Chapter 2 – Part 2 Cell Theory Cell Types
advertisement

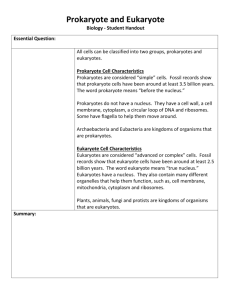
Chapter 2 – Part 2 Cell Theory Cell Types The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells Cell Size There are many types of cells in our body, each with a different shape and function Some cells, like human egg cells, can be seen with the naked eye Other cells are very small, like sperm cells, and need a microscope to be seen Cell Size Cell Size Humans have trillions of cells in the body Size of cells range from 5µm to 20µm in size http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/cont ent/begin/cells/scale/ Cell Size Continued… Small cells function more efficiently than large cells If surface area to volume ratio is too low, substances cannot enter and leave the cell well enough to meet the cell’s needs Small cells have high surface area to volume ratio Surface Area-to-Volume Types of Cells Prokaryote – “Before nuclei” Eukaryote – “True nuclei” Prokaryotes Consists of unicellular organisms Ex: Bacteria and archea Can live in many environments Ex: extreme temperatures, pH, and radiation Prokaryotes Some can make their own food Grow and divide rapidly using asexual reproduction Prokaryote Cells -Lacks a nucleus and most organelles -Much smaller than a eukaryote cell -One single circular strand of DNA found in the cytoplasm Prokaryote Cells Continued… Plasmid: Circular strand of DNA Flagella: Aids in movement Pili: Helps bacteria attach to surfaces Capsule: a polysaccharide barrier used for protection Eukaryotes Consists of unicellular and multicellular organisms Ex: Plants, animals, fungi, protists… Organisms can asexually and sexually reproduce Eukaryote Cells Contains a nucleus with DNA and membrane-bound organelles Larger, more complex cells May have evolved from a prokaryotic cell Types of Eukaryote Cells Plant Cells and Animal Cells