Grammar Guide: Appositives, Semicolons, Pronouns & Adverbs
advertisement

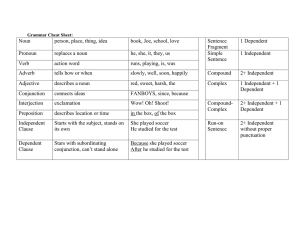
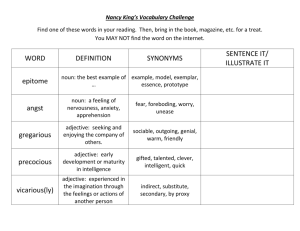
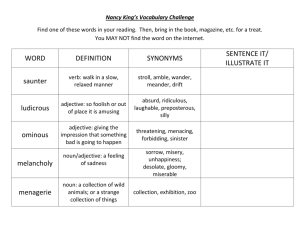
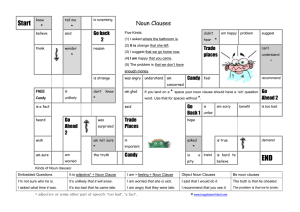
Appositive phrases • Provides more information about a noun. • Most often appears directly after the noun it identifies or renames: Arizona Bill, "The Great Benefactor of Mankind," toured Oklahoma with herbal cures and a powerful liniment. • Commas are used to separate phrase from rest of sentence! • May appear in front of a word that it identifies: A dark wedge, the eagle hurtled earthward at nearly 200 miles per hour. Make a three column graph labeled with the following: semicolons; colons: hyphens- 1. Used after a prefix that is followed by a proper noun or adjective 2. Combines two independent clauses 3. Used to write a fraction as an adjective 4. Used on warning labels 5. separates words when dropping down to next line on composition 6. Used after the salutation in a business letter 7. Used to separate words in a compound noun 8. Separates hour from minutes 9. Used before a conjunctive adverb 10.Used to introduce list of items 11. Used to separate two-word numbers Relative Pronouns Begins a subordinate clause and connects it to another idea in the same sentence. There are five relative pronouns: that which who whom Independent clause Subordinate clause Here is the earring that Tara lost. She is a painter who has an unusual talent. Is this the woman whom you saw earlier? She is the one whose house has a new alarm. whose Conjunctive adverbs • Used to connect complete ideas (compound sentence) or to transition by showing comparisons, contrasts, or results. • Use a ; BEFORE the word and a , AFTER • That movie was great; however, I still prefer the book. accordingly consequently indeed otherwise again finally instead then also furthermore moreover therefore besides however nevertheless thus