapeutic tx of malignant carcinoid 5-HT2 R antag. Both anti5-HT & antiH fxs. Symptomatic tx of carcinoid and allergic infl. rxns, also tx migraine headaches. 5 HT2 antag. platelet aggregation 5-HT3 R antag. Anti-emetic Granisetron (kytril) Agonists metoclopramide (Reglan) cisapride (propulsid) sumatriptan (imitrex) busprone (Buspar) Reuptake inh/releasing agents Fenfluramine Dexfenfluramine (Redux) 5-HT3 R antag. Atni-emetic 5 HT4 R agonist Anti-emetic/prevents gastro-esophageal reflex. 5 HT4 R agonist 5-HT1 R agonist. Most effective tx for migraine headache 5-HT1 R agonist. Subtypes of 5-HT1 R, some cause vasoconstriction and others anxiolytic. also elicits direct 5 HT R agonist fxs. Act in brain to prod anxiolytic and anorexigenic. 2X as potent as fenfluramine. Effective anorexigenic. Can cause fatal pulm HTN. Histamine* Bound histamine (mast and basophils) in pathophys, degranulation promoted by allergic rxns to drugs (not allergic response) basic drugs and 4’ amines (morphine, codeine, tubocruraine, guanethidine, chloroquine) or Ag-Ab mediated allergic release (Pcn, other antibiotics). Unbound (gastric mucosa & hrt) in normal phys. Arteriolar dil in most vasc bedscutaneous and systematic reflex tachy ; chronotropic and inotropic fxs; constri of larger arteries and veins (esp. pulm) pulm BP and edema (also due to perm.), bronchocontri and mucus sec’n. GI sm. m. contr.; stim of local pain and itching, mediator of allergic and local infl rxns; stim of gastric glands. CNS NT 1’ in hypothalamus. Inh of allergic H release catecholamines (epi & iso) Methylxanthines (theophylline & aminophylline) antihistamines diphenhydramine (benadryl) & demenhydrinate (dramamine) promethazine cyproheptadine chlorpheniramine terfenadine fexofenadine astemizole (Hismanal) loratadine(Claritin Chlorpheniramine or acrivastine + pseudoephedrine (semprex-D) H2 R antag cimetidine (Tagamet) 2 R on mast cell and basophils. Adenylate cyclase activat’n inh degranulation. Also causes bronchodilation inh PDE and allow cAMP to accumulate inh degranulation. Bronchodilat’n H1 R local infl, edema, vasodil/constri, perm, H2 R gastric sec’n H1-R antag. Drowsiness, antimusc (dry mouth) , antiemetic, antitremor (b/c anti-chol), anti 5 HT and.sedation. Tx also colic or G.I. hypermotility, nausea and vomiting, tremors, and insomnia. O.D. CNS stimconvulsions H1 R antag. Anti-coli, safe in infants. Produce drowsiness which is desirable in infants. H1 R antag. also anti 5 HT, tx migraine also. H1 R antag. No S.E.’s, some drowsiness but less than any of the drugs above. H1 R antag. NO CNS fxs and no drowsiness and sedation. Tx allergic rhinitis, acute urticaria (itching), and drug allergies. Terfenadine (pro-drug, toxic) fexofenadine (active species, nontoxic) For terfenadine and astemazole only, cardiac arrhythmia can be fatal, conc in parent drug due to P450 inhibition. Avoid erythromyocin, ketoconazole, and grapefruit juice (?). terfenadine analog Acrivaastine similar to terfenadine. This combo most effective. Pseudoephedrine prevents drowsiness, in fact may produce CNS stim. inh gastric acid sec’n, tx ulcer. Well tolerated but significant relapse occurs. suicide substrate, irreversibly inh P450. Ranitidine (Zantac) famotidine (Pepcid) nizatidine proton pump inh Omeprazole (prilosec) Lansoprazole(prevacid) some inhibition of P450 do not inh P450 can cause complete inh of HCl sec’n, causing achlorhydria, pH allows for bacterial infection. For short term tx for healing and symptomatic relief of erosive esophagitis (moderate to severe gastro-esophageal reflux) and active duodenal ulcers. Cautiously for long term tx of path hypersec gaastric cond. Anticoagulant, antiplatelet and fibrinolytic drugs Heparin Dalteparin sodium Heparin antagonist protamine sulfate Orally effective anticoag.(lipid sol) coumarin class Warfarin dicumarol phenprocoumon Antiplatelet drugs aspirin accelerates interxn of antithrombin III and thrombin inactiv. thrombin S.C. or i.v. bolus/infusion. NOT absorbed by p.o. Does not bind to plasma prot and remains w/n intravasc. comp’t. Hepatic metabolism (0’) and renal exc’n of unchanged drug. S.E. hemorrage; thrombocytopenia of immediate and delayed onset. Also hypersensitivity rxns, fever, alopecia, hypoaldosteronism and osteoporosis. Contraindicated in GI ulcers, HTN, recent neurosurgery, visceral carcinoma, spinal anesthesia. Use caution in renal/hepatic dysfcn, prior hx of occult bleeding, taking antipletelet drugs, oral anticoagulants. Many basic drugs (antiH, quinidine, phenothiazines, tetracyclines) can chemically inactivate heparin. Goal = whole blood coagulation time 2-3x normal, or an APTT of 1.5 to 2.5 normal. Indicated for prophylaxis of DVT, pulm/arterial embolism, prevention of arterial emboli arising from heart valves, MI and coronary art dz. heparin prep for injection. 1x/day. For prophylaxis against deep vein thrombosis. Basic prot bind to and neutralize neg. charged heparin in cases of serious hemorrhage. Slow I.V. infusion only work in vivo. Inh of hepatic synthesis of Vit K-dep clotting factors (prothrombin, factors VII, IX, and X) of the intrinsic and extrinsic systems and of protein C. Actual mechanism is to block regeneration of KH2 (active hydroquinone form of Vit K) by an epoxide reductase. Delayed onset of action depending on drug pharmK and t1/2 of the 4 Vit K dep clotting factors, which must be catabolized first before anticoag effect evident. Action potentiated by intake of vit K/fat, or by disorders that vit K absorption. S.E. hemorrhage. Rare side fxs = diarrhea, urticaria, alopecia, dermatitis Contraindicated in GI ulcers, thrombocytopenia, renal/hepatic dz, severe HTN, recent neurosurgery, chronic alcoholism, pregnancy, physically hazardous occupations. Other drugs used prior or at same time can or effective dosage of anticoag. Indicated for prophylactic tx of arterial emboli from heart valves, cond of high thromboembolic risk, MI and cornoary art dz. rapidly and almost completely absorbed after p.o. Extensive plasma albumin binding long plasma t1/2 (1.5 days and duration of 2-5 days). Displaced by other plasma prot bound drugs. Hepatic metabolism. erratic and delayed p.o. absorption. Higly variable t1/2 (1.5-5 d) and duration (2-10 d) because erratic and incomplete absorption from GI. Difficult to use clinically long acting coumarin der. t1/2 6.5 days and duration of 1-2 wks. prophylaxis of arterial thrombosis Lo doses of aspirin inh platelet TXA2 formation, and hi doses inh formation of both Ticlopidine platelet TXA2 and endothelial PGI2(endothelial cells can synth COX). Combo therapy w/ dipyridamole, or sulfinpyrazone inh ADP pathway in platelets. For pts who can’t tol aspirin. Dypridamole dextrans sulfinpyrazone Nitric oxide Fibrinolytic agents streptokinase urokinase Tissue plasminogen activator antifibrinolytic agens aminocaproic acid tranexamic acid not very effective clinically. Coronary vasodilator platelet adhesiveness to damaged vascular endothelium by platelet cAMP. Does NOT alter bleeding time/platelet aggregation. Combo therapyw/ oral anticoagulants glucose polymers as plasma vol expanders, platelet adhesiveness by coating platelets and intimal lining and by other mechanisms. comp inh of COX. Weakly affects platelet fcn. postinfarction “sudden death”. inh platelet aggregation and adhesion. Nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, isosorbide dinitrate = vasodil and anti-platelets. lyse already formed clots indirectly activates plasminogen. I.V., intracoronary infusion, topical. directly activates plasminogen. I.V. and intracoronary infusion. endogenous activator of phys. fibrinolysis. I.V.-effective thrombolytic drug antag of plasmin, reverse effects of thrombolytic agents. I.V. or p.o analog Antipyretic-analgesics salicylates (aspirin most important) Use: Antipyretic (central)for fever; Analgesic headache (0.6-0.9g/d), myalgia, arthralgia, dysmenorrhea and antiinfl (peripheral)ARF, rheumatoid arthritis (5-8 g/d). Toxicity starts w/8-10g/d or when conc exceeds 30 mg%. Mean lethal dose 20-30 g. 0’ b/c hepatic enz sat. O.D. in adults. GI distressnausea, vomiting, diarrhea. Local irritation b/c weak acid, PG synthesis gastric acid sec’n and getting rid of mucosal surface. @hi dose, stim CTZ; CNS stim: tinnitus (#1 reliable sign for O.D.), dizziness, hyperapnea (both depth & rate, reg by medulla). W/ conc, get CNS deprresp failure; Blood coag: internal bleeding. @ v. lo doses, platelet aggregation by TXA2 formation to prevent 2nd infarct. Irrev. Inh of COX. To regenerate COX, must wait for platelets to turn over which is 6-8 d, b/c platelets can’t synth own COX. @ doses, hypoprothrombinemia by vit K dep factors. Stim of met. rate: @ hi dose, uncouples ox. phos., generates a lot of heathigh fever and sweating. Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, by stim glycogenolysis. plasma free FA by inh lipolysis Acid-base balance disturbances: hyperventilationresp alkalosis (#2 sign in adult) renal compensation by elim of bicarb (last stage in adult before death). Urine has K to neutralize bicarb. Children progresses rapidly thru these stages. Then goes to hypoventilat’n b/c CNS deprresp depresp acidosismetabolic acidosis (adding aspirin which is acid in blood phys. rxns in bodyGet ketone bodies prod in liver). Child lingers in this stage H2O/electrolyte imbalance: dehydration (diuresis b/c elim a lot of electrolytes) and hypokalemia Contraindicated: in children w/ chicken pox or influenza. Otherwise Reye’s Syndrom(liver and brain damage) peptic ulcer, bleeding disorders, acute gout b/c inh exc’n of uric acid, asthma (hypersensitive to aspirin). High plasma prot bindingenhance warfarin and dicumarol action(usu some residual COX fcn. Do not want to inh it completely)hemorrhage. choline salicylate salicylic acid (keratolytic) methyl salicylate (rubefacient take off warts. So if taken p.o., will wipe out esophagus causes local axonal reflex vasodil and warmth, and LT relieves tenderness ( PG5 syntnh which normally provides neg feedback to inh lipoxygenase). Tx of salicylate O.D. acetaminophen (Tylenol, Tempra) analgesic & antiyretic but NOT antiinfl. Used in all pts contraindicated for aspirin. Basic drug absorbed in small intestine rather than stomach. Toxicity: @ therapeutic dose, little to no GI distress/bleeding. O.D. phase II metabolism of benzoquinone generates F.R. depletes GSHliver cirrhosis and kidney necrosis. Reversible is intervene w/n 24 hrs. Tx by giving N-acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) to regen GSH. NSAID salicylates indomethacin ibuprofen (motrin, advil) Ketoprofen (orudis) fenoprofen(Nalfon) fluribiprofen(ansaid) naproxen (Naprosyn) Tometin (Tolectin) meclofenamate (Meclomen) mefenamic acid (Ponstel) piroxicam (Feldene) diclofenac (Voltaren) diflunisal (Dolobid) oxaprozin (Daypro) sulindac (Clinoril) alkalinize urine, i.v. infusion of NaHCO3. If at endstage of OD., do not give it. Gastric lavage with 3-5% NaHCO3, which delays salicylate absorption from GI. Emesis w/ syrup of ipecac delay gastric emptying/absorpt’n by milk or activated charcoal (much more effective than previous two) Supportive