Prokaryotes - The first life forms on the planet
advertisement

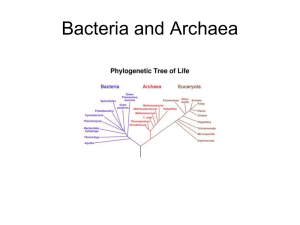
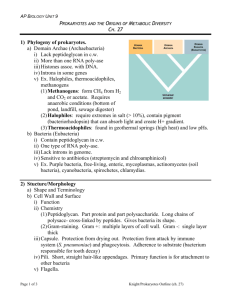
"PROKARYOTES" As we discussed in class, the term prokaryote really is not so valid anymore, since we can now examine these organisms at the molecular level, and can describe them in positive terms, not by what they are not. Nevertheless, you are expected to understand this and other outdated concepts because the science education establishment is afflicted with a condition known as paradigm paralysis. For those of you with the Princeton Review study guide, you can find what the science education gurus expect you to know. I'm jaded and cynical, so for the sake of that SAT II, stay close to your text and the study guides. Prokaryotes - (synonym = monerans - also a ridiculously outdated term) The first life forms on the planet. - All prokaryotes are unicellular, though some form colonies with specialized cells, which puts them on the borderline of being multicellular. - Prokaryotes lack a nucleus (that's what prokaryote means), and other subcellular, membrane-bound organelles. - Oxidative respiration in aerobic bacteria utilizes the plasma membrane to create the necessary proton gradient. Remember, no mitochondria. Cell structure - page 160-161 Reproduction - binary fission, page 318-319 "Chromosomes" - 13.3, page 347 Classification - page 483 Ecological roles - Photosynthesis; cyanobacteria - Nitrogen cycle: fixation;free- living and symbiotic in plant roots; denitrification; ammonification - Decomosition - Mutualistic symbiotic relations; too numerous to list - Pathogens of animals and plants - Unknown (there are a lot of microbes out there, and one in particular might be the most abundant life form on the planet, yet we don't understand its role in the biosphere. The same is true of many Bacteria and Archaea Structural features - cell wall; peptidiglycan; gram positive and gram negative (Bacteria only) - flagella Mechanisms for genetic exchange (sexy time) - conjugation, transformation, transduction. These mechanisms are collectively referred to as Horizontal or Lateral Gene Transfer (HGT or LGT). This is opposed to the vertical gene transfer that results from direct inheritance. - conjugation = direct transfer of partial genome between cells - transformation = uptake of discarded genes from the environment - transduction = viruses carry genes from one cell to another just like mosquitos carry West Virus and Malaria.