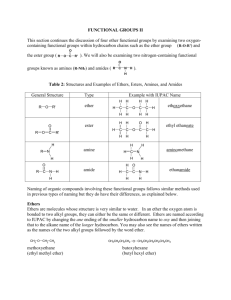
naming of ethers
advertisement

ETHERS Ethers are characterized by the functional group R – O – R, two alkyl groups joined by an oxygen atom. Due to its shape ethers have a slight polarity and due to the absence of hydrogen bonding, ethers have much lower boiling points than alcohols. Consider the hydrogen bonding of the following compounds: O /\ H H water > O /\ R H alcohol > O /\ R R’ ether water is greater than alcohol, alcohol is greater than ethers. NAMING OF ETHERS 1) 2) Choose the longest alkyl group as the parent alkane. Treat the second alkyl group as the branch alkyl group. This is named by replacing the “yl” with “oxy”. The alkoxy group that is adding on to the main chain should be located onto the main chain with an appropriate number. Eg. CH3 – O – CH2 – CH3 CH3 – CH2 –O – CH – CH3 methoxyethane \ CH3 2- ethoxypropane EXERCISE 1. Name the following ethers. a) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – O – CH3 b) CH3CH2CH2CH2 – O – CHCH2CH2CHCH2CH3 | | CH3 CH3 c) CH3 – CH – O – CH2 – CH – CH2 – CH3 | | CH3 CH3 2. Draw the following ethers. a) 1- methoxy propane b) 3 – ethoxy-4-methylheptane c) 2 – methoxy – 2- methylpropane PROPERTIES OF ETHERS Due to the angle between the two carbon groups, the two C-O dipoles counteract each other slightly (as opposed to a C=O bond). Since a C-O bond is less polar than an O-H bond, an ether is less polar than an alcohol. There is no hydrogen bonding because there is no O-H bond. 1) 2) 3) Solubility in water – low molecular mass ethers are soluble in water. As the mass of a molecule (size of the alkyl group) increases, the solubility decreases. Melting and Boiling points – the melting and boiling points of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols. Flammability – like alcohols, ethers are extremely flammable.