Measures; Correct electrolyte /H2O imbalance by i.v. fluids maintain good renal fcn. Use osmotic diuretic (mannitol), provided patient not hypokalemic control convulsions w/lo dose sedatives (watch for resp depr) control high fever w/ sponge baths. Control hemorrhaging w/ dose of vit K and blood transfusions dialysis used for rheumatoid arthritis (need hi doses. Compliance a problem. Can exacerbate gout), ankylosing spondylitis, ARF not used any more, pharm actions same as aspirin. (NOT need to know) Use: rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis of hip, nonarticular rheumatism, acute gouty arthritis, analgesic for dysmenorrhea. S.E.: GI distressmost ulcerogenic drug by inh COX1 (constitutive form) more. PG inh gastric acid sec’n; severe frontal headache, hallucinations GI distress < aspirin b/c inh COX 2 more than COX 1, but NOT selective dizziness @ v. high doses, skin rash rare Drug interxns and contraind similar to aspirin, except for children w/ varicella/influenza. more potent than ibuprofen and more toxic. Tinnitus, gastric and duodenal ulcers (some pts more sensitive to the GI irritation), rash, fluid rention, O.D. agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, acute renal failure. Aspirin prod more tinnitus than any other drug. Lo dose can inh COX, so high dose won’t further affect platelet agg. Higher incidence of toxicity expected, esp @ hi doses. Good. analgesia w/ minimal gastric irritation. Non NSAID’s chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine Gold salts D-Pencillamine Glucocorticoids Not antiplatelet, or gen anti infl, or analgesic. antimalarial drugs also for tx rheumatoid arthritis and discoid lupus erythematosus. S.E. subacute or chronic chorioretinitis, reversible if drug stopped. I.M. tx rheumatoid arthritis. Cause complete remission in some pts w/ severe rheumatoid arthritis. Last resort drug b/c only 30% respond. Takes 5-10 wks to work, very toxic. Severe S.E.: skin rash, hepatic/renal damage, blood dyscrasias (inh cell prolif in bone marrow) tx rheumatoid arthritis tx rheumatoid arthritis b/c anti infl. Gout acute gouty arthritis colchicine NSAIDs (except aspirin) chronic tophaceous gout allopurinol probenecid sulfinpyrazone used prophylactically and therapeutically. Dramatic relief w/n 90 min. Mechanism = binding to tubulin, inh assembly of microtubule and therefore lysosome fusion w/ other vesicles and lysosome release. In gout, acute local pain in reaction to uric acid crystals deposited in jts. Slight O.D. extremely toxic: GI ulceration b/c it inh spindle fiber formation and cell division arrested in metaphase severe abdominal pain (80%) agranulocytosis/aplasatic anemia profound alopecia, but reversible as soon as drug withdrawn. for pts who can’t tolerate colchicine. Anti infl and analgesic. By inh xanthine oxidase, uric acid in blood and shift equilibrium to sol form of blood. But can ppt later acute flare-ups (sxs of acute gouty arthritis). uricosuric agent by inh sec’n of uric acid @ lo dose & inh sec’n and reabsorption @ hi doses. can cause acute flare-ups. Gen well tol. Used in combo with Colchicine = colbenemid, to minimize acute flare-ups and renal damage. uricosuric agent, also has weak gen anti infl. SE more serious than probenecid, include GI distress and skin rash. Asthma Isoproterenol Epi Terbutaline metaproterenol albuterol bitolterol salmeterol formoterol ephedrine Bronchial asthma—reversible airway obstruction extrinsic—allergic, in children, tx w/ anti-infl Intrinsic—nonallergic, nonspecific hyperreactivity, mostly in older adults. Mucosal infl/edema, triggered by cold water, dust and exercise. Vagal component reflex vagal discharge via local contraction and can be tx by anti-musc. Status asthmaticus—severe acute bronchospasm 1/2 agonist. Used therapeutically for bronchodil and inh of mediator release (2). Must be given locally at lungs. Quick onset and metabolism. S.E: myocardial stim, hand tremor, CNS stim. Tachyphylaxis. ventilation/perfusion ratio because dilates previously constricted BV in areas of poor perfusion. b2 R agonist. Used therapeutically by inhalation and prophylactically by oral. S.E.: hand tremor and mild cardiac stim. Reflex sympa stim not as bad as iso. These drugs short duration of action: 1-5 hr long duration of action: 12 hr bronchodilation and pulm decongestant. S.E: intense CNS and cardiac stimlots of deaths. phenylephrine theophylline aminophylline Cromolyn sodium and nedocromil sodium Anti infl glucocorticoseroids Beclomethasone dipropionate flunisolide budesonide triamcinolone anticholinergice agents Ipratropium bromide N-Acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) Zileuton (leutol) Zafirlukast (Accolate) selective a1 R agonistmucosal vasoconstriction and pulm decongestion. Used with isoprot to alleviate vent/perf ratio & arterial hypoxemia associ. PDE inh. P.o. as prophylactic agent. S.E.: GI upset, CNS & cardiac stim. Very toxic, but causes sustained inh of mediator release and bronchodil. Both methylxanthines have low therapeutic index. water sol salt of theophylline. Cause intense vasoconstriction. CNS stim—seizures, convulsions. Plasma level must be closely monitored. I.v. to tx status asthmaticus. prophylactically (takes days to work) by inhalation. Tx exercise induced asthma. Effective in children. V. safe. Mast cell stabilizer = no degranulations, fx on mast cell > basophil. prophylactically by inhalation. Removes sensory n. stim and therefore vagal stim. P.O cause severe S.E., adrenal atrophy, diabetes, cataract and ulcer. Major SE = fungal infection in pharynx and larynx b/c inh Plipaase A2 and therefore PG and LT, also cytokine prod by T-lymphocyte in airway. Not much systemic SE block vagally mediated bonchospasm in intrinsic asthmabronchodil. Toxicity = inspissation of mucus and mucociliary clearance. prophylactically by inhalation. No serious SE b/c 4’ ammonium compound. Anti-chol effect on bronchial sm. m. but not on epithelial cells. No insipissation effect. Mucolytic agent. By inhalation. N-Acetylcysteine—reduces disulfide bonds in hard mucus plus to free -SH groups. 5-lipoxygenase inhibtors. P.O. LT-D4 R Antag Diuretic Drugs—organic acid and base secretory systems delivers diuretics into tubular lumen. High intrinisic activity, in proximal tubule memb, inh Na bicarb reabsorption by Carbonic anh. inh acetazolamide (diamox) inhibiting CA. bicarb hyperchloremic metab. acidosis, b/c NaCl reabsorption downstream. Urine alkaline. Na exc’n K exc’n when presented to CCT TX: glaucoma by inh aq humor form’n, intraocular p. Alkalinization of urineelim acidic agents, e.g. uric acid and cystine. Metabolic alkalosis, eg. Acute mtn sickness. Take it a few days prior to climbing to minimize resp alkalosis by bicarb in body. Loop diurectics High intrinsic activity. inh Na+/K+/2Cl transporter in thick ascending limb, also inh reabsorption of Mg and Ca. Inh K cycling which normally drives Mg and Ca furosemide* reabsorptionhypomagnesemia but not hypocalcemia b/c Ca absorbed in DCT. torsemide exc’n of Na, Cl and Kdiuresis and hypokalemia. Prolonged hi doses bicarb bumetanide* exc’n. (HOW?) ehtacrynic acid* highly bound to plasma prot. Elim unchanged in ruine and feces. Inh uric acid sec’n in proximal tubule b/c use same transporter. Use: acute pulm edema, hyperkalemia, in pts w/ impaired renal fcn or acute renal failure, CHF. SE: #1= rapidly circulating blood voldizziness, headache, ortho hypo. Hyponatremia (@ hi dose or prolonged therapy, for alkalosis also), hypokalemia and hyperuricemia. Major toxcity = hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis b/c drug elim of H+ (maybe hypomagnesemia ) Benzothiadiazides inh NaCl co-transporter in DCT, inh uric acid sec’n in proximal tubule by (thiazide) competitionexacerbate gout. Probenecid inh thiazide from getting into lumen Chlorothiazide* by competing w/ secretory transporter. hydrochloro-* thiazide benzthiazide trichlormethiazide chlorthalidone* indapamide K sparing diuretics Low intrinsic activity b/c low Na reabsoption here. act in cortical collecting tubule and late distal tubule to produce mild natriuresis and diuresis but K and H exc’n. Delayed onset of axn. Tx essential HTN (mild), CHF, cirrhosis, states of mineralcort excess. Used w/ thiazides or loop diuretics to minimize hypokalemia. SE: hyperkalemia in pts w/ impaired renal fcn or K intake, or synergistic fx in pts taking b blockers which renin sec’n or AT II formation (ACE inh). Hyperchloremic (?) metabolic acidosis can develop. sprionolactone Aldosterone R antagonist. Synthetic steroid acts as comp antag to aldosterone. SE: GI distress, drowsiness and reversible gynecomastia b/c blocks androgen formation. Tx hirsuitism. Na channel blocker. Usu Na absorp’n generates lumen-neg potential, which enhances K and H sec’n. Amiloride is a direct vasodil also. Given i.v.. water soluble, freely filterable, poorly reabsorbable nonelectrolytes. USE: maintain renal fcn (urine format’n) in renal dynamics, intraocular P, ICP in surgery, elim of ingested toxic substances. SE: mobilization of fluid from IC to EC comp’t acute pulm edema and acute CHF (when kidney can’t elim the displaced water). Also headache, nausea, vomiting and chest pains. Triamterene amiloride Osmotic diuretics mannitol, glycerin isosorbide Enhanced apical Ca reabsorption on apical membrane. Possible mechanism Na/Ca exchange in basolateral membNa elim and Ca reabsorption. Unmask hypercalcemia caused by hyperparatyroidism. SE: Hypokalemia w/dosage or prolonged therapymuscle weakness, drowsiness, dizziness, irritability, cardiac arrhythmias, correct by giving K supplGI irritation, can eat fruits instead. Also hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, hyperuricemia, hyperglycemia in diabetic pts, hyperlipidemia and allergic rxns. Highly bound to plasma prot. Elim unchanged, renal 60% hepatobiliary 40% Use: 1st line for essential HTN (mild edematous, mild to moderate HTN) b/c lo level of diuresis, CHF, cirrhosis, idiopathic hypercalciuria. indapamide Elim 1’ by hepatic-biliary sec’n (80%), for people w/ renal dysfcn. Carbonic anhydrase inh Antianginal and vasodilator drugs typical angina variant angina organic nitrate esters nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate) Isosorbide dinitrate erythrityl tetranitrate pentaerythritol tetranitrate organic nitrite esters isoamyl nitrite, isobutyl nitrite sodium nitroprusside in myocardial oxygen requirement pain sudden coronary vasospasm inadequate supplyeven at rest short term therapy lipophilic, short acting, met to NO in vasc sm. m. Venodil preload, major mech for relief in typical angina, tx CHF and acute MI; arteriodil afterload. Both O2 demand. Tx variant angina by coronary arteriodil. Extensive 1st pass. Adm subling (buccal), transdermal patch, and i.v. infusion. SE: hypotension headache, ortho hypo, flush, relex tachy. Methemoglobinemia and tolerance uncommon with lo dosage. longer acting organic nitrate ester, no 1st pass metabolism, adm p.o. Last two can be taken prophylactically potent vasodil. I.v. infusion. Spontan. release of NO. BP in HTN emergency or crisis or during surgical procedures. -adreneric R agonists propranolol Metoprolol atenolol pindolol nadolol Ca channels blockers nifedipine nicardipine nitrendipine nisoldipine amlodipine Mibefradil (Posicor) verapamil Diltiazem bepridil AntiHTN drugs diuretics (loop & thiazide) vasodilators hydralazine Minoxidil (Rogaine) myocardial sympa response to stress & exercise myocard oxygen demand. tolerance to exercise but also less vigorous exercise possible. Long term therapy, used w/organic nitrate esters to offset each other’s SE’s. block HR ( reflex tachy in nitroglycerin use) diastole LVDV, LVDP (blocked by nitroglycerin) oxygen demand. Avoid abrupt w/drawal b/c will get upreg of R. Do not use nonselective blockers for variant angina. Normally epi released during stress acts on 2 R vasodil. block leads to unopposed 1 R activation by NE worsen coronary vasospasm. 