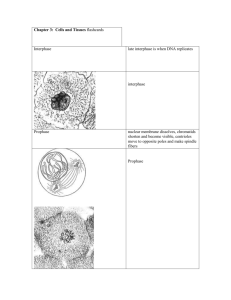
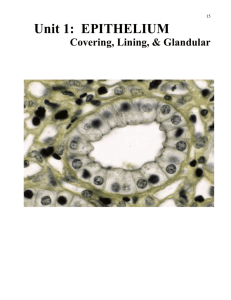
A & P – Chapter 3 – Tissues
advertisement

A & P – Chapter 3 – Tissues Matching: 1. tissue _______ A. any growth benign or malignant 2. intercellular material _______ B. nerve cell 3. interstitial fluid _______ C. intercellular substance 4. matrix _______ D. gristle 5. pleural fluid _______ E. produces mucous secretions which lubricate epithelial surface 6. pericardial fluid _______ F. secretion found between the layers of the pleura 7. endothelium _______ G. tissue fluid 8. goblet cells _______ H. group of cells 9. adipose tissue _______ I. material found between the cells 10. plasma _______ J. cancerous 11. neoplasm _______ K. growths that are not cancerous 12. tumor _______ L. white blood cells 13. benign _______ M. growths of a particular group of cells 14. malignant _______ N. red blood cells 15. neuron _______ O. fatty tissue 16. leukocytes _______ P. fluid secreted by the cells covering the heart 17. thrombocytes _______ Q. platelets 18. erythrocytes _______ R. cells forming the thin inner walls of all blood vessels 19. cartilage _______ S. a type of bone tissue that forms the bony material 20. osteoblasts _______ T. forms the fluid part of the blood Listing/Fill in the Blank: 21. Name (3) main solid components found in the blood: ______________________ ________________________ ________________________ 22. Males should not exceed _________% body fat. 23. Females should not exceed __________% body fat. 24. __________________ contains the liquid connective tissue used for circulating food and removing waste. 25. __________________ connective tissue is found in the major part of ligaments and tendons. 26. __________________ is osseous tissue which forms the framework of the body. 27. The _________________ tissue accounts for 40 to 50% of the body weight. 28. The _________________ tissue collects and transmits information by means of nerve cells. 29. The _____________________ tissue consist of various types of cells, fibers, and a mixture of proteins. The tissues found in muscles, tendons, ligaments, and walls of blood vessels. 30. _______________________ tissues cover surfaces and line the internal structures and cavities of the body. 31. Once a nerve cell is destroyed can it ever be replaced naturally? (yes or no) ___________ Matching: A. simple squamous epithelium C. simple cubodial cells E. ciliated epithelium B. stratified squamous epithelium D. simple columnar epithelium 32. ___________ - these cells are commonly found in the secretory portions of glands or in the tubules of the kidneys and the tissue covering the ovary. 33. ___________ - the main function of these cells is for the protection of some body surfaces that may be subject to mechanical injury. 34. ___________ - these cells are longer than they are broad. They are found in the lining of the digestive tract. 35. ___________ - these cells are flat and scale-like. They are found in the lining of the blood vessels and in the covering of the lungs and heart. 36. ___________ - these cells contain cilia. Listing: 37. Name (3) types of muscle tissue: ______________________ ________________________ ________________________ 38. Name (3) groups of neurons and tell what each group is responsible for: 1)__________________________________________________________________________________ 2)__________________________________________________________________________________ 3)__________________________________________________________________________________ 39. Name (3) important roles that fat plays a part of in the human body: 1)__________________________________________________________________________________ 2)__________________________________________________________________________________ 3)__________________________________________________________________________________ 40. Name (2) types of neoplasms: ______________________ ________________________ 41. Name (4) primary kinds of tissue: ______________________ ________________________ ______________________ ________________________ KEY A. 12 B. 15 C. 4 D. 19 E. 8 F. 5 G. 3 H. 1 I. 2 J. 14 K. 13 L. 16 M. 11 N. 18 O. 9 P. 6 Q. 17 R. 7 S. 20 T. 10 21. red blood cells (erythrocytes), platelets (thrombocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes) 22. 18 23. 28 24. blood 25. fibrous 26. bone 27. muscle 28. nervous 29. connective 30. epithelial 31. no 32. C 33. B 34. D 35. A 36. E 37. skeletal, cardiac, smooth 38. 1) sensory – receives impulses from sense organs, 2) motor – carries impulses to muscles, 3) associative – relays impulses from sensory to motor 39. 1) serves as a reserve supply of energy, 2) padding to absorb jolts and jars (cushioning), 3) insulator 40. 1) malignant (cancerous), 2) benign 41. 1)epithelium, 2) connective, 3) nervous, 4) muscle