[1] - Boswellsgmt
advertisement
![[1] - Boswellsgmt](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006603407_1-fadfbce8d94050a9fb3c38a07d86e8ee-768x994.png)
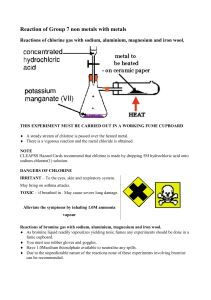
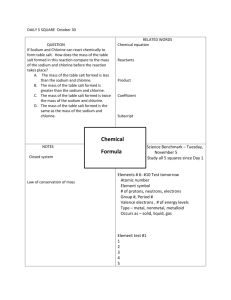
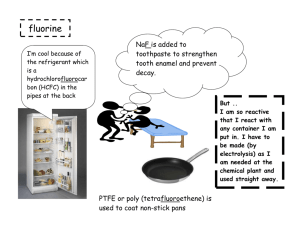
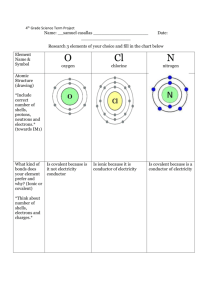
Unit 4: Ideas in Context [Additional] May 30th exam The dangers and delights of chlorine and bromine Practice Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What are the chemical formulas for each of the halogen molecules? Explain why the halogens are described as being diatomic atoms? Write the electron configurations for fluorine, chlorine, and bromine. Write the electron configurations for the fluoride, chloride, ad bromide ions. Write the symbols of the fluoride, chloride, ad bromide ions. Name the similarities and differences between each of the halogens. State the trends of the halogens, in terms, of the colour of compound, state at room temperature, reactivity, and boiling and melting point. 8. Why is chlorine a gas at room temperature, use the table on page 4 of the article to help? 9. Draw the hazard symbols for: toxic, corrosive, harmful, and irritant. 10. Why is fluorine more toxic than chlorine? 11. Why would chlorine cause health problems, explain the mechanism of how it would cause these problems. 12. Explain why if chlorine is a hazard it is safe to use swimming pools. 13. What is the process used to separate chlorine from sea water? 14. Draw and annotate this process. 15. During this process, why does the chlorine compound have to be in solution form? 16. What does an ionic compound mean? 17. Write down the formula for sodium chloride and magnesium chloride and explain why they are different. 18. Write down the equation for the reaction of sodium and chlorine, with symbols and state symbols. 19. What does electrostatic attraction mean and how does this relate to question 18. 20. List some uses of chlorine and bromine. 21. Explain what is meant by the term displacement. 22. Why is bromine separated through the process of displacement, what are some advantages of this process. 23. Write the symbol equation of sodium bromine and fluorine. 24. What is the state of a substance when it is dissolved in water? 25. What are the hazards with chlorine and bromine?