1 R blocker 1, 2 R blocker L-type (large in conductance) predominant in cardiac and sm. m. fxs: SA node (brady); AV cond vel, and cardiac contr. CO. Vasc sm. m > nonvasc sm m (airway, GI, uterine, etc). Arterial sm m > venous, so ortho hypo not common SE. Ca channel antagonists only partially interfere w/ Ca movememnt thru R gated Ca channels. T(secr) and N (neurons) types are less sensitive to blockade by Ca channel blockers. Vasodil SVR BP reflex symp stim ( not much HR and contr b/c Ltype in hrt blocked) + renin sec’n b/c T type not blocked bl. Vol, edema in obese elderly; can be by diuretic) SE: brady, AV-block, card arrest, acute CHF. Less serious SE = flushing, edema, dizziness, nausea, and constipation. a dihydropyridine, tx both typical and variant. Also essential HTN. Vasc > heart. Arteriodil afterload > venodil preload. Cornoary arteriodil stops vasospasm. Mild myocard depr b/c CO. New T-type blocker (tetralol class). New analogs of nifedipine w/ longer duration of action. Greater effect on vasc sm m than nifedipine. Tx essential HTN also. Blocks renin sec’n edema. T-type channel blocker. T-type channel blocker: act on SA node brady, does NOT CO. Relax arterial sm m. No reflex tachy. Tx both typical and variant oxygen demand. heart > vasc. Severe neg inotropic fx and brady pts on blockers v. sensitive to cardiodepr fxs. NOT used for angina. For antiarrhythmia. vasc = heart. Neg chronotropic axn most prominent. 1’ for antiarrhythmia. used alone to tx mild-mod essential HTN. Thiazid preferred over loop unless want more diuresis. Beware of electrolyte loss. In combo for severe HTN: Triple combo. Vasodil BP reflex symp. Stim HR ( by blocker ) + renin sec’n ( by blocker and by diuretics, which also bl. vol) BP. arterial > venous, thus ortho hypo not a problem. Never used alone. See flowchart above b/c will have reflex tachy and renin sec’n. regional arteriodil (renal/splanchnic), works in vivo only. Tx moderate-severe essential HTN, by SVR, in combo w/ diuretic and blocker. SE: vasodil headache, flushing, nasal congestion, rare rxn is SLE. Mech unknown widespread arteriodil via gKhyperpolarization close inward Ca channel sm diazoxide nitroprusside nifedipine Adrenolytic agents methyldopa clonidine (guanabenz) Ganglionic blockers trimethaphan Depletors of NT reserpine guanethidine (guanadrel) Adrenergic R antagonist prazosin terazosin doxazosin propranolol metoprolol atenolol acebutolol alprenolol esmolol ACE inhibitors captopril* enalapril* enalaprilat lisinopril fosinopril ramipril benazepril quinapril perindopril moexipril AT II R antagonist m relaxation. Normally K channel closed and Ca flux maintained. Tx: moderate-severe essential HTN. SE: headache, flushing, nasal congestion, (more severe than hydralazine) hypertrichosis (topical for hair growth, could cause hypotension if excessive amt applied). potent widespread arteriodilator. Mech same as above. I.V. in HTN emergencies and to produce controlled hypotension during surgical procedures. potent widespread vasodil (both art. & veins) 1st choice for HTN. L-type blocker. Used in combo w/ a diurectic but NOT w/ blocker because blocker unmasks a severe cardiac depr axn brady, CHF, severe AV block ( CO), and arrhythmias. central actions, agonist of 2 R. NE release arteriodil BP MILD reflex symp stim venodil ortho hypo. Tx mild-moderate essential HTN, also typical and variant angina, in combo w/ diuretics & maybe blockers. SE, in absence of blockers: mild ortho hypo, mild tachy, drowsiness, nasal congestion, dry mouth ( Ach release @ salivary gl, parotid gl swelling), and constipation ( Ach release in GI), ejac. Avoid abrupt w/drawal. i.v. for HTN emergencies. No reflex b/c ganglion blocked. for moderate-severe essential HTN, in combo w/ diuretics and cautiously w/ blocker. lipophilic, penetrates CNS, causes depletion slowly, headache, drowsiness b/c NE deplet’n. Dopamine depletion causes depression and Parkinsonian tremor contraind in depr and PD. NO CNS fx. arteriodil BPmoderate reflex symp b/c NE in nerves involved in reflex symp. W/phentolamine (1, 2 blocker) get very severe reflex symp; Venodilortho hypo. SE: initially get HR and BP b/c amphetamine & cocaine like action. Then get BP reflex. Also get ortho hypo, nasal cong, ejaculation, diarrhea b/c NE to inh 2 Ach release. 1 blockers. For mild, moderate, severe essential HTN, in combo w/ diuretic and block. Moderate reflex symp stim, more serious than clonidine. SE: moderate ortho hypo, mild tachy/palp, nasal cong, infrequent impairment of ejac. NO CNS/GI effects. nonselective blocker 1 blocker. Not helpful for essential HTN b/c it’s mainly a problem of SVR. depr HR and SV, not SVR. Used w/ diuretics and vasodil to prevent reflex symp of vasodil. Can be used alone in young adults and tx HTN brought on by stress/anxiety. used in pts w/ renin-AT axis HTN. BP in pts w/ renin sec’n. BP in other pts b/c it’s also ACE = bradykininase. bradykinin vasodil. Used alone or w/ diuretics, but generally do not need diuretics, b/c renin-AT inhibited. SE assoc. w/ captopril and enalapril agranulocytosis/glomerulonephritis. For all drugs, accumulation of bradykinin, an autacoid persistent coughing in most pts, also get angioedema and skin rash. When used for CHF in pts w/ severe renin-AT component and PVR marked hypotension and renal fcn. Must have good renal fcn to begin with. losartan (Cozaar) losartan & hydrochlorothiazide (Hyzaar) works well in 1’ HTN, less well in essential HTN extremely effective for essential HTN, b/c SVR and circulating vol Cholesterol and hypocholesterolemic drugs to plasma cholesterol cholestyramine Drug of choice for type 2a hypercholesterolemia. Bile acid sequestrant. LDL by 20colestinpol 25%. Does NOT TG. A 4’ ammonium anion exchange resin. P.O. exchange Cl for bile salts exc’n in feces. B/c removes product 7 Ohase + breakdown. SE: well tol but can cause constipation. Drug interxn: interferes w/ GI absorpt’n of many drugs. Should not take other drugs concurrently. Niacin (nicotinic acid) Tx hypercholest, hyperTG, & type 2b hyperlipoproteinemias. cholest & TG, but mainly on TG. synth of TG hepatic sec’n of VLDL, which give rise to LDL circulating LDL and thus cholesterol. cholest (15-30%) and TG (60%) SE: flush + pruritus (itching), which are by aspirin but not acetaminophen. Less frequent are jaundice, glycosuria, hyperuricemia. Contraindicated: hepatic dysfcn and peptic ulcer. Tx type IIa heterozygous familial hypercholest. Inh cholest synth by inh HMG CoA Lovastatin Simvastatin reductase hepatic LDL R synth and removal of LDL from circulation. In combo pravastatin with bile acid sequestrant. fluvastatin SE: Long term use reversible skeletal muscle disorder of moderate to extreme pain, which w/ gemfibrozil use. Contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation b/c cholest necessary for fetal and early post natal development. probucol bis-phenol LDL by producing struct altered LDL rapidly removed from circulation. Not ideal b/c both LDL and HDL. neomycin aminoglycoside anatibiotic inh reabsorption of cholest and bile acids moderate in LDL. No TG . SE: v. toxic. Nausea, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, enterocolitis, hepatic and otic toxicity as well. Best used w/ niacin. To plasma TG clofibrate hypoTG by stim of lipoprot lipase remove TG from circulation30-40% reduction. Hypocholest by both inh of cholest synth and stim of exc’n in bile and feces. For type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia b/c stim degradation of IDL. Pro-drug, hydrolyzed by GI and serum esterases to clofibric acid (active species). SE: nausea, diarhea, wt gain. More serious is gallbladder or hepatobiliary neoplasia. These SE limit its use. Drug interxn: dispace coumarin from plasma prot b/c it’s plasma prot bound. Fenofibrate benzafibrate gemfibrozil new and safer analogs Tx type 2, 4 and 5 hyperlipoproteinemias. der of fibric acid. VLDL TG by 35%+ by inh VLDL synth by liver, and clearance of VLDLs from circulation. LDL some. HDL by stim VLDL catabolism. Used w/ lovastatin muscle pain Drugs for CHF clinical managemt of CHF + inotropic agent: digoxin K sparing diuretic vasodil: venodilator (isosorbide dinitrate) and vasodil (hydralazine) digitalis glycosides digoxin digitoxin amrinone milrinone dopamine dobutamine ACE inh: must be careful in pts w/ v. lo BP b/c further BP could renal fcn more. delays but not change mortality. Active species = aglycone, w/steroid nucleus and lactone ring. Compare to catecholamines: cardiac wk/oxygen consumption ratio. NO in cardiac metabolism of cAMP levels or HR. Myocardial performance and wk index . Tx CHF, esp pts w/ concurrent supraventricular tachyarrhythmias, which responds b/c vagomimetic action of dig by cond vel and ERP in AV node. Mechanism: inh Na/K ATPase by binding to K binding site intracellular Na turns off the Na/Ca exchanger b/c Na can’t enter Ca intracellular bound Ca into free form cardiac contrac’n. Effect: in normal person, SV counteracted by HR. Vasocontriction by digitalis prevents CO. No diuresis because CO unchanged. In CHF, vasodil happens b/c reflex sympa stim and better renal and systemic perf afterload, LVEDV and heart size. Get diuresis b/c CO and renal flow. Get HR b/c direct and indirect (vagomimetic, sensitizes baroreceptor in carotid sinus, vagal outflow bradycardia and AV block, fx blocked by atropine) on SA node. @ hi doses, toxic to SA and can’t be blocked by atropine. Toxicity: Narrow margin of safety. Discont if toxic sxs occur. arrhythmias and cond disturbances common. Less neg transmemb pot by disrupting Na/K ATPase extrasystoles, AP amplitude, and cond vel prolonged PR interval. Ca automaticity. ERP in AV node, but in Purkinje fibers and ventricles. All sets stage for reentry in ventricles. Reverse arrhythmias by adm of K salts, phenytoin or lidocaine. If lifethreatening, give anti-digitalis Ab to neutralize the drug. CNS: CTZ stim vomiting. Diarrhea from activation of dorsal motor n. of vagus GI motility. Also anorexia, lethargy and fatigue, visual problems (hazy vision, disturbed color perception, photophobia), dizziness and headache. Vasculature: vasoconstr of art and veins b/c intracellular Ca in sm m cells. Coronary arterioconstr MI Skeletal m: Fatigue and muscle weakness b/c electrolyte imbalance. Predisposing factors = hypokalemia (by diuretic) digitalis binding; hypercalcemia extrasystoles. Impaired renal (digoxin) (quinidine competes w/ clearance) and hepatic (digitoxin) fcn. Hypothyroidism ( t1/2 of digitalis via renal clearance of drug (digoxin) Drug interxn: 1 blockers and antiAchE, adrenolytic, same fxs. Worst combo = use w/ Ca entry blockers (verapamil) b/c contr + cond vel. Drug of choice. 