Earth Science: Earthquakes & Plate Tectonics Matching Worksheet
advertisement
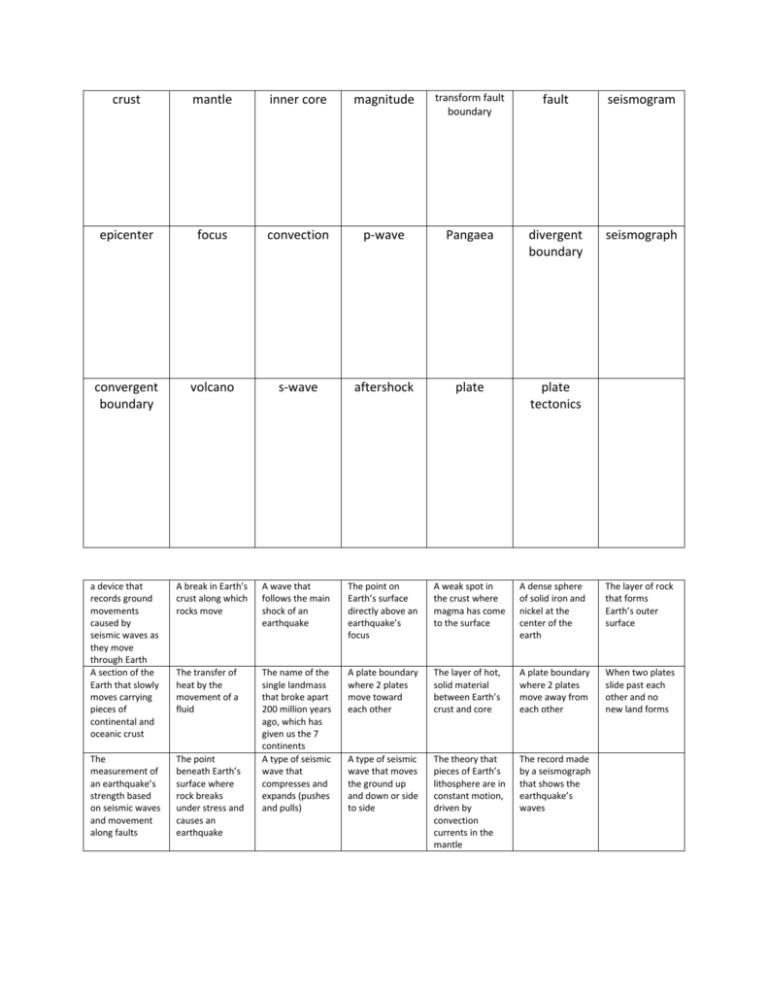
crust mantle inner core magnitude transform fault boundary fault seismogram epicenter focus convection p-wave Pangaea divergent boundary seismograph convergent boundary volcano s-wave aftershock plate plate tectonics a device that records ground movements caused by seismic waves as they move through Earth A section of the Earth that slowly moves carrying pieces of continental and oceanic crust A break in Earth’s crust along which rocks move A wave that follows the main shock of an earthquake The point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s focus A weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface A dense sphere of solid iron and nickel at the center of the earth The layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer surface The transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid A plate boundary where 2 plates move toward each other The layer of hot, solid material between Earth’s crust and core A plate boundary where 2 plates move away from each other When two plates slide past each other and no new land forms The measurement of an earthquake’s strength based on seismic waves and movement along faults The point beneath Earth’s surface where rock breaks under stress and causes an earthquake The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago, which has given us the 7 continents A type of seismic wave that compresses and expands (pushes and pulls) A type of seismic wave that moves the ground up and down or side to side The theory that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle The record made by a seismograph that shows the earthquake’s waves