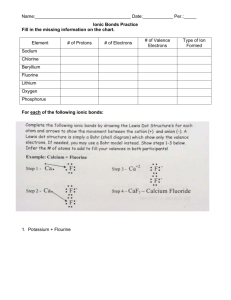
Chapter 8, 9 and 19 Review for Test

CH 9, 10, and 11 Test
Redox, Net Ionic and Stoichiometry
The combination of hydrogen gas and chlorine gas produce the compound hydrogen chloride gas.
1. Write the balance chemical reaction.
2. What type of reaction(s) is this?
3. If 40.0 L of chlorine gas reacts with excess hydrogen gas at STP, how many liters of hydrogen chloride would be produced?
4. If 23.4 g of chlorine gas reacts with 65.8 L of hydrogen gas, how many grams of hydrogen chloride can be produced?
5. Give the oxidizing agent and reducing agent.
6. Predict the products of aluminum sulfate combining with barium chloride.
7. Write the balance chemical reaction for #5( include phase).
8. Give the net ionic equation.
9. If you are given 89.6 g of aluminum sulfate and 45.6 g of barium chloride, how many grams of barium sulfate could be produced?
10. Give the net ionic equation for the reaction in #9.
Silver combines with hydrochloric acid.
11. Write the balanced chemical reaction (include phase)
12. What type of reaction(s) is this?
13. Write the oxidation and reduction reaction.
14. Give the net ionic equation.
Potassium bromide reacts with chlorine gas to produce?
15. Finish the word equation
16. Write a balanced chemical equation (include phase).
17. What type of reaction(s) is this?
18. How many liters of chlorine gas are needed to react with 43.5 g of potassium bromide?
19. Given 4.67 g of potassium bromide and 5.00 L of chlorine gas at STP, how many grams of potassium chloride?
Magnesium carbonate breaks down when heated to magnesium chloride and carbon dioxide.
20. Write the balanced chemical formula.
21. How many grams of magnesium carbonate is needed to produce 16.7 L of carbon dioxide at STP?
Sulfuric acid and potassium hydroxide combine.
22. Give the balanced chemical equation (include phase).
23. How many grams of water can be produced from 89.4 g of sulfuric acid?
24. How many grams of water can be produced if 30.0 g of potassium hydroxide reacts with 39.0 g of sulfuric acid?
25. How much excess?
26. Why sometimes can you not write a net ionic reaction?
27. What does it mean when an element has been reduced?
28. What does it mean when an element has been oxidized?
29. Why do chemical reactions always have a limiting reactant?
30. What does it mean when a reaction has gone to completion?