periodic table assignment - Glossopdale Community College
advertisement

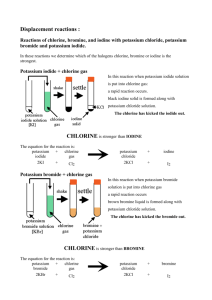
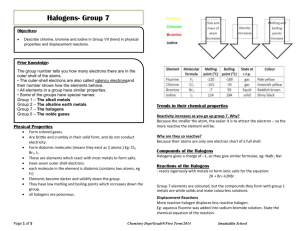
Glossopdale Community College Science Department Course Title: BTEC First extended certificate in Applied Science Assessors Name : Assessment Title Periodic table Learners Name Time needed. 2 weeks Start date Finish by Chemistry and our Earth Scenario It is important for analytical chemical technologists and forensic scientists to be able to identify patterns and trends in metallic and non-metallic elements in the periodic table. It is also important for them to understand how reactive certain elements are and the properties of their ionic, covalent and/or metallically bonded substances. This understanding helps them in their role when testing and analysing materials found at a crime scene or an environment pollution spillage or in the detection of substances in food or water supplies. You have been asked to investigate the electronic and atomic structures of certain elements and to describe/explain patterns and trends that you have found. Assessment Evidence, tables, practical results, report. Achieved Grading Criteria The grading criteria that this assignment relates to: P3 Describe atomic structures of elements 1-20, found in the periodic table P4 Carry out an investigation into the chemical properties of elements in groups 1 and 7 M3 Describe the trends within the atomic structure of groups 1 and 7 in the periodic table M4 Explain why the elements of groups 1 and 7 are mostly used in the form of compounds D2 Explain the trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements of groups 1 and 7 in relation to their electronic structure Assessor’s Comments/Feedback Internal Verifier’s comments Learner’s Signature Task 1 Using diagrams and a table, describe the atomic/electronic structures of the first 20 elements of the periodic table. Element Symbol Atomic number Mass number Electronic structure (a) In your description include information on the number of charges of the sub-atomic particles in each of the atoms. (b) Some elements have more than one type of atom. What are these different types of atoms called and describe the difference between two atoms of chlorine. P3 Task 2 (a) Carry out a practical investigation on the the reactivity of the elements within group 1 and 7 of the periodic table, using the attached practical worksheets. P4 Task 3 (a) Describe any patterns and trends of chemical properties that you have observed from your practical investigation. M3 Task 4 (a) From your findings in the above investigations explain why are group 1 and 7 elements usually found in compounds M4 Task 5 (a) Relate the number of electrons in the outer shells of group 1 and group 7 to their group number and the distance of the outer electrons from the nucleus. (b) Explain the patterns and trends within groups 1 and 7 in the period table. (c) Mention the electron arrangement, radii of atoms, and charges of particles D2 Experiments Apparatus Goggles Bench mat Test tube and test tube rack Teat pipettes 0.2M potassium chloride solution 0.2M potassium bromide solution 0.2M potassium iodide solution chlorine water bromine water iodine water Methods 1. Leave space to write your own Methods, then copy the table shown below into your file. 2. Add about 1cm3 (about half a pipette-full) of potassium bromide solution to the test tube. 3. Add one drop of chlorine water and gently shake the test tube to mix the contents. 4. If you see a colour change, make a note of it in your table. If you do not see a colour change, add up to 9 more drops of chlorine water (remembering to shake the test tube after each drop) and make a note of any colour change in your table. If you still do not see a colour change, write No Reaction in your table. 5. Wash out your test tube. 6. Repeat steps 2 – 5 for each of the following combinations: chlorine water added to potassium iodide bromine water added to potassium chloride bromine water added to potassium iodide iodine water added to potassium chloride iodine water added to potassium bromide Results Potassium Potassium Potassium Number of chloride bromide iodide reactions Chlorine No Reaction water Bromine water No Reaction Iodine water No Reaction Conclusions Count the number of reactions seen in each row and write the results in your table. The halogen that produces the most reactions is the most reactive of the three. 1. Write the names of the halogens in order of reactivity, from the most reactive to the least. 2. Compare your reactivity series with Group 7 in the Periodic Table – what do you notice? 3. What results might you get if fluorine water and potassium fluoride were in the experiment too? 4. Write word equations for each of the reactions seen in the experiment. For example: chlorine + potassium bromide potassium chloride + bromine Atomic information data sheet The atomic information for the different elements, from the planet Oldhamic, identified by the NASA scientists 23 Na 1 H 12 C 4 He 16 11 1 6 2 8 7 24 32 19 20 3 Li 9 4 11 5 12 Mg 27 Be B 13 28 14 16 S 14 Al Si 6 35 17 40 18 9 F 14 C Cl Ar 7 39 19 10 O Ne 40 N K 20 31 15 Ca P