12-hydroxy digitoxin. Polar and no plasma prot binding or hepatic metabolism. Elim unchanged by kidney. T1/2 = 40 hr tissue accumulation. lipophilic extensive plasma prot binding and hepatic met. Easily displaced by other plasma prot binding drugs. Renal elim of polar metabolites. T1/2 = 5-7 days more tissue accumulation. short term i.v. therapy of severe refractory CHF. CO and PVR. Inh PDE, just like methylxanthines. Toxicity and myocard oxygen demand. amrinone analog. More potent, less toxic, given p.o. short term management of severe refractory CHF, sxs of acute CHF in cardiogenic shock. 1 stim potentially dangerous. Cardiac Arrhythmias antiarrh drugs suppress abnormal automaticity and cond in depolarized cells, but Class I (IA, IB, & IC) Class IA quinidine procainamide disopyramide Class IB lidocaine Tocainide mexiletine phenytoin Class IC minimally affecting activity in normally polarized regions of the heart. @ hi doses, cond in normal tissue drug induced arrhythmias. Cond. Vel fcn of phase 0 dp/dt and amplitude. Na channel blockers. upstroke and amplitude of AP cond vel 1’ in injured tissue and prolong ERP and AP of both normal (?) and injured Purkinje fibers and cardiac muscle. Na channels blocked in activated state by binding to h gate. Depr of ectopic pacemaker rate, cond vel , prolong ERP. Prolong AP by partial blockade of K channels w/ in repolarizing outward current. Most common p.o. antiarr drug. Completely absorbed after p.o., bound to plasma prot. Partial hepatic met and partial elim by kidney unchanged. Cardiac toxicity: antimusc HR and cond in AV node. E.g. use quinidine in presence of atrial flutter vent rate v. tach CO syncope. Lo dose of digitalis (vagomimetic) given b/f quinidine counteracts antimusc axn. Also can give diltiazem to cond @ AV node. Hi dose AV block and contr cardiac arrest. Asystole in pts w/ depr SA node. Extracardiac toxicity: 1 R block vasodil hypotension and reflex tachy. Also GI distress and cinchonism (CNS-mediated headaches, dizziness, and tinnitus). Thrombocytopenia rare. Contrax: AV block, severe hypotension, hyperkalemia, digitalis toxicity, M.G. (can aggravate it b/c partial NMJ blocker) Tx: Works best in ischemia. Mainly atrial and some ventr. arrhythmias. E.g. premature atrial contr, paroxysmal atrial flutter and fibrillat’n, reentrant arrhy, WolffParkinson/White tachy, and v. tachy. Drug interxn: digoxin blood levels by renal elim. Hi dose potentiate blockers. action of coumarin anticoagulants. drug of 2nd choice after lidocaine for v. arrhyth. Less intense fx than quinidine. Cardiac toxicity: Less atrial and v tach, and hi doses cause SA and AV depr b/c less antimusc. Extracardiac tox: Ganglionic blocking activity hypotension, neg inotropic fx, CO. SLE, skin rash, hepatitis, and GI distress. p.o but NOT bound to plasma prot. Hepatic met to N-acetylprocainamide (active metabolite) accumulation = toxicity. Parent and met. both elim by kidney. Contraind similar to quinidine drug of 2nd line for v. arrhyth. in pts who can’t tol either quinidine or procainamide. MORE antimusc (atropine like sxs) and neg inotropic actions than quinidine. P.o. and highly plasma prot bound. Long duration of axn and hepatic met is active. Contraind similar to quinidine but also in glaucoma. Na ch blockers in both activated and inactivated states for ventricle disturbances, no fx on nodal or cond tissue. Mech unkown. AP duration and prolong diastole. Works on depolarized tissue (ischemia, dig tox), not on normal tissue (atrial flutter and fib). NO antichol. 1st choice for v tach and prevent of v fib after acute MI. Also for E disturbances of dig tox. Extensive 1st pass & hence p.o. Metabolites less active but could accumulate. NO cardiac tox = safest antiarr drug. . Extracard tox: CNS toxicity, paresthesias, tremor, convulsions, nausea, and drowsiness. Contraind in pts w/ 2 nd or 3rd degree block b/c blocks idiovent pacemaker. struc analogs of lidocaine. Resistant to 1st pass hepatic metabolism. Can be p.o. but need hi doses. Similar to lidocaine in all aspects. Also cause blood dyscrasias, e.g. leukopenia, agranulocytosis and thrombocytopenia. anticonvulsant w/ limited antiarrh prop. 2nd line drug. Similar but less fs as lidocained. Tx E disturbances assoc w/ dig tox. Block both Na ch and slow inward Ca current (depolarization) evoked by dig (?). Potent Na ch blockers for v arrhyth. phase 0 AP cond vel w/o fx on ERP or AP in Purkinje fibers. Suppress premature ventricular contr and v. response to atrial flecainide Class II Class III bretylium amiodarone sotalol Class IV flutter or fib. SE: CNS related dizziness and blurred vision marked cond vel, CNS: numbness in finger and feet. 1 R blockers, esp in nodes automaticity. Prolong AP/ERP, no in cond vel. Indirectly Ca influx. Tx sinus tach caused by anxiety or thyrotoxicosis or pheochromocytoma; v tach during atrial flutter or fib; dig induced arrhy; PAT. Contraind in pts w/ CHF, dig tox (?) asthma prolong AP/ERP in ventricle w/o altering phase 0 depol/memb pot. strength of E stim needed for v fib. Also for intractable (when fails to respond to other drugs) v tach and controlling fib. emergency tx of intractable v tach Tx PAT and v arrhyth. Ca >>Na blocker sinus rate and AV nodal cond. Must dose to SE: hypotension, neg inotropy, photosensitivity, corneal deposits, pulm fibrosis, hepatic necrosis, affect thyroid fcn b/c releases iodide from drug and long t1/2 = 3-4 mos b/c Vd, accum in fatty tissues. Like bretylium. In add’n, blocks R. Ca ch antag. Block slow inward Ca current during phase 0-4, esp in SA and AV nodes, not in cardiac mscles. cond vel and ERP. Verapamil, diltiazem and bepridil. Tx reentrant supravent tachy and PAT by converting atrial flutter or fib to normal rhythm. SE: neg inotropic, contraind in pts w/ CHF, or taking blockers. Hypotension b/c vasodil assoc w/ diltiazem. Cancer Chemotherapy alkylating agents nitrogen mustard der. Mechlorethamine* (HN2) chlorambucil melphalan (L-PAM) cyclophosphamide* (CYC) ifosfamide (w/mesna) busulfan nitroureas Carmustine* (BCNU) lomustine* (CCNU) semustine (methyl CCNU) streptozocin (antibiot) alkyl sulfonates busulfan (Myleran) ethylenimines trethylenethiophosphor amide (thiotepa) triazenes dacarbazine *(DTIC) Radiomimetics. Methyl gp on N highly reactive and alkylate G @ N-7. Resistance by DNA repair enz. Vesicant or highly irritating action on skin if extravasation should occur during i.v. must be i.v. b/c so reactive. Alkylat’n of DNA by ethylenimonium ion (interstrand xlinking). Rapid inactivation. GI, BM, alopecia, extravasation. Tx Hodgkin’s dz. p.o p.o. very stable. i.v. /p.o. Biotransformation required @ liver to acrolein (F.R., combined w/N-cysteine, a FR scavenger) and phosphoramide mustard (p.m.). P.m is the active anticancer metabolite. SE: GI, BM, hemorragic cystitis (developed in 30% of pts. @ hi dose acrolein toxicity, bladder, ureter + renal pelvis, hemauria prevented by mesna), alopecia. Tx: lymphomas, breast ca… ifosfamide analog of CYC. mesna a potent FR scavenger to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis. BM, CNS, renal failure, even more hem cystitis. Tx testicular ca, sarcomas. unique toxicity = interstitial pulm fibrosis, also severe BM suppression. toxic against brain tumors and lymphomas, b/c lipophilic and XBBB. Delayed marrow toxicity. BM tox last longer (4-6 wks) than by other alkylating agents (2-3 wks). SE: Addisonian like, BM fibrosis, blood count, dosage for BM transplant b/c profound BM suppression. Tx: chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) Sim to N mustard, but more stable. Toxicity similar. nonclassical alkylator that causes formation of DNA adducts. Also an anti-metabolite procarbazine* platinum cisplatin *(DDP) Carboplatin (paraplatin) antibiotics anthracyclines doxorubicin* (adrimycin) Daunorubicin* (cerubidine) idarubicin* bleomycin* Miscellaneous dactinomycin* Plicamycin (mithramycin) mitomycin streptozocin* mitoxantrone Plant derivatives vinca alkaloids vincristine* Vinblastine* b/c a purine. Light sensitive; N-demethylation by p450 toxic (alkylates DNA) once converted. SE: principal tox on GI (nausea and vomiting), little BM suppression. Good drugs to combine with other drugs that cause serious BM. Tx: Hodgkin’s dz; melanoma. highly reactive oxygen radicals degradation of DNA. XBBB. xsomal breakage mutagenic, teratogenic, and carcinogenic. Used 1’ in MOPP rgimen for Hodgkin’s. SE = GI and BM. CNS tox (sedation and depr) and skin rashes, esp @ hi doses. Only cancer drug that has disulfiram rxn. Also a MAO inhibitor. Given @ set dose based on renal toxicity. Tx: In combo therpay for esp metastatic testicular ca, also germ cell ovarian ca and small cell lung ca. Cis Cl is the active form that binds to DNA at nucleophilic sites intrastrand DNA x-link on G’s. Unionized in extracellular space b/c Cl rich. Becomes unionized in Cl depleted cell. Not phase specific and highly bound to proteins. Renal clearance can cause renal failure (dose related and cumulative), so must give w/mannitol for diuresis. SE also includes ototoxicity, neurotox (peripheral neuropathies—tingling, numbness), severe emesis (tx w/ 5 HT3 antag, Ondansetron); mild BM. Given @ higher dose than cisplatin. Mech the same, but rate of active metabolite generation slower longer plasma t1/2. More BM, rare nausea. Less renal tox. Not for curative intent. Tx: ovarian ca, lung ca. Mech: interaclation steric hindrance interfere w/ DNA synth.. Topo II inh. Also Metal ion chelation; FR formation Extensive biotransformat’n in liver. SE: vesicant upon extravasation. BM, severe alopecia, GI, cardiac damage b/c sensitive to FR. Give w/ FR scavenger to cardiac tox, but may anti-cancer fx. Cardiac toxicity (damage to myofibrils CHF) dose related. Given < 500 mg/m body surface for life time. Exacerbated by exposure to alkylating agent, radiation therapy, radiation recall (drug given after radiation). Tx: malignant lymphomas, breast ca, sarcomas tx leukemia bifunctional w/ DNA binding and active redox sites. In the absence of Fe3+ and O2 no damage. In the presence, Fe2+ releases electron to DNA covalent binding. Renal clearance. SE: bleomycin hydrolase = degrad enz absent in lung and skin pulm fibrosis. Most toxic drug to lung. Also skin rash, esp in fingers. Also get anaphylaxis/hypersensitivity. Not much BM @ hi dose, inh DNA, @ lo dose, inh RNA. Tx Wilms’ tumor. Tx hypercalcemia. Toxicity to bone by inh bone formation hemolytic uremia syndrome (kidney damage and platelets b/c consumption of platelets) an antibiotic but acts like nitrosoureas. Tx insulinoma b/c causes Islet cell damage. Otherwise, cell tox = SE DM in pts similar to doxorubicin, but less cardiotox. work just like cochicine excpet much more potent v. toxic