The Cell
advertisement

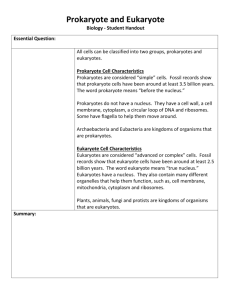
BSCS Unit 2, Chapter 6 The Cell: Homeostasis and Development 1. Look at the scanning electron micrograph opposite p. 153. What are these cells doing? 2. Look at the photo on p. 154. What type of environment do these unicellular organisms live in? 3. What do they appear to have on the outside of their cells? What is their purpose? 4. Be able to state the cell theory! 5. What did the following contribute are to the cell theory: Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow. 6. What was von Leeuwenhoek’s contribution? Robert Hook’s? 7. What is the difference between a transmission electron microscope and a scanning electron microscope? 8. Compare and contrast in the Venn Diagram below prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 9. In the diagram below, label the parts of the prokaryote cell. 10. One structure is not found on this diagram,(sometimes there is more than one) a smaller circular loop called a plasmid. What macromolecule is made of? 11. Label the parts of the following two eukaryote cells: plant and animal 12. What structures are in animal cells but NOT in plant cells? 13. What structures are plant cells but NOT in animal cells? 14. What structures that are found in eukaryote cells but NOT in prokaryote cells? 15. All cells have certain structures in common. Give their names and their functions. 16. What is the “9+2” arrangement? (see diagram below) 17. What is the evolutionary significance of this? 18. Why does metabolism depend in eukaryotic cells on the endoplasmic reticulum, but prokaryotes survive without this unique transport system? 19. What three organelles enable an organism to move? 20. What structure in prokaryotes functions to attach to substrates and also in sexual reproduction? 21. What are biofilms? What is their importance in society? 22. What would be the advantage for an organism to be multicellular vs. unicellular? 23. Why are specialized systems that make up complex organisms necessary? 24. Differentiate between plasmodesmata, gap junction, tight junctions, and desmosomes. 25. Be sure to know and understand the hierarchy of organizational levels of the family of life on p. 180. 26. Can a single cell form a system or a tissue? Explain your answer.