Essential Questions, vocab, and practice quiz
advertisement

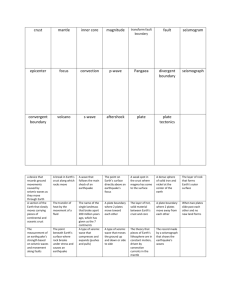
STANDARD 3 MODULE 7 Objective 4 Compare rapid and gradual changes to Earth’s surface. A. Describe how energy from the Earth's interior causes changes to Earth’s surface (i.e., earthquakes, volcanoes). B. Describe how earthquakes and volcanoes transfer energy from Earth's interior to the surface (e.g., seismic waves transfer mechanical energy, flowing magma transfers heat and mechanical energy). C. Model the process of energy buildup and release in earthquakes. Vocabulary: Eruption: A volcanic process where hot lava is extruded onto the Earth’s surface. Earthquake: What is felt on the surface of the Earth after two stuck plates release stored energy. Seismic wave: The mechanical wave released from two tectonic plates rupturing. Mechanical energy: Energy of motion. a synonym for kinetic energy Potential mechanical energy: Mechanical energy that is stored and can be released Magma chamber: A huge glob-like mass of molten rock inside the earth. Plate tectonics: The idea that huge plates in the lithosphere float around on the asthenosphere Convection current/cell: The cyclic rising and falling of molted rock that makes tectonic plates move Convergent plate boundary: Two tectonic plates coming together Transverse plate boundary: Two tectonic plates that slide past each other Divergent plate boundary: Two plates that move away from each other. Learning Activities Inductive Grouping Activity (events that are gradual and rapid and Earth effects) Double Bubble Plate Tectonics SMARTNotes Weathering, erosion, deposition calculations activity. STANDARD 3 MODULE 7 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1.) Place the following terms and events (just the letter is ok) in the correct order. This “chain reaction pathway” is how energy is produced and affects rocks and layers in the Earth. Some are already placed to help you. 7.) 5.) 6.) 4.) 1.) 2.) 3.) a.) Radioactive decay in the core b.) Rocks get melted d.) Magma gets to surface through volcano e.) Plates move energy c.) Magma rises f.) Plates catch and store g.) Plates slip and release energy: seismic waves 2.) Energy affects rocks and rock layers in many ways. Identify each of the examples below as mechanical/kinetic energy, heat energy, potential mechanical energy, magma “stuck” tectonic plates seismic waves rising magma pushing rock layers out of the way rocks thrown out of a volcano 3.) Where does the energy come from that drives plate tectonics? 4.) What are the 2 ways that energy gets to the Earth’s surface? 1.) 2.) 5.) Explain 2 ways that earthquakes can change the surface of the earth. 1.) 2.) 6.) Explain 2 ways that volcanoes can change the surface of the earth. 1.) 2.) 7.) Explain the entire energy pathway that leads up to an earthquake. 8.) Explain the entire energy pathway that leads up to a volcanic eruption. 9.) Explain how energy builds up and is released in an earthquake. STANDARD 3 MODULE 7 PRACTICE CONTENT QUIZ 1. Which of the following best describes how volcanoes transfer energy? A. Volcanoes carry heat from the surface to the deep interior of Earth. B. Volcanoes gather heat from the sun and give it off as light and sound. C. Heat and mechanical energy are transferred as magma flows from a volcano. D. Lava produced by a volcano can carry heat but not energy. 2. What must be added to the model to create an earthquake? The model should have: A. energy added to it by pressing it together, pulling apart or moving side to side. B. waves added to it by shaking it up and down and letting the pieces fall to the floor. C. another piece added to it on the top to create pressure and weight on the center. D. heat should be added to the sides to create the earthquake waves. 3. What best describes how earthquakes happen? A. tectonic plates move, slip, plates get stuck, release energy in seismic waves B. plates get stuck, tectonic plates move, slip, release energy in seismic waves C. tectonic plates move, slip, release energy in seismic waves, plates get stuck D. tectonic plates move, plates get stuck, slip, release energy in seismic waves 4. How would the model look after a simulated earthquake? A. The left block will have moved up and will stay there B. The right block will have moved up and then back down. C. The center block will have moved up, down, or sideways D. The blocks will be lined up but lower than when they started. 5. Earthquakes are the result of what type of energy transfer? A. heat, mechanical potential of plates catching, mechanical of fault slipping and creating seismic waves, movement of plates B. mechanical of fault slipping and creating seismic waves, heat, movement of plates, mechanical potential of plates catching C. heat, movement of plates, mechanical potential of plates catching, mechanical of fault slipping and creating seismic waves D. heat, mechanical of fault slipping and creating seismic waves, mechanical potential of plates catching, movement of plates 6. As radioactive decay happens deep in the Earth, heat is given off. This heat melts rock, drives convection cells and helps to move large plates around. This heat and motion transmit energy to the surface of the Earth in two main ways. Which are the two main ways this energy gets to the surface of the Earth and changes the surface of the Earth? A. Earthquakes and sunlight B. Volcanoes and electricity C. Earthquakes and respiration D. Volcanoes and earthquakes STANDARD 3 FORMATIVE VOCAB PRACTICE QUIZ 1. Two tectonic plates that slide past each other A. Convection current/cell B. Convergent plate boundary C. Transverse plate boundary D. Divergent plate boundary 2. Two plates that move away from each other A. Convection current/cell B. Convergent plate boundary C. Transverse plate boundary D. Divergent plate boundary 3. Two tectonic plates coming together A. Convection current/cell B. Convergent plate boundary C. Transverse plate boundary D. Divergent plate boundary 4. The cyclic rising and falling of molted rock that makes tectonic plates move A. Convection current/cell B. Convergent plate boundary C. Transverse plate boundary D. Divergent plate boundary 5. A volcanic process where hot lava is extruded onto the Earth’s surface. A. Eruption B. Earthquake C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 6. The mechanical wave released from two tectonic plates rupturing. A. Eruption B. Earthquake C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 7. Mechanical energy that is stored and can be released A. Eruption B. Earthquake C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 8. What is felt on the surface of the Earth after two stuck plates release stored energy. A. Eruption B. Earthquake C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 9. Energy of motion. A synonym for kinetic energy A. Eruption B. Mechanical energy C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 10. A huge glob-like mass of molten rock inside the earth. A. Plate tectonics B. Magma chamber C. Convection current/cell D. Eruption 11. The idea that huge plates in the lithosphere float around on the asthenosphere A. Plate tectonics B. Magma chamber C. Convection current/cell D. Eruption STANDARD 3 MODULE 7 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS KEY 1.) Place the following terms and events (just the letter is ok) in the correct order. This “chain reaction pathway” is how energy is produced and affects rocks and layers in the Earth. Some are already placed to help you. 7.) 5.) 6.) 4.) 1.) 2.) 3.) a.) Radioactive decay in the core b.) Rocks get melted d.) Magma gets to surface through volcano e.) Plates move energy c.) Magma rises f.) Plates catch and store g.) Plates slip and release energy: seismic waves 2.) Energy affects rocks and rock layers in many ways. Identify each of the examples below as mechanical/kinetic energy, heat energy, potential mechanical energy, magma heat “stuck” tectonic plates potential mechanical energy seismic waves mechanical/kinetic energy rising magma pushing rock layers out of the way rocks thrown out of a volcano mechanical/kinetic mechanical/kinetic 3.) Where does the energy come from that drives plate tectonics? radioactive decay in the mantle 4.) What are the 2 ways that energy gets to the Earth’s surface? 1.) heat (lava) 2.) mechanical energy (earthquakes) 5.) Explain 2 ways that earthquakes can change the surface of the earth. 1.) shake the surface of the earth and cause landslides 2.) they can create large canyons 6.) Explain 2 ways that volcanoes can change the surface of the earth. 1.) lava can flow out of them and change the earth’s surface 2.) they can build up higher and higher like a mountain 7.) Explain the entire energy pathway that leads up to an earthquake. radioactivity melts rock in the mantle, then the rock moves up and down in a convection cell, plates in the lithosphere move around on top of the asthenosphere, the plates pull apart, collide or slide past each other, sometimes the catch and store energy until they snap and release the energy as an earthquake. 8.) Explain the entire energy pathway that leads up to a volcanic eruption. radioactivity melts rock in the mantle, then the rock moves up and down in a convection cell, sometimes the magma gets to the surface and erupts 9.) Explain how energy builds up and is released in an earthquake. plates move on the asthenosphere from convection currents, the plates catch or stick together and store energy (mechanical potential) until they snap or break apart and produce an earthquake and release the energy as mechanical energy in the form of a seismic wave STANDARD 3 MODULE 7 PRACTICE CONTENT QUIZ KEY 1. Which of the following best describes how volcanoes transfer energy? A. Volcanoes carry heat from the surface to the deep interior of Earth. B. Volcanoes gather heat from the sun and give it off as light and sound. C. Heat and mechanical energy are transferred as magma flows from a volcano. D. Lava produced by a volcano can carry heat but not energy. 2. What must be added to the model to create an earthquake? The model should have: A. energy added to it by pressing it together, pulling apart or moving side to side. B. waves added to it by shaking it up and down and letting the pieces fall to the floor. C. another piece added to it on the top to create pressure and weight on the center. D. heat should be added to the sides to create the earthquake waves. 3. What best describes how earthquakes happen? A. tectonic plates move, slip, plates get stuck, release energy in seismic waves B. plates get stuck, tectonic plates move, slip, release energy in seismic waves C. tectonic plates move, slip, release energy in seismic waves, plates get stuck D. tectonic plates move, plates get stuck, slip, release energy in seismic waves 4. How would the model look after a simulated earthquake? A. The left block will have moved up and will stay there B. The right block will have moved up and then back down. C. The center block will have moved up, down, or sideways D. The blocks will be lined up but lower than when they started. 5. Earthquakes are the result of what type of energy transfer? A. heat, mechanical potential of plates catching, mechanical of fault slipping and creating seismic waves, movement of plates B. mechanical of fault slipping and creating seismic waves, heat, movement of plates, mechanical potential of plates catching C. heat, movement of plates, mechanical potential of plates catching, mechanical of fault slipping and creating seismic waves D. heat, mechanical of fault slipping and creating seismic waves, mechanical potential of plates catching, movement of plates 6. As radioactive decay happens deep in the Earth, heat is given off. This heat melts rock, drives convection cells and helps to move large plates around. This heat and motion transmit energy to the surface of the Earth in two main ways. Which are the two main ways this energy gets to the surface of the Earth and changes the surface of the Earth? A. Earthquakes and sunlight B. Volcanoes and electricity C. Earthquakes and respiration D. Volcanoes and earthquakes STANDARD 3 FORMATIVE VOCAB PRACTICE QUIZ KEY 1. Two tectonic plates that slide past each other A. Convection current/cell B. Convergent plate boundary C. Transverse plate boundary D. Divergent plate boundary 2. Two plates that move away from each other A. Convection current/cell B. Convergent plate boundary C. Transverse plate boundary D. Divergent plate boundary 3. Two tectonic plates coming together A. Convection current/cell B. Convergent plate boundary C. Transverse plate boundary D. Divergent plate boundary 4. The cyclic rising and falling of molted rock that makes tectonic plates move A. Convection current/cell B. Convergent plate boundary C. Transverse plate boundary D. Divergent plate boundary 5. A volcanic process where hot lava is extruded onto the Earth’s surface. A. Eruption B. Earthquake C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 6. The mechanical wave released from two tectonic plates rupturing. A. Eruption B. Earthquake C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 7. Mechanical energy that is stored and can be released A. Eruption B. Earthquake C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 8. What is felt on the surface of the Earth after two stuck plates release stored energy. A. Eruption B. Earthquake C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 9. Energy of motion. A synonym for kinetic energy A. Eruption B. Mechanical energy C. Seismic wave D. Potential mechanical energy 10. A huge glob-like mass of molten rock inside the earth. A. Plate tectonics B. Magma chamber C. Convection current/cell D. Eruption 11. The idea that huge plates in the lithosphere float around on the asthenosphere A. Plate tectonics B. Magma chamber C. Convection current/cell D. Eruption