Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
advertisement

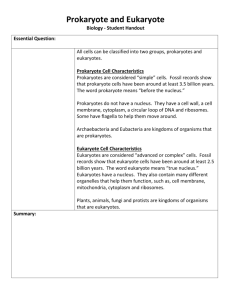
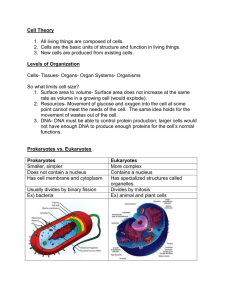
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryote • Single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound cell parts (organelles) Features of Prokaryotes • Cannot carry out specialized functions • Lived at least 3.5 billion years ago and were only organisms on the planet for nearly 2 billion years Warrawoona Formation, Australia, 3.5 billion years ago, prokaryotes (no nucleus, probably cyanobacteria) Features of Prokaryotes continued • Modern prokaryotes are informally called bacteria. • Genetic material is a single circle of DNA • Have a cell wall for structure and flagella for movement Eukaryote • An organism whose cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles • Organelle is a structure that carries out a specific function Eukaryotes continued Flagella whip back and forth. They are structurally different from the flagella found in prokaryotes. Cilia are shorter and beat stiffly in one direction. • Many single-celled eukaryotes use flagella or cilia to move around and/or to move material across cell membrane Eukaryote vs. Prokaryote