Flowers and Fruit, Powerpoint for March 30.
advertisement

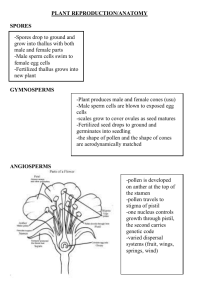
Flowers and Fruit Flower Structure • Generalized flowers - 2 outer sets of sterile parts, 2 inner sets of fertile parts • Outer sterile part - sepals, collectively the calyx - may do photosynthesis, protect flower, usually like leaves in texture, protect bud - form outer covering of bud • Next sterile part - petals - not like leaves in texture, usually not green, collectively called corolla - petalloid - petal like in appearance • Both sepals and petals can be fused - so sepals joined together, petals joined together • Perianth - calyx and corolla together - used when the two cannot be distinguished - sometimes sepals and petals are called tepals for perianth if very similar in appearance – like in Tulips • If only one set of sterile parts, they are always called sepals; sometimes whole perianth is missing • First fertile parts - stamens - male – androecium - Can be sterile and modified to look like petals • Innermost fertile parts - pistils, female - gynoecium Wild Rose Yellow rose – many “petals” are actually modified sterile “petalloid” stamens Carpels and Ovaries • Flowering plants always have enclosed ovary wrapped in a carpel - nonflowering plants don't • Carpel is highly modified leaf - a simple pistil is one ovary • Pistil may be made up of one carpel or several fused carpels • Often the bottom part called the ovary, with stigma at top to receive pollen, style connects them - fused carpels may have separate style and stigma or they may all be fused Helleborus – five separate carpels Malus – crab apple – typical flower structure Plant Sexuality • Monoecious - separate flowers for male and female both on one plant - corn • Dioecious - male and female plants are separate - separate sexes - gingko • Perfect flower - flower has stamens and carpels – bisexual flowers • Imperfect flower - lacks either stamens or carpels - will be staminate or carpellate (pistillate) • Complete - has sepals, petals, stamens and carpels • Incomplete - lacking one of the 4 main flower parts Complete and Incomplete Flowers Jatropha – monoecious but insect pollinated Female left, male right Dioecious - Holly Female flower Male flower Berries on female Inflorescence terms • Often flowers, especially small flowers, are gathered into a structure known as an inflorescence – an aggregation of flowers on a single flowering branch • bract - more or less modified leaf that subtends flower or flower groups - bract can look like normal leaf • bract can also look like petal - petalous - dogwoods have big white "petals" that are really petaloid bracts • peduncle - stalk of cluster of flowers • pedicel - stalk of individual flower • petiole - leaf stalk Dogwood with petalloid leafy bracts Types of Inflorescence 1. indeterminant - youngest flower at apex in theory could produce flowers forever some may by fruiting while apex still flowering - include - racemes, panicle, spike, corymb, head, umbel, catkin 2. determinant - oldest flowers at apex moving down younger flowers - cyme, scorpiod cyme Raceme Larkspur Panicle Panicum - switchgrass Spike – prairie blazing star Corymb Yarrow Umbel Wild parsnip Queen Anne’s Lace Sunflower – Composite head inflorescence Catkin Alder catkin Scorpoid