Exploring the Cell PPT
advertisement

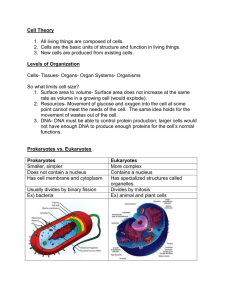
A cell is the basic unit of life. The development and enhancement of microscopes made the observation and description of microscopic organisms and living cells possible. The cell is the basic unit of life. All living things are made of cells. Cells come from pre-existing cells. 1665 Looked at cork under the microscope and saw tiny empty chambers that he called cells. 1674 Improved the microscope First to see single celled organisms 1838 All plants are made up of cells. 1839 All animals are made up of cells 1855 Proposed that all cells come from existing cells, completing the cell theory. 2 Types of Cells Prokaryote Eukaryote The simplest life forms Unicellular Exist in two major forms: eubacteria and archaebacteria. Lack a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Example: Bacteria Eukaryotes arose from prokaryotes and became larger more complex. Eukaryotes contain a nucleus and organelles surrounded by a membrane. Can be unicellular or multicellular Contain a nucleus in which their genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell. Examples: plants, animals, fungi, and protists EXAMPLES OF EUKARYOTIC CELLS Robert Hooke- observed that cork has small chambers which he called “cells”. Anton van Leeuwenheok- helped improved the first microscope Matthais Schleiden- all plants are made up of cells. Theodor Schwann- all animals are made up of cells. Rudolph Virchow- discovered that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Basic unit of life. Cell theory All living things are composed of cells Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things New cells are produced from existing cells Prokaryotes Do not contain a nuclei Smaller and simpler than eukaryotes Do contain genetic material Unicellular only Example: bacteria Eukaryotes Contain a nucleus, which contains their genetic material Larger and more complex than prokaryotes Unicellular and multicellular Examples: plants, animals, fungi, and protists