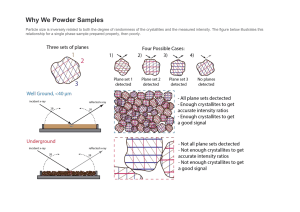
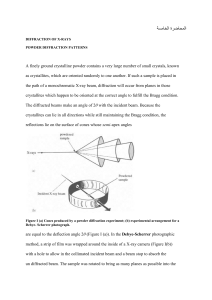
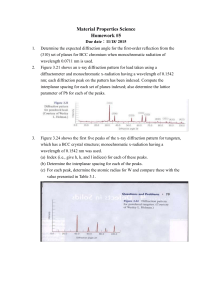
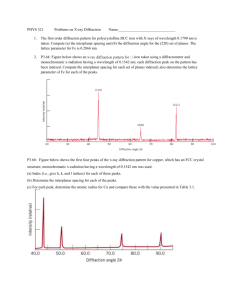
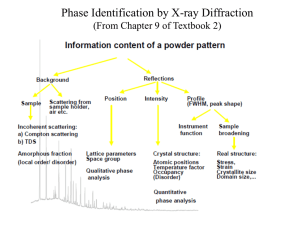
A Brief Introduction Notes on Powder X
advertisement

Powder X-ray Diffraction Experimental Set-up: Need ca. 20mg or more of microcrystalline powder Individual crystallites ca. 50microns Normally use monochromatic Cu-K radiation- Wavelength 1.54Å Use 40kV, 50mA and 2kW sealed X-ray tube. Measure to max. Bragg 2 of ca. 40o for organics, or 80-100o for inorganics Results: Get 1-D diffraction pattern or 'spectrum' of Bragg angle versus diffraction intensity. This should be unique for each type of crystalline substance. Results tell whether sample is a) Crystalline or not - peaks should be sharp and strong b) Simple pattern - high symmetry or preferred orientation c) Allows phase identification - compare with other samples d) Comparison with 'JCPDS' file - allows identification of compounds in database e) For mixtures can use for semi-quantitative analysis f) Can refine the unit cell parameters by indexing the reflections. g) Can even solve or refine the structure if done carefully. (Rietveld analysis) This is non-routine and a 'model' structure must normally be used as a starting point. Problems with Powder Diffraction: a) Preferred Orientation Peak intensities can vary quite strongly from one sample to the next. The database records patterns of substances prepared as microcrystalline samples. If your crystallites have a different shape then peak intensities will be affected by the probability that the crystallites are in diffracting orientation. b) Comparing Samples The d-spacings of your unit cell and the diffraction angles that result should not vary greatly. Sometimes there is a 'zero offset' error when you run the pattern. Try subtracting or adding 0.1 or 0.15o and see whether two sets of peaks now overlap ! Be careful in comparing mixtures with pure samples - i.e you may have two sets of overlapping peaks, rather than a new material ! CHEM 534 Class Exercise: Symmetry Operations, Equivalent Positions and Space Groups The general positions for the monoclinic space group P2 are 1. x, y, z 2. -x, y, -z What are the general positions for the following monoclinic space groups ? a) Pm b) P21 (Total of 2) (Hint: Change 2-fold to 2-fold screw) c) C2 (total 4) (Hint: add C-lattice centering to ab faces) d) P21/m (total 4) (Hint: combine answers to P21 and Pm) (Total of 2) (Hint: Change 2-fold to a mirror)