microtubule damage, mainly in nervous system metaphasal arrest and inh axonal transport. Hepatic clearance. Peak short lasting though prolong terminal plasma t1/2 = long tail accumulation in nerve. SE: neurotoxic; extravasation. Tx ALL, less so for lymphomas. microtubule damage mainly in myeloid cells of BM. Short terminal t1/2 and no long tail (conc x T= exposure of rapidly dividing cells to drug). BM, neurotox rare. Tx germ cell tumors; lymphomas; breast ca. Vinorelbine (Navelbine) epipodophyllotoxins etoposide (VP-16) Teniposide (VM-26) Yew tree der paclitaxel (taxol) taxotere Camptothecin der (irinotecan [CPT 11]) antimetabolites Methotrexate* 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)* floxuridine (FUDR)* Cytarabine* (cytosine arabinoside; ara-C) purine analog* 6-mercaptopurine * (6-MP) Allopurinol* Complexing w/Topo II SS breakage of DNA. Phase specific (S and G2). Schedule dependent (given 3-5/d, to chance of hitting ca cells during specific phases of cell cycle); hepatic biotransformation; renal clearance. SE: BM, GI, alopecia, vesicant action at site of injection, vasomortor hypersensitivity, neuropathy. Tx: refractory testicular ca; small cell lung ca. New drug under developmenttx children’s tumor. Given w/ cremifor (caastor oil), i.v. 3-24 hr infusion. Large Vd. Hepatic metabolism and nonrenal clearance. Promotes assembly of microtubule and stabilizes them abnormal arrays of microtubules thruout cell cycle apoptosis. SE: BM (dose limiting), hypersensitivity, hypotension or bradycardia, peripheral neuropathy, arthralgia/myalgia, severe alopecia, occasional hepatic dysfcn. Tx: ovarian ca (in relapse), breast ca. mech same as paclitaxel. Water soluble, 1-hr infusions (w/o cremifor). SE: skin rashes, effusions and endothelial damage edema, tx w/ corticosteroids; rare hypersensitivity. BM. Alopecia. Tx same as above. Topo I inh (during SS cleavage, binds to strand (?), prevent DNA reannealing and stop repl fork. Prodrug w/ complex biotransformat’ns, schedule dependent. SE: BM, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, mucosistis, alopecia. Only tx for fluoropyrimidine resistant colorectal ca. inh active site of enz or allosteric site., or act as false substrate. folic acid analog. Inh dihydrofolate reductase. Can directly be injected into CSF since does not xBBB. But can leak into systemic circ. So give leucovorcin (N-formyl FH4) to prevent BM suppression. Also, @ hi dose of MTX, it can bypass carrier and go into the cell. Then give leucovorin which rescues normal cells preferentially b/c they can conc leucovorin better. This way, get selective killing of cancer cells. Renal exc’n, so need good renal fcn. Monitor blood level of MTX. SE: BM; GI, liver dysfcn; mucositis. Efficacy: IT (?)leukemia, mg/m2 head and neck, choriocarcinoma, breast. gm/m2, osteosarcoma adjuvant, childhood ALL. pyrimidine analog. curative in early stage and palliative when advanced. Inh thymidylate synthetase , which forms 4’ complex w/ leucovorin @ hi dose of leucovorinenhance 5-FU). Extensive metabolism. 5-FdUMP=active metabolite. SE: BM (bolus), GI (cont infusion or w/ leucovorin mucositis/diarrhea). Tx: advanced colon ca (for stage 3, 5-FU 1/3 cure rate improvement after lymph node resection), breaast ca. complete 1st pass if given via hepatic artery. SE: cholangitis. Tx: colon ca metastic to liver. pyrimidine analog competitive inh DNA pol in S phase. Inh also DNA repair. Forms defective DNA. Must give 2x/d for 5-7 days to gets cells sensitive. Biotransformat’n, including intracellular. Schedule dep. must be given continuously e.g. 2-wk cont infusion. SE: BM, GI, @ high dose cause neurotox. Mucositis. Tx Acute myelogenous leukemia 6-thioguanine, acts as false precursor. Not degraded by xanthine oxidase. No drug interxn w/ allopurinol. Can only be a maintenance therapy for low tumor burden if used w/o allopurinol. BM. Tx acute leukemia. Purine analog. inh purine ring synth by inh several enz systems, and acting as false precursor. Similar to Imuran. Normally degraded by xanthine oxidase, so must give hi dose. If given w/allopurinol, must dose. SE: BM; liver damage. Tx acute leukemia (childhood ALL) a supportive agent, not an anticancer drug by itself. Xanthine oxidase inhibitor. Pts w/ large tumor masses or extensive met ca metab lots of purines from malignant cells into uric acid via xanthine oxidase. Allopurinol prevents uric acid nephropathy. Purine nucleoside analogues fludarabine deoxycoformycin 2chlorodeoxyadenosine miscellaneous hydroxyurea Hormones + hormone antagonists diethylstilbestrol (DES) tamoxifen* Prednisone* dexamethasone Megestrol acetate or Megace androgens flutamide Leuprolide, goserelin/Zoladex aminoglutethimide Octreotide acetate sandostatin miscellaneous procarbazine (Matulane) Mitotane (o,p-DDD) Not need to know. Yay! L-Asparaginase* Estramustine phosphate levamisole all requires intracellular activation and inh intracell enz. BM. Tx chronic lymphocytic leukemia. inh ribonucleotide reductase and DNA pol. inh adenosine deaminase causes DNA strand breaks and apoptosis. Tx hairy cell leukemia. replaces usulfam for CML. Also for essential thrombocythemia. fetal Hb exp’n in sickle cell anemia pts. Mech: Inh ribonucleotide reductase. Well absorbed orally. BM (rapidly reversible). Tx prostate (b/c suppress androgen synth), also breast ca (?) synthetic nonsteroidal mixed antagonist/agonist on estrogen Receptor. Hepatic biotransformation. t1/2. SE: flushing, leukopenia and rare hypercalcemia, hot flashes, vaginal dryness or discharge.. Tx: breast ca by directly inh growth of ca cells w/R, but no effect on cells w/o R. (Estrogenic effect improves cardiac and osteoporosis risks. But estrogen also a carcinogen b/c see small in endometrial ca. Try to elim estrog fx by designing anti-estrog drugs. NONE available. glucocorticoids. Used in MOPP and other combo. SE: hi dose feeling of well being prompt weak pt to overexert. Prednisone short t1/2, and dexa long t1/2. Tx ALL, lymphomas, toxicity of chemo. progestins, Tx endometrial ca. 2nd line therapy for breast ca. Used in HIV pts to stim appetite (prevent wasting). Used occasionally for breast ca antiandrogens. For prostate ca. LHRH and GNRH agonists downreg of R @ the pituitary medical castration. Effect of initial testosterone surge blocked by antiandrogens. aromitase inhibitors. For females who converts peripheral androgen to estrogen, can use this drug to block the conversion. somatostatin analogue. T1/2 = min. Maintains GI mobility, for pts w/ diarrhea. S.C. injection for symptomatic tx of carcinoid syndrome (malignant, seen in ileum/stomach, bronchus, somtimes testes/ovary. Carcinoid prod 5-HT (tricuspid fibrosisinsufficiency), bradykinin severe flushing and diarrhea. nonclassical monofunctional alkylator. XBBB. SE: GI, BM, disulfiram/antabuse like rxn, neurotoxic, pyridoxal phosphate, MAO inh, allergy, skin rashes, most potent carcinogen and causes delayed carcinoma. Classic drug in combo therapy for Hodgkin’s dz. DDt relative. Conc in adrenal cx. Adrenocortical necrosis palliation of inoperable adrenocortical adenocarcinomas. Must be given w/ adrenal replacement. SE: skin rashes; encephalopathy, anorexia, nausea, diarrhea, lethargy, dizziness. Large bacterial protein given IM/IV. Acts extracellular (EC) to depletes tissue Lasparagine. Deaminates EC L-asparagine to aspartic acid inh protein synth and apoptosis. Asn usu a nonessential AA. But essential in ca cells b/c they lose asparagine synthetase. Therefore this targets sensitive cells but also select for cells that can produce synthetase. Only produce remission for a brief period, but must be combined w/cytosine roboside and antibiotics. SE: anaphylaxis; serum proteins, pancreatitis, encephalopathy, clotting factor abnormalities, ammonia toxicity in CNS. Tx acute lymphoblastic leukemia. combines alkylating agent w/hormone localization of alkylating agent at hormonally responsive tumor site. Minimally useful for prostate ca. immunomodulation and deworming agent in animals. Allergic rxns, blood count depr. Hepatic lesions mimics metastatic ca. Used as adjuvant therapy for colon ca (w/ 5-FU) all-trans-retinoic acid Investigational. induction of cell differentiation. SE: skin cracking, headache, blood cholesterol and TG, WBC and platelet, liver tox, cardioplulm distress. Tx promyelocytic leukemia. Antimicrobials Abbreviations used in this section: R = resistance p.o.= absorbed well orally X-sensitivity = cross sensitivity X-R = cross resistance Def= deficiency Met = metabolism Vd = distrib well throughout tissues = lots/long/many Folate Antagonists sulfonamides sulfasalazine Sulfadiazine* sulfisoxazole sulfamethoxazole* sulfacetamide trimethorprim Co-trimoxazole Mech: inh synthesis of FH4 inh formation of purines, pyrimidines, and certain AA bacteriostatic. No longer drugs of choice for UTI’s b/c of SE and R. Plasma prot binding. Hepatic met. Renal elim. SE: Metabolites ppt at acidic pH crystalluria, need adequate fluid intake and alkalinization of urine. Hypersensitivity. Hematopoietic: agranulocytosis, megaloblastic anemia, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia uncommon. Hemolytic anemia* in pts w/ G-6-PD deficiency. Kernicterus in newborns b/c displace bilirubin from albumin bilirubin XBBB irrev. brain damage. Adverse Drug Interxn: potentiation of sulfonylurea hypoglycemic drugs, orgal anticoag, phenytoin, and MTX via prot binding or competition for hepatic metab and renal sec’n. not well absorbed p.o tx Infl Bowel dz, e.g. Crohn’s dz and ulcerative colitis. worst crystalluria. Used in combo therapy. Metabolite 5-aminosalicylate works just like aspirin = anti-infl. W/ pyrimethamine to tx malaria. Conc best in CSF and brain. least likely to cause crystalluria. Most useful when used alone least likely to cause crystalluria. Used in combo therapy. topically for eye infections competitive inh of dihydrofolate reductase inh FH2 going to FH4. Low affinity to mammalian enz. Bactericidal. Lipophilic Vd. SE: No rashes or other hypersensitivity. GI distress. Folate def BM. Tx OD by giving FH2 and/or FH4. trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole. Synergistic. Sulfonamide FH2 formed FH2 to compete w/ trimethoprim for dehydrofolate reductase. Combo bactericidal. SE since dose. SE: hypersensitivity and GI distress. Tx UTIs, resp, GI and gonorreha infections, and PCP and isospora belli (diarrhea) in AIDS pts. Also uncomplicated UTIs and prostatitis caused by Enterobacteriaceae, orchitis and epididymitis caused by susceptible bacteria and chalamydiae. Inhibitors of cell wall synthesis Pencillcins Bactericidal, against rapidly dividing bacteria that synth a peptidoglycan cell wall. Synergistic w/ aminoglycoside antibiotics. Forms covalent bond w/transpeptidase weakened cell wall. Murein hydrolases (autolysins) which normally remodels cell wall continue to work cell lysis. Incompletely absorbed p.o. alter intestinal flora tx salmonella derived enteritis. Vd but no bone/CSF unless these areas infl. bind to plsma prot (> 90%). Tubular sec’n (90%). Probenecid inh sec’n plasma levels. dose in pts w/ impaired renal fcn. SE: Natural