What does it mean to be a cell
advertisement

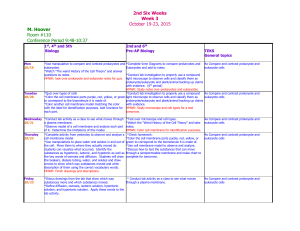
Unit 3 Biology What does it mean to be a cell? Guiding Questions 1. When did Hooke build his microscope? 2. What magnification did Hooke’s microscope have? 3. What did Hooke call the empty plant cell walls he observed when examining cork with his microscope? 4. What was the magnification of Leeuwenhoek’s microscope in the early 1800’s? 5. What were the first living cells observed using a microscope? 6. When was the cell theory first postulated and by whom? 7. What are the three basic statements that make up the Cell Theory? 8. 9. 10. 11. Name three other ways we study cells? What scale of measurement do we use for cell size? What scale of measurement do we use for smaller organelles and macromolecules? What scale of measurement do we use for small molecules and atoms? 12. What does a cell need to do to ensure it continues to function, grow and respond to stimuli? 13. What governs cell size and complexity? 14. Why does a cell need to maintain an adequate surface area:volume ratio? 15. How do molecules within a cell usually diffuse? 16. How does the size of molecules within a cell influence cell size? 17. What are the two main types of cells? 18. What is the first key difference between them? 19. What is the size of a prokaryote cell? 20. What is the organisational structure of a prokaryote cell? 21. What is the size of a eukaryote cell? 22. How else does a eukaryote cell differ from a prokaryote cell? 23. Why are organelles important in eukaryote cells? 24. 25. 26. 27. How do prokaryote cells reproduce? How do eukaryote cells reproduce? In which cell type does endocytosis and exocytosis occur? In which cell type is RNA processed least?