Displacement reactions : Reactions of chlorine
advertisement

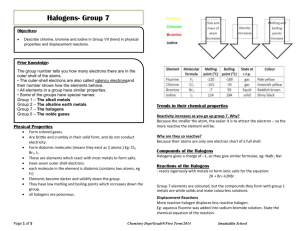
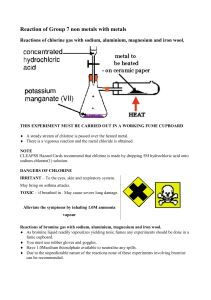
Displacement reactions : Reactions of chlorine, bromine, and iodine with potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide. In these reactions we determine which of the halogens chlorine, bromine or iodine is the strongest. Potassium iodide + chlorine gas In this reaction when potassium iodide solution is put into chlorine gas: a rapid reaction occurs. black iodine solid is formed along with potassium chloride solution. The chlorine has kicked the iodide out. CHLORINE is stronger than IODINE The equation for the reaction is: potassium + chlorine iodide gas 2KI + Cl2 potassium chloride 2KCl + iodine + I2 Potassium bromide + chlorine gas In this reaction when potassium bromide solution is put into chlorine gas a rapid reaction occurs brown bromine liquid is formed along with potassium chloride solution. The chlorine has kicked the bromide out. CHLORINE is stronger than BROMINE The equation for the reaction is: potassium + chlorine bromide gas 2KBr + Cl2 potassium chloride 2KCl + bromine + I2 Potassium chloride + chlorine gas In this reaction when potassium chloride solution is put into chlorine gas – No reaction occurs. CHLORINE and CHLORIDE are of equal STRENGTH - hence no reaction Potassium iodide + bromine liquid In this reaction when potassium iodide solution is put into bromine liquid : a rapid reaction occurs black iodine solid is formed along with potassium bromide solution. The bromine has kicked the iodide out. BROMINE is stronger than IODINE The equation for the reaction is: potassium iodide 2KI + bromine vapour + Br2 potassium bromide 2KBr + iodine + I2 From these findings the order of reactivity is (STRONGEST FIRST) CHLORINE > BROMINE > IODINE






![[1] - Boswellsgmt](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006603407_1-fadfbce8d94050a9fb3c38a07d86e8ee-300x300.png)