penicillins penicllin G (benzylpcn) procaine pcn G benzathine pcn G penicillin V (phenoxymethylpcn) Antistaphylococcal pcn vancomycin ciproflxacin rifampin imipenem/cilastatin Extended spectrum pcn ampicillin amoxicillin Clavulanic acid sulbactam tazobactam Antipseudomonal pcn azlocillin mezlocillin piperacillin ticarcillin or carbenicillin + clavulanic acid hypersensitivity in 5% of pts: hepatic met to penicilloic acid haptenized urticaria, angioedema, and anaphylaxis. X-sensitivity. Diarrhea**: altered intentinal flora C. difficile peudomembranous colitis from toxin. Neurotoxicity: seizures upon intrathecal injection esp in pts w/ epilepsy. Platelet dysfunction** inh platelet aggr by carbenicillin and ticarcillin (binding to ADP R). CI in pts predisposed to hemorrhage. cation toxicity: carboxy pcn adm as salts. Should use a more potent pcn to avoid this problem. For G+ and G- cocci, G+ bacilli and spirochetes. Unstable in stomach must be i.m. Pcn G salts in i.m repository. More acid stable better than Pcn G for p.o. V&G inactiv by -lactamases. Less effective than Pcn G against G- (Neisseria and Haemophilus and some anaerobic species), NOT effective against aerobic G- enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonias. Tx strep, penumoncoccal, anaerobic(except B. fragilis), gonococcal infections, syphilis. used for methicillin resistant staphylococci only. less potenet than Pcn G against G+ and G- cocci. Drugs of choice for G+ bacillus, Listeria monocytogenes. Also for G- bacilli & G- Enterobacteriaceae. Tx URTI caused by Haemophilus, and also uncomplicated UTI. not well absorbed p.o. GI distress, overgrowth of other organism, and diarrhea. SE: rash (maculopapular) occurs most frequently w/ampicillin. completely absorbed from GI no diarrhea and no altering intestinal flora. penicillinase inhibitor. Used with ampicillin and amoxicillin. effective against many G- bacilli including P. aeruginosa and enterobacteriaceae. NOT effective against klebsiella b/c consitutive -lactamase present. most potent of the group adm i.v. b/c not absorbed p.o, inh platelet aggr, also adm as Na or K salt hyperkalemia and hypernatremia. Tx klebsiella Cephalosporins 1st gen cefazolin 2nd gen struct, fcn, mech just like pcn’s. More resistant to -lactamases. Unstable in stomach i.v. Renal elim and little hepatic metab, except for cefoperazone and ceftriaxone (hepatobiliary route). Hypersensitivity common but less freq. 15% x-sensitivity w/ pcn so CI in pts sensitive to pcn. R to staph penicillinase. Against G-, e.g. Proteus mirabilis, E. coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae (PEcK). Good acitivity against G+ and moderate activity against G-. Tx UTIs, resp and skin infections. most popular iv. surgical prophylaxis. Less active than 1st gen against G+, but activity against G-. Also inh H. influ, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Neisseria (HENPEcK). Do not inh Psudomonas species or bacteroides except for cefoxitin, which tx B. fragilis. Tx UTIs, resp infections, aspiration cefotetan 3rd gen cefixime Cefotaxime cefamandole cefoperazone pneumonitis, intraabdominal and pelvic infections. tx intraabdominal and pelvic infections b/c activity against most enterobacteriaceae and anaerobic species. Little activity against G+ (cocci), but superior activity against G- bacilli. Spectrum = Those of 2nd gen plus Pseudomonoas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens. Tx nosocomial resp infections, UTIs, skin struct infections, osteomyelitis. only drug given p.o., Tx Haempophilus and gonorreha. drug of choice for meningitis caused by H. influenza (most lipophilic b/c XBBB). Disulfram like rxn don’t drink. Also inh formation of vit-K depedent clotting factors bleeding. Don’t give w/ aspirin, dicoumarol/warfarin. Other -lactam antibiotics carbapenems imipenem + cilastatin Monobactams aztreonam synthetic -lactam. Broadest spectrum -lactam. Active against penicillinase-producing G+ and G-, anaerobes, and P.aeruginosa. But R in P. aeruginosa begin to appear. Renal elim and No hepatic metabolism. XBBB. O.D. seizures. SE: hypersensitivity & Xsensitivity to pcn. Adm i.v. Rapid i.v. infusion nausea and vomiting. Extensive hydrolysis in kidney metabolites nephrotoxic, & [parent drug] effectiveness in treating UTIs. Must be given w/cilastatin, an inhibitor of renal dihydropeptidase. Together tx serious infection of unknown origin. very narrow spectrum but R to -lactamases. Inh only aerobic G-, mainly enterobacteriaceae and P. aeruginosa. Tx bacteremia, UTIs, resp infections, osteomyelities and skin struc infections. i.v./i.m.. Renal elim unchanged. V.safe. No hypersensitivity. Good substitute for Pcn in pts allergic to Pcn and have G- infection. Non -lactams but inh bact cell wall synthesis vancomycin bacitracin Inh cell wall synth by binding to free COOH of D-Ala (end of pentapeptide), interfere w/ elongat’n of peptidoglycan backbone. Inh only G+, b/c its MW and can’t X OM of G-. Bactericidal against G+ cocci and bacillli, e.g. staph and strep. Bacteriostatic against enterococci (faecalis and faecium). W/aminoglycoside =synergistic/ bactericidal. Not absorbed p.o. tx pseudomemb colitis caused by C. difficile or staph in colon. Only for serious infections, mainly staph in pcn allergic pts and methicilliln R staph. Also prophylaxis to prevent endocarditis in pts w/ valvular heart dz undergoing dental/surgical procedures. SE: w/aminoglycosides ototocity that occurs @ hi doses, also nephrotoxicity. Phlebitis caused by i.v., prevented by adm of diluted sol’n. Older prep impure red man syndrome = head and neck erythema and hypotension b/c extensive histamine release. mixture of polypeptides that inh cell wall synth. Bactericidal against a wide variety of G+. Topical, not systemic b/c of its nephrotoxicity. Combined w/ neomycin (aminoglycoside) and/or polymyxin (a detergent that breaks OM of G-) Inhibitors of prot synthesis Tetracyclines Mech: Entry into G+ E dependent, G- by diffusion thru porins of OM into cytoplasm thru prot-carrier. Binds to 30S ribosomes. Weakly bound to ribosomal prot. R via drug efflux prot induced by drug + mutations in OM prot. Broad-spectrum. But widespread resistance limit its use. Drugs of 1st choice Mycoplasma pneumoniae, chlamydial infect’n affecting sexual organs, syphilis if on long therapy. No longer used for N. gonorrhoeae, or UTIs. P’kinetics: absorption: Dairy foods, Mg/Al antacids, Fe prep GI absorption if given p.o. b/c chelates w/ cations. Distribution: bind to calcifying tissues, e.g. teeth and bones. Partial hepatic met (glucuronidat’n) and partial renal elim unchanged. CI in pts w/ renal dysfcn except when using doxycycline. All X placenta and conc in fetal bones and tooth. For the 2 drugs below Minocycline doxycycline SE: GI—irritation of gastric mucosa, controlled by co-adm of foods other than dairy products. Deposition in bone and 1’ dentition during calcificati’n during growth discorloration and hypoplasia of teeth and temporary stunting of growth. Avoid use in pregnancy and children under 8. Fatal hepatotoxicity—in pregnant women w/ pyelonephritis. Phototoxicity: severe sunburn if exposed to sunlight only for a short period. Worst = doxycycline and demeclocycline. Suerinfections: get candida in vagina or resistant staph in intestine. V. lipophilic enter G- thru OM and porins, less affected by drug resistance, escapes chelate formation absorbed the best . Bacteriostatic. Tx rickettsial dz such as Rocky Mt Spotted Fever and typhus prophylactic to eradicate carrier state of meningococci b/c XBBB best w/o infl. But rifampin = preferred drug. SE: Ototoxicity vestibular problems: dizziness, nausea, vomiting b/c it conc in endolymph of ear. prevent traveler’s diarrhea, but worst phototoxicity and R limit use, not recommended. Used w/ H blockers for ulcers. Complete biliary exc’n, used in pts w/ renal dysfcn. Aminoglycosides amikacin Tx serious infections due to aerobic G- bacilli, 1’ against Enterobacteriaceae /P. aeruginosa, Staph and strep inh. Tx endocarditis from enterococci or viridans strep but must be adm w/ pcn. Gentamicin preferred b/c streptomycin R common. Bactericidal against only aerobic, but not anerobic bacteria. Transport thru bact cell wall and cyto memb. Not need to know transport: assoc b/t cationic drug and anionic surface penetration thru pores of OM of Gbacteria, or disrupt OM & uptake thru nonporin ch, or water filled areas of peptidoglycan wall in G+. Then binds to transport molecule in ETC moves X memb, oxygen dependent binds to 30S polysome disaggr to monosomes and misread mRNA Transport inh by divalent cations. Resistance via uptake b/c oxygen dependent transport is altered 30S binding site affinity. Enz modification of aminoglycoside plasmid mediated drug affinity for 30S not accum w/n bact. P’kinetics: polar and polycationic p.o. absorption, must be i.v. or i.m. NOT XBBB. Conc most in renal cortex and endolymph/perilymph of inner ear nephrotoxic/ototoxic. X placenta and accum in fetal plasma and amniotic fluid. No hepatic met b/c so polar already. Renal elim. dose in pts w/ renal dysfcn/failure. SE: Nephrotoxicity -Rev (b/c renal tubular cells can regen) renal impairment in 5-25% of pts on drug for > 3d. Trapped in lysosome and inh PI specific phospholipases inh PG synth unopposed AT II vasoconstrict’n and inh glom filtration. Also inh sphingomyelinases and ATPases and alter mito fcn and ribosomes in prox tubular cells. Ototoxicity—vestibular (damages organ of Corti, esp outer hair cell in basal turn)/cochlear (hair cells of ampullar cristae) directly related to peak plasma level and duration of tx. NMJ block—in pts w/ MG and pts undergoing surgery on anesthetic and NMJ blockers. By inh presynaptic release of Ach and postsynaptic R blockade. resistance develops least to it. More auditory toxicity. So does kanamycin. neomycin streptomycin must be topical b/c most severe nephrotoxicity. least nephrotoxic. More vestibular toxicity. So does gentamicin Erythromycin—macrolide antibiotic broad spectrum same as Pcn G, bacteriostatic. Bind to 50S. R via uptake and affinity for 50S. P’kinetics: Vd, enhanced by infl, except no XBBB. Accum in prostatic fluids and Mphages and liver. Metabolism: extensive p450, then renal elim. Active drug goes thru enterohepatic circulation. SE: epigastric distress poor patient compliance. Cholestatic jaundice b/c hypersensitivity. Transient deafness @ high doses. CI in pts w/ hepatic dysfcn b/c accum in liver. Adverse Drug interxn (not need to mem): inh met of theophylline, cyclosporine, carbamazepine, corticosteroids, and digitoxin. Fatal common combo = terfenadine/astemizide + erythromycin @ hi dose fatal arrhythmia “torsades de pointes”. Azithromycin clarithromycin troleandomycin Chloramphenicol chloramphenicol Not widely used. Broad spectrum against bact and nonbact, esp for B. fragilis. but limited to life-threating infections b/c its toxicity. Generally bacteriostatic but can be bactericidal against certain org. Tx rickettsial dz if pt can’t tol tetracycline. Do not use for UTI, resp or brucellosis infections b/c other less toxic drugs available. Mech similar to erythromycin. Resistance via an R factor for acetyl co-enz A transferase inactivates drug. Also by permeability. p.o, also given i.v. Vd b/c lipophilic (pleural, axcites and abscess fluids. XBBB and other organs). Hepatic met (to glucuronide) and renal elim. SE: hemolytic anemias in pts w/G-6-PD deficiency. (sim to tox. of primaquine, sulfonadmide). Rare, aplastic anemia as idiosyncratic rxn and usu fatal. Also more common rev anemia. Gray Baby Syndrome: in neonates b/c lo hepatic and renal fcn drug accum mito ribosome fcn cyanosis, usu fatal. Adverse drug interxn: Inh P450 met of phenytoin, tolbutamide, chlorpropamide, and dicumarol. Clindamycin Mech and R similar to erythromycin. X-R not a problem. Inh most G+ cocci and many anaerobes but not aerobic G-. Most enterococci are R but actinomyces are inh. Used 1’ for intraabdominal and gyn infections caused by anaerobic bact such as B. fragilis. Alternative to pcn. P’kinetics: p.o. Vd except no XBBB. Good entry into bone. Extensive met in liver (CI in pts w/ hepatic dysfcn) and renal elim. Some exc’n by bile and feces. SE: Allergic skin rashes. 