The laboratory diagnosis of tuberculosis
advertisement

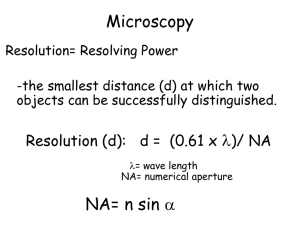
British Society for Microbial Technology The laboratory diagnosis of tuberculosis 25 years of progress D A Mitchison St George’s, University of London With assistance from FINDdiagnostics Diagnostic testing at different levels of health system Peripheral health centre Proportion of TB tests patients Peripheral centre 60% None Microscopy centre 35% Microscopy Referral laboratory 10% Culture, DST Reference laboratory 5% Reference methods Sputum: 25 years ago (1985) 1. Poor countries: Microscopy alone 2. Richer countries. Microscopy, LJ culture , DST 3. Advanced countries. Microscopy, Liquid culture, ID, DST Sputum bacteriology UK (1985) • Direct smears • Culture on LJ slopes (3-6 weeks) • Identification as M. tuberculosis (Chemical; PNB, niacin, catalase) • Drug susceptibility tests (DSTs) (Rifampicin screen) FIND and Carl Zeiss Micro Imaging GmbH have co- developed a fluorescent LED microscope based on the proven Primo Star platform. FIND/Zeiss microscope offers superior optics, reflected light illumination, easy switch from brightfield to fluorescent light Direct smears Fluorescence v. Bright field microscopy Fluorescence: Introduced in 1940s. 5x more rapid than Bright field BUT: Mercury vapour bulb: Expensive. Limited life. Gradual decline. LED illumination introduced during past 5 years Find/Zeus collaboration Culture: solid v. liquid Solid: LJ slopes. 7H11 slopes or plates. Liquid: Early attempts high contamination. 1971 Selective medium paper (Mitchison et al J Med Microbiol 1971; 5: 165) Penta used in Bactec machine Automated liquid systems v. solid media Sensitive. Rapid. Contamination. NTMs v. TB. Genetic systems Equipment cost Cost specimen (£) Sensitivity Sm + Sm – Cult + Cult + Specifity Hain TBDR+ Moderate 48 98% 100% Gene Xpert (Cepherd) High (£100,000) 40 99% 87% 97% LAMP (Eiken) Low Low 98% 49% 99% Culture, identification & DSTs HAIN MDTBDR plus PCR & Line probe based 1. Identifies as TB complex. 2.DSTs for RIF & INH (95%) Can be used directly on sputum avoiding culture What to do about MDR TB? (MDR = Resistance to INH & RIF) Genetic tests for reserve drugs not adequate yet. Therefore cultures in liquid or on solid medium necessary as well as genetic techniques. Reserve drugs Fluoroquinolones Moxifloxacin Levofloxacin Injectables Streptomycin Amikacin (Kanna) Capreomycin Ethambutol Pyrazinamide Ethionamide Prothionamide Cycloserine PAS Linezolid Amoxicillin/clavulanate MGIT 960 Reserve Critical Concentrations Drug Study 1 Study 2 Study 3 Amikacin 1.0 1.0 1.0 Kanamycin ND 2.5 ND Capreomycin 2.5 2.5 1.25 Ethionamide 5.0 5.0 ND Proteonamide 2.5 ND 2.5, 5.0 Ofloxacin 2.0 2.0 1.0 Moxifloxacin ND 1.0 0.125 Levofloxacin ND ND ND Rifabutin 0.5 ND 0.5 1Rusch-Gerdes S et al. JCM 2006;44:688-92. C et al. IJTLD; 2008;12:1449-55. 3Kruuner A et al. JCM 2006;44:811-8. 2Rodrigues PAS ND 4.0 ND Linezolid 1.0 ND ND DSTs Phenotypic Classic on LJ slopes or 7H11 plates. Takes 7 weeks +. MGIT or other automated liquid tests. Microcolony methods • Liquid medium: Mods. Sensitive, time consuming, ?dangerous • Solid medium: Thin layer agar (TLA): Quicker. Less dangerous Phenotype DST Thin-layer agar plate (TLA) method 7H11 thin layer plates made selective Each plate with up to 6 strains in quadrants Control: no drug PNB (p-nitrobenzoate): TB inhibited. INH 0.2 µg/ml RIF 2.0 µg/ml SM 2.0 µg/ml PZA 2,000 µg/ml nicotinamide etc What is drug resistance? Defined from distribution of MICs on ‘wild’ strains Studies of early bactericidal activity define the ‘therapeutic’ margin EBA titrations of INH, RMP & SM 0.6 300 600 0.5 150 0.4 Standard EBA INH RMP 1 RMP 2 SM 75 0.3 600 38 0.2 1.5 g 19 0.1 0 150 0.38 g -0.1 9 -0.2 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 Log drug concentration 3 3.5 Can high drug dosage still have an effect on resistant strains? Isoniazid Mutants katG – high MIC inhA – low MIC Quinolones Mutants Mainly in gyrA – low MIC Early clinical trial Guinea-pig study