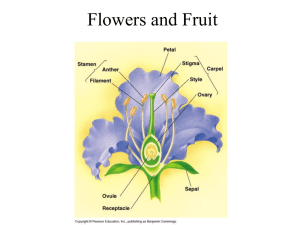
PLANT REPRODUCTION/ANATOMY
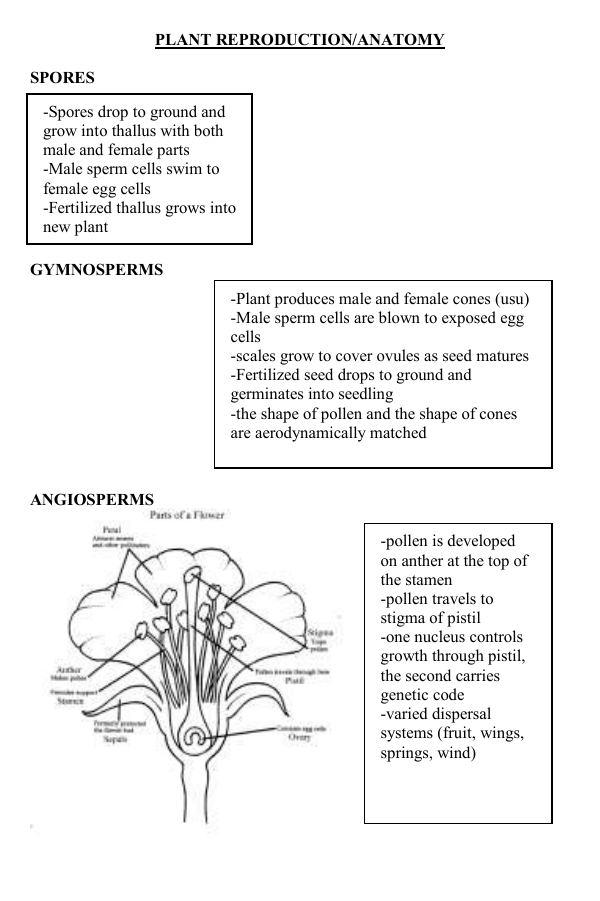
PLANT REPRODUCTION/ANATOMY
SPORES
-Spores drop to ground and grow into thallus with both male and female parts
-Male sperm cells swim to female egg cells
-Fertilized thallus grows into new plant
GYMNOSPERMS
ANGIOSPERMS
-Plant produces male and female cones (usu)
-Male sperm cells are blown to exposed egg cells
-scales grow to cover ovules as seed matures
-Fertilized seed drops to ground and germinates into seedling
-the shape of pollen and the shape of cones are aerodynamically matched
-pollen is developed on anther at the top of the stamen
-pollen travels to stigma of pistil
-one nucleus controls growth through pistil, the second carries genetic code
-varied dispersal systems (fruit, wings, springs, wind)
NALIFORNIA PLANT FAMILIES (common NAL species)
-key words
OTHER
PINE (Pine, Fir, Hemlock, Spruce)
-1-5 wrapped needles
CYPRESS/CEDAR (Cedar, Cypress, Juniper)
-small, scaley leaves
-aromatic
MORMON TEA (Mormon Tea)
-produce cup-like naked-seeds (instead of cones)
-jointed green stems
DICOTS
ASTER/SUNFLOWER (dandelion, thistle, yarrow, sagebrush, chamomile, aster)
-composite “flower:” each part of the flower is actually it’s own flower
-every seed is from a “disk flower” (these are fertile)
-every “petal” is from an infertile “ray flower”
BUTTERCUP (larkspur, buttercup, columbine)
-3+ simple pistils often with hooked tips
POPPY (California popp)
-petals in 4’s, numerous stamens
-milky sap
STINGING NETTLE (Stinging Nettle)
-hairy plants
-petal-less flowers
-string-like clusters from leaf axis
CACTUS (prickly-pear, cholla)
-succulent with spines
-numerous flower parts
MALLOW (apricot mallow, cotton)
-mucilaginous
-5 separate petals, numerous stamens fused into one
GOURD (wild cucumber)
-vining with tendrils
-funnel-shaped flowers
-large, 3-4 celled fruits
WILLOW (poplar, cottonwood, aspen, willow)
-trees/bushes in moist soil
-alternating leaves
-catkin (small, slim, flower-cluster) develop into capsules
MUSTARD (black mustard, watercress, wild radish)
-4 petals, 6 stamens—4 tall and 2 short
-seed pods in “raceme” (spiral stair-case)
INDIAN PIPE (Pine drops, snow plant)
-saprophytes (no chlorophyll, feed on dead organic matter in soil)
-leaves alternate and reduce to scales
ROSE (strawberry, rose, blackberry, cherry, plum, apple,)
-5 sepals, 5 petals, numerous stamens
-oval, serrated leaves
PEA (alfalfa, cat claw, mesquite, palo verde, tamarind, lupine, locoweed, clover, sweet pea)
-Banner, wings, keel
-pea-like pods (duh!)
-often pinnate leaves
CASHEW/SUMAC (poison oak, lemonade berry, laurel sumac)
-shrubs with three-lobed or pinnate leaves
-fruits are single-seeded, red or white
PARSLEY (poison hemlock, carrot, fennel, parsley)
-compound umbels (short flower stalks from common points)
-usually hollow flower stalks
-5 petals, 5 stamens
NIGHTSHADE (pepper, jimson weed, Indian tree tobacco, tomato, potato, eggplant)
-alternate leaves
-5 united sepals, 5 united petals, 5 stamens
MORNING GLORY (morning glory, sweet potato, bindweed)
-vining, tubular, funnel-form flowers
-5 separate sepals, 5 united petals
MINT (mint, chia, culinary sage)
-square stalks
-opposite leaves
-5 united sepals, 5 united petals (2 up 3 down), 4 stamens (2 long, 2 short)
MONOCOTS
RUSH (rush)
-tiny lily-like flowers (3 green sepals, 3 green petals, 6 stamens, 1 pistil)
GRASS (wheatgrass, crabgrass, rye, barley, rice)
-grassy (duh!)
-knee-like nodes on flower stems
LILY (mariposa lily, onion, asparagus, blue dicks, agave, yucca, aloe,
-parts in threes (it’s a monocot, remember??!)
-sepals and petals are usually identical
IRIS (Douglas iris, blue-eyed grass)
-“lilies with leaves in a flat plane”
ORCHID
-irregular monocot flower