3-5% of pts on clindamycin develop pseudomemb colitis b/c overgrowth of C. difficile. This tx by p.o. vancomycin. Spectinomycin binds to 30S, i.m. Drugs of 2nd choice for acute gnorrhea caused by penicillinase producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae (usu tx 1st by ceftriaxone if pt not allergic to pcn and cephalosporins), or by nonpencillianse producing org in pts allergic to pcn. Quinolones. Nalidixic acid (prototype) New fluoroquinolones Norfloxacin* Ciprofloxacin* Sparfloxacin* ofloxacin enoxacin lomefloxacin levofloxacin pefloxacin All quinolones: Bind cations p.o. absorption Renal exc’n. tx recurrent UTIs. Inh Topo II and IV (DNA gyrase). No X R with other antimicrobials. R assoc w/xsome, not plasmid. By mutation in Topo and permeability. Effective aginst most G- that cause UTIs. G+ are resistant. Vd. Met to a more active metabolite. SE: nausea, vomiting, ab pain. Less common are urticaria, photosensitivity, and fever. CNS: headache and visual disturbances rare. for norfloxacin and ciproxacin: less freq emergence of resistant strains. Most susceptible to resistance = P. aeruginosa and Strep pneumoniae b/c only marginally sensitive. Vd. SE: CNS mediated nausea, headache, and dizziness. Caution in pt w/ CNS disorders. Crystalluria @ hi doses. CI: pregnancy and children under 18 b/c cartilage toxicity in immature animal occurs. All fluoroquinolones: hepatic inactivation. P450 < that of erythromycin. More potent than nalidixic acid, tx both G+ and G-. For complicated and uncompl. UTIs and prostatis. More potent than norfloxacin but similar spectrum. Every drug from ciprofloxacin on tx many ststemic infections and multiple R bact, e.g. many enterobact and G- bacilli. Both i.v. and p.o. Alternative to toxic drugs such as aminoglycosides or drugs that require i.v. e.g. extended spectrum pcn and cephalosporins. not metab by P450, renal elim ( dose in pts w/renal dysfcn) Not need to memorize. Antimycobacterial Drugs Vd = can reach most tissue b/c need to reach caseous granuloma chemotherapy of TB isoniazid rifampin ethambutol must use combo therapy to prevent R during the long duration of therapy, up to 2 yrs. 1 st line drugs = isoniazid, rifampin, ehtambutol, pyrazinamide inh synth of mycolic acids. R via no uptake. No X R. Bacteriostatic in stationary phase and bactericidal in rapid division. Selective for TB and M. Kansasii. p.o. but by Al in antacids. Vd but [CNS] lower. Met by acetylation and hydrolysis. SE: peripheral neuritis (paresthesia) most common in slow acetylators, from pyridoxal deficiency. Isoniazid bind to pyridoxal deriv no vit activity. Corrected by pyridoxine (vit B6). X milk. Hepatotoxicity: most serious SE, 1% incidence, jaundice, in fast acetylators. Idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity: if taking rifampin and alcohol @ same time. Hypersensitivity = rashes and fever. Memory impairment and convulsions. P450 met. e.g. inh phenytoin met nystagmus and ataxia. Fast acetylators at risk. inh DNA-dep RNA polymerase (Inh initiation but not elongat’n). Selective for prokaryotes. R emerges rapidly via enz affinity for drug never give drug alone for TB. Usu w/isoniazid. Spectrum: Bactericidal for both IC and EC mycobacteria. For TB and leprosy, prophylactic for meningitis in Neisseria meningitidis or H. influ. Inh most G+ bact such as staph and strep, many enteric species (Pseudomonas, Legionella, mycoplasmata and chlamydiae). Most anaerobic (C.difficile and B. fragilis) P’kinetics: lipophilic, p.o. and Vd, XBBB. P450 induction, observed the most. SE: Nausea, vomiting, rash and fever. Hepatotoxicity rare. bacteriostatic and selective for M. TB and M. kansasii. Used in combo w/ isoniazid, rifampin and pyrazinamide for TB. CNS entry adequate for TB meningitis. SE: optic neuritis visual acuity and poor discrim b/t red and green (rev upon w/drawal). Worsen gout b/c inh uric acid exc’n by kidney. pyrazinamide 2nd line of drug for TB ethionamide cycloserine Aminoglycosides Chemo for leprosy dapsone clofazimine p.o. bactericidal, Short Term initial therapy in combo w/ isoniazid and rifampin. 1-5% on this combo get hepatotoxiity. Urate retention precipitate acute attack of gout struct analog of isoniazid but mech unknown. SE: GI distress and CNS: headache and depr Vd. CNS: convulsions and exaggerated epileptic seizures, and peripheral neuropathies. streptomycin, kanamycin, and amikacin dapsone + clofazimine + rifampin. Must be in combo b/c R can develop to any one drug during the long duration of the tx. related to sulfonamide, bacteriostatic by inh folate synth. p.o, Vd, liver met. SE: hemolytic anemia and methemoglobinemia via oxidation by hepatic metabolite. GI distress, headache, peripheral neuropathies, psychoses, tinnitus, and skin rashes. Can provoke lepra rxns, controlled by glucosteroids. Can tx PCP in AIDS pts. bactericidal to M. leprae by binding to DNA. P.o. and accum in fatty tissue w/t1/2 = 90 d. SE: red discoloration of skin and eosinophilic enteritis. Antifungal Drugs for subcutaneous and systemic mycoses amphotericin B Flucytosine (like 5-FU) ketoconazole fluconazole for superficial mycoses griseofulvin Tx systemic mycoses. Used w/ flucytosine to doses of amphotericin B. Mech: binds to ergosterol pores disrupts memb fcn, electrolytes (esp. K) and small molecules to leak out cell death. R via ergosterol content of fungal memb. Spectrum: Fungicidal/fungistatic. Against candida, Histoplasma capsulatum, Cryptococcus neoformans, coccidioides immitis, many strains of aspergillus, and Blastomyces dermatitidis. P’kinetics: i.v., Vd except CSF. Intrathecal to tx meningitis if it’s sensitive to this drug. Biliary exc’n. Plasma prot bound. Long t1/2 = 2 wks. SE: Low therapeutic index. Fever and chills on 1st i.v. adm. Renal impaiment in 80%+ of pts, rev but hi dose can cause permanent damage. Hypotension (shock like) along w/ hypokalemia toxicity of digitalis. Need K supplementation. Normochromic, normocytic anemia by rev suppression of RBC prod, worsened in HIV pts taking zidovudine. Intrathecal route cause neurological effects. tx systemic mycoses only in combo w/amphotericin B synergistic (amphotericin pokes holes for flucytosine to enter) and prevents R. For subcut chromomycosis, used alone. Mech: Converted to 5-FdUMP, which inh thymidylate synthetase. Also met to 5FUTP and incorp. into fungal RNA disruption of protein synth. Spectrum: fungistatic, tx candidiasis, cryptococcosis, aspergillosis, and chromomycosis. P’kinetics: p.o, Vd including CSF. Partial met and renal elim. SE: hematological—reversible neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, BM, b/c of 5-FU. Hepatic dysfcn. GI. tx systemic mycoses. Mech: inh fungal P450 inh conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol. Additive effect w/flucytosine in tx of candida, but antag amphotericin B. No R reported. Spectrum: fungistatic or fungicidal depending on dose. Most effective against histoplasmosis in lung, bone, skin and soft tissue even though tissue penetration limited. Also for nonmeningelal cryptococcosis and blastomycosis, candida, and various dermatophytic infections (including ones R to griseofulvin). P.o., but absorption need acidic pH (impaired by food, antacid, cimetidine..) Does not go in CSF. P450 induction. Biliary exc’n. SE: GI, inh gonadal and adrenal steroid synth gynecomastia. Allergy, hepatic dysfcn. Drug interxn: potentiates nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine b/c inh its met. most recent drug and most useful. Same mech as ketoconazole. P.o or i.v. XBBB of normal/inflamed meninges. No need for acidic pH for GI absorption. Less P450 induction. 70% drug elim unchanged. Spectrum: Candida, cryptococci, blastomyces, and histoplasma. Not aspergillus or other filamentous fungi. Drug of choice for crytococcal meningoencephalitis, disseminated histoplasmosis, and coccidioidomycosis (cond in immunocomp pts) disrupt mitotic spindle and inh mitosis. Tx dermatophytic infections b/c accum in nystatin Miconazole clotrimazole econazole tolnaftate infected, newly synth, keratin tissues = hair and nails. LT therapy need until normal tissue replaces infected tissue. R via lack of E dependent uptake. Spectrum: fungistatic. Effective against Trichophyton, microsporum, and epidermophyton. Tx severe refractory tinea infections. P’kinetics: p.o. enhanced if w/ high fat diet better uptake as micelles. NOT effective topically. P450 induction and renal elim. SE: safe but can cause allergic rxn, headache and nausea, hepatotoxicity rare, potentiate effect of alcohol b/c its slight CNS depr, teratogenic in lab animal, CI in pts w/ acute intermittent prophyria b/c heme synthesis along w/ P450. related to amphotericin B. Restricted to topical tx of candidiasis (oral, vaginal and Candida esophagitis) b/c systemic tox. Never i.v.. B/c not absorbed p.o, given p.o. for local oral and intentinal candidiasis. OTC. Topical, rarely i.v. b/c severe tox. Prop similar to ketoconzaole. Tx Candida and superficial dermatophyte infections like ringworm topical against dermatophytes but not against Candida. Mech unknown and no tox. Antiviral drugs Tx of Resp viruses amantadine Rimantadine ribavirin Tx of HSV acyclovir valacyclovir famciclovir Vidarabine idoxuridine prophylactic against influenza A. (ineffective after 48 hrs of exposure) Weak base buffer in endosome prevent acidification needed for uncoating of virus. Influenza B lacks the M2 protein needed for amantadine to bind to. R not common, but via mutations in M2. P’kinetics: p.o, Vd including CNS. Not met. Renal elim. SE: CNS: insomnia, dizziness, headache. Hallucinations and seizures. Antichol CI in pts w/ glaucoma and urinary rentention, and in pregnant women. struct analog. Does NOT XBBB NO CNS SE. synthetic guanosine analog. Broad spectrum. Mech: Adenosine Kinase P furter P to triP deplete GTP inh GTP dep capping of mRNA inh viral prot synth, also inh virus RNA pol. Rhino and entero have preformed mRNA R. Spectrum: for infants and young children w/ severe RSV causin bronchopneumonia. Maybe Hep A and influ A. Also mortality and viremia of Lassa fever. Given p.o., i.v., and aerosol. Vd except CNS. No more met, then renal elim. SE: Bronchospasm in asthmatic pts. In HIV pts, CNS, GI, dyspnea, extravascular hemolysis. Dose dep macrocytic anemia after 2wks of therapy. Teratogenic and CI in pregnant women. all nucleotide analogs, work on acute phase of infection, not latent phase. guanine analog mono P by viral thymidine kinase. Further P by host kinase. TriP gets trapped incorporated into viral DNA premature DNA chain terminat’n; or binds to viral DNA pol inactiv pol; Comp inh DNA pol. Altered thymidine K and DNA pol confer R. Spectrum: HSV-1+2, and VZV. EBV and CMV R b/c lack thymidine K. Drug of choice for herpes simplex encephalitis, survival better than vidarabine. Most common, tx genital herpes infections. P’kinetics: p.o, i.v., or topical. Vd, XBBB. Partial met and partial renal elim unchanged. SE: GI distress and headache from p.o. Renal dysfcn from i.v. Local irritation from topical. 100% bioavailability can be p.o., wheraeas acyclovir 30% bioavail, should be i.v.. new acyclovir analog most effective of the nucleotide analogs and least toxic. Adenosine analog convered to triP. Selective effect on virus. Mech: Inh virus DNA pol (alter struc confer R), virus ribonucleotide reductase, and incorporation into viral DNA. Spectrum: HSV 1+2, VZV. Used for herpes simples keratitis, encephalitis, and VZV in immunocomp pts. P’kinetics: i.v. over long time and in large vol b/c lo solub. XBBBfor HS encephalitis. Ointment for herpetic and vaccinial keratitis and HS keratoconjunctivitis. Met in liver and renal elim of changed/unchanged forms. SE: CNS fxs harmful in pts w/ hepatic or renal dysfcn. restricted to topical use b/c systematic toxicity. Thymidine analog. Incorporated into ganciclovir AIDS zidovudine (AZT) zalcitabine (DDC) didanosine (DDI) stavudine (Zerit) lamivudine Atovaquone Protease inh saquinavir ritonavir indinavir nelfinavir Miscellaneous trifluridine fluorouracil Foscarnet viral and mammalian DNA systemic teratogenic and mutagenicity. SE assoc w/topical use conjunctiva contact irritation, pain, itching, and photophobia. acyclovir analog for CMV in immunocomp pts. 1’ for CMV retinitis. Mech similar to ones above. Vd after i.v. Accum in pts w/ renal failure. Most serious SE = dose dep neutropenia. AZT P by mammalian thymidine K, then incororated into viral DNA by RT chain term. AZT monoP inh P of dTMP to diP. Also inh host DNA Pol only @ v. high conc lo tox. P.o. and XBBB. Met to glucuronide and t1/2=1hr. SE: BM anemia and leukopenia. CNS headaches, seizures, enhanced by other drugs that are also glucuronidated, such as probenecid, acetaminophen, lorazepam, cimetidine and indomethacin. analogs for pts intol to AZT. Neurological SE. analogs for pts intol to AZT. Less toxic than AZT to BM but caused fatal pancreatitis. New AZT analog. t1/2 = 3-6 hrs. Neuro SE New AZT analog. t1/2 = 3-6 hrs antiprotozoal for acute oral tx of PCP in pts intol to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Mech: ubiquinone like inh ETC inh synth of nucleic acids and ATP. used in combo w/ RT inhibitor, otherwise develop R. All met by P450. Don’t give terfenadine or astemazole. topical topical. Esp for warts. new. Inh DNA pol and RT, and active aginst HSV, CMV, HIV and hepadna virus. Antiprotozoal Drugs chemo of amebiasis metronidazole Diloxanide furoate Paromomycin chloroquine Emetine hydroemetine Chemo of Leishmaniasis sodium stibogluconate tx both acutely ill pt and asymptomatic carriers to prevent relapse or infectious state. Intestinal amebae feed onnormal flor tx w/ antibiotics to elim flora. Antibiotics must be used w/antiprotozoal drugs. mixed amebicides. Both luminal and systemic. Combo w/ luminal amebicidal such as diloxanide furoate cure rate > 90%. Toxic for amebae, anaerobic org including bact, also anoxic/hypoxic cells. Binds to prot in ETC in protozoa and inh DNA/RNA synth cell death. Drug of 1st choice for E. histolytica, Giardia lamblia, Trich vaginalis. Tx infections by anaerobic G+ and G-, and brain abcesses caused by them. p.o, Vd including CSF. P450 met. SE: GI, unpleasant metallic taste. Oral moniliasis or candidiasis and neurotoxicity (dizziness, vertigo, and paresthesias in PNS. Disulfram rxn. luminal. Drug of choice for asymptomatic carrier, intestinal amebiasis. Rapid hydrolysis and inactivation in lumen. SE mild: fart, dryness of mouth, pruritus and urticaria. luminal amebiasis/tapeworm, since not absorbed p.o. Aminoglycoside. Direct amebicidal (cell memb damage and leakage) and by destroying flora. SE: GI distress and diarrhea. systemic. W/metronidazole and diloxanide furoate to tx and prevent amebic liver abscess. Also elim trophozoites in liver abscesses in malaria. systemic. 2nd line drug b/c toxicities. Close monitoring. SE: pain at site of inj, nausea, cardiotoxicity, neuromusc weakness, dizziness, and rashes. sandflies transfers promastigote phag by Mphage changed to nonflagel amstigotes kill cell newly released amastigote phag and cycle cont. antimony deriv effective only in vivo. Inh parasite glycolysis. I.v. and renal elim unmet. SE: GI and cardiac arrhythmias. Chemo of Trypannosomiasis melarsoprol pentamidine nifurtimox suramin Chemo of toxoplasmosis Chemo of malaria primaquine Chloroquine quinine mefloquine pyrimethamine chloroguanide der of mersalyl oxide. For trypanosomes only. Reacts w/ SH on prot in both org and host. Parasitic enz more sensitive, and mammalian cells less permeable. R via permeability. Slow i.v., caution b/c local irritation. XBBB. Drug of choice to tx T. rhodesiense, which rapidly invades CNS, and in meningoencephalitis caused by T.brucei gambiense. Rapid oxidation and inactiv short t1/2. SE: CNS, hypersensitivity, vomitng, ab pain. CI in pts w/ G6PD def. Drug of choice in prevention and tx of nematologic stage of T. brucei gambiense. Mech: E, hi affinity uptake. Bind to parasite’s DNA and glycolysis. R via no uptake. Spectrum: Drug of 2nd choice in tx PCP. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole =drugs of 1st choice for PCP. Tx systemic blastomycosis. P’kinetics: i.m. or aerosol. No i.v. b/c cause abrupt BP and tachy. Conc and stored in liver and kidney for long time tissue damage. No XBBB. Not met and slow renal elim. SE: serious renal dysfcn but rev upon w/drawal. experimental. Tx only T. cruzi. Suppressive rather than curative. Serious SE: CNS, hypersensitivity, GI. 1’ in tx and esp prophylaxis of African trypanosomiasis. Inh metabolic enz. Drug of choice for filarial parasite such as Onchocerca volvulus. SE: GI, shock, unconsciousness, acute urticaria, and neuro. Drug of choice = pyrimethamine. Combo of sulfadiazine + pyrimethamine also effective. Other folate synth inh ineffective. tissue schizonticide. Used in combo w/blood schizonticide. Eradicates 1’ exoerythrocytic forms of P. faciparum and P. vivax and 2’ exoerythrocytic forms of recurring malarias (radical cures of vivax and ovale). Gametocidal for all 4 plasmodia. Mech: oxidizing metabolites schizonticidal, toxicities of hemolysis and metHb. P’kinetics: p.o, but does NOT conc in tissues. Renal elim of active/inactive metabolites. SE: hemolytic anemia in pts w/ G6PD def. Ab pain when given w/ chloroquine. blood schizonticide. Enters RBC and blocks protozoal DNA and RNA synth. Uptake by binding to ox. heme, formed from Hb in infected RBC memb damage and lysis of both parasite and RBC. R via drug efflux. Spectrum: 1’ drug for tx falciparum. Highly selective for asexual form of vivax and faciparum. Also tx extraintestinal amebiasis. P’kinetics: p.o, conc in RBC, liver, spleen, kidney, lung and other tissues, XBBB. P450 met. 4 d of therapy needed for total cure. SE: very little at lo doses. Visual disturbances, e.g. blurred vision and difficulty in accomodation. blood schizonticide. For malarial strains R to other drugs. Used in combo w/pyrimethamine, and sulfonamide. SE: cinchonism = nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, and vertigo. blood schizonticide. Suppress and cure mutlidrug-R forms of P. falciparum. Damgae parasite memb. Extensive met and feces elim. SE: @ hi dose, GI, CNS—dizziness, disorientation and depr. blood schizonticide for radical cure and sporonticide in mosquito’s gut. Inh plasmodial dihydrofolate reductase. Used alone for P. falciparum. In combo w/ sulfonamide, against P. malariae and Toxoplasma gondii. blood schizonticide and sporonticide. Antifolate. Rapid emergence of R limits use. Antihelmintic drugs Tx for nematodes mebendazole roundworms w/complete dig tract, including mouth and anus synthetic benzimidazole, against wide spectrum of nematodes. Drug of choice in infections by whipworm (tricuris trichura), pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis), and hookworm (Necator americanus, ancylostoma duodenale). Mech: bind and interfers w/ synth of microtubules glc uptake. Affected parasite expelled in feces. Poorly thiabendazole Pyrantel pamoate diethylcarbamazine ivermectin Tx of trematodes praziquantel oxamniquine metrifonate Tx of Cestodes niclosamide absorbed from GI local action w/ little SE. @ hi doses, small amt of drug absorbed rev alopecia and neutropenia. CI in pregnancy b/c teratogenic. also synthetic benzimidazole. Against strongyloidiasis cutaneous larva migrans (creeping eruption) and trichinosis (Trichinella sprialis), and strongyloides stercoralis (threadworm). More serious SE: readily absorbed from GI nusea, vomiting, anorexia, and dizziness. Severe allergic hepatitis when used for > 2 d, as in severe infestation of sm. intestine. tx roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides), pinworm, and hookworm. Poorly absorbed from GI. Depolarization Persistent activation of nicotinic R paralysis expulsion of helminth. Drug of choice in filariasis (Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi). Mech: immobilization of parasitesparalysis. Alter helminthes surface memb more susceptible to host immune system. Rapidly absorbed from GI, partially met, and renal elim. Dying parasites cause pruritus and wheals, systemic cond such as GI, jt pain, fever, swelling of inguinal lymph nodes and chorioretinitis. control nematodes in animals by stim GABA R paralysis. Tx Onchocerca volvulus in humans. Recently shown that ivermectin better than diethylcarbamazine in W. bancrofti and B. malayi. No mouth/dig tract Drug of choice for all forms of schistosomiasis. permeability to Ca easier for Abmediated adherence of leukocytes to kill helminth. Rapidly absorbed after p.o. and distrib to CSF. Extensive liver met and short t1/2. SE: drowsiness, dizziness, malaise, anorexia and GI. Most pts no SE. Largely replaced by praziquantel drug of choice. Cysticercosis in CNS treated w/prednisone or dexamethasone. Mech: uncouple ox phos in mito of parasites and host. Absorbed by gut-dwelling cestodes but not nematodes. Novel ETC in parasite susceptible to niclosamide paralysis expelled with feces. NOTE: must give laxative first to expell dead segment to prevent release of eggs, which may lead to cysticercosis. SE: minor: ab discomfort, malaise, fever, some pruritis.