Plate Tectonics Jeopardy Game
advertisement

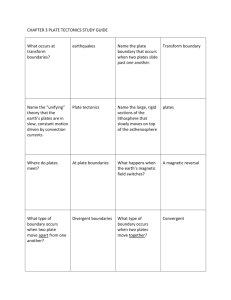
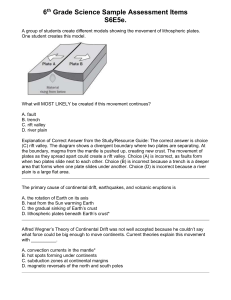
THIS IS With Your Host... Sea-Floor Spreading Theory of Plate Tectonics More Plate Tectonics 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Earth’s Interior Convection Currents Drifting Continents 100 100 200 This is the “ology” that means the study of planet Earth. A 100 What is geology? A 100 These are the two forces that shape Earth’s landforms. A 200 What are constructive and destructive? A 200 These are the waves that are produced by earthquakes. A 300 What are seismic waves? A 300 These are the three main layers that make up the Earth’s interior. A 400 What are the crust, the mantle, and the core? A 400 This causes Earth’s magnetic field. A 500 What is the inner core spinning faster than the rest of the Earth? A 500 This is the movement of energy from a warmer object to a cooler object. B 100 What is heat transfer? B 100 These are the three types of heat transfer. B 200 What are radiation, conduction, and convection? B 200 This is an example of radiation. B 300 What is heat from the sun or heat from a fire? B 300 This is an example of conduction. B 400 What is a spoon heating up in a pot of soup? B 400 This is an example of convection. B 500 What is the movement of soup in a heating pot? (Heat moves up the middle, cools, and then moves down the inside edge of the pot.) B 500 This is the name for the supercontinent of all lands joined together. C 100 What is Pangea? C 100 This is the name of the scientist who developed the Theory of Continental Drift. C 200 Who is Alfred Wegener? C 200 Any trace of an ancient organism preserved in rock is called this. C 300 What is a fossil? C 300 DAILY Place A Wager DOUBLE C 400 These are three areas of evidence that support the Theory of Continental Drift. C 400 What are: Landforms Fossil Distribution Climate C 400 This is the scientific term for an educated guess. C 500 What is a hypothesis? C 500 This is the longest chain of mountains in the world. D 100 What is the mid-ocean ridge? D 100 This is the device that bounces sound waves off underwater objects. D 200 What is sonar? D 200 This is what sonar is used for. D 300 What is determining the distance to an object and mapping the ocean floor? D 300 These are the three types of evidence for sea-floor spreading. D 400 What are molten material magnetic stripes and drilling samples? D 400 This is the name for deep, underwater canyons. D 500 What are deep-ocean trenches? D 500 This is the name for the broken sections of the lithosphere. E 100 What are plates? E 100 These are the lines where different pieces of the lithosphere meet. E 200 What are plate boundaries? E 200 This is a deep valley that forms when two plates pull apart. E 300 What is a rift valley? E 300 This is a break in the Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other. E 400 What is a fault? E 400 This is the boundary caused by plates moving apart. E 500 What is a divergent boundary? E 500 This is the boundary caused by plates moving together, or “colliding”. F 100 What is a convergent boundary? F 100 This is the boundary caused by plates moving past each other in opposite directions. F 200 What is a transform boundary? F 200 As the plates collide, this determines which plate comes out on top. F 300 What is density? F 300 This is the word for one plate moving under another. F 400 What is subduction? F 400 This landform is created when two continental plates collide. F 500 What is the formation of mountain ranges? F 500 The Final Jeopardy Category is: “Where will we be in another million years?” Please record your wager. Click on screen to begin This is how fast plates move. Click on screen to continue What is one to ten centimeters per year? Click on screen to continue What is one to ten centimeters per year? Game Designed By C. Harr-MAIT