Parts of Speech - Mohawk College
advertisement

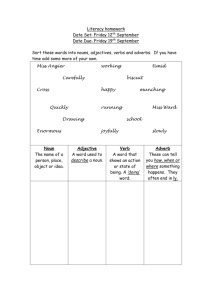
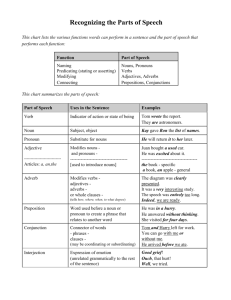
PARTS OF SPEECH Noun: A person, place or thing. Examples: John walked over to the house. A cat sat on the fence. Pronoun: Is used in the place of a noun. Try to use pronouns in order to avoid repetitiveness in your writing. Example: Jane was happy with her new house. She loved the flowers that grew in the garden. (Jane is the noun; her and she are the pronouns) Adjective: A description word, used to describe the noun or pronoun. Example: The famous chef prepared the main dish. (famous is an adjective that describes the noun chef) Verb: This is also known as the “action word”. Examples: The ball rolled along the floor. The dog walked along the sidewalk with me. Adverb: Modifies a verb or an adjective. Example: The vibrantly red roses sat on my windowsill. (vibrantly is the adverb that modifies the adjective red) Preposition: Used to link nouns, pronouns and phrases to other words in the sentence. (e.g. on, in, at, over, under, beside) Example: The movies are on the television stand. The popcorn is in the bowl. Conjunction: You can use a conjunction to link words, phases and clauses. Use the acronym FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) to remember the conjunctions. Example: I love dogs, and I love cats. I like baseball, but I would rather watch football. Interjection: An interjection is a word added to a sentence to convey emotion. Examples: Ouch, that really hurt! Hey, stop that! Content words are open – they can be anything, and new ones are created all the time (Lexical). Content words include: Nouns Verbs Adjectives Adverbs Grammar – function words are a fixed set of words (Non-Lexical). Function words include: Conjunctions Prepositions Pronouns Articles Interjections Developed by: The Communications Centre / Michelle Morrow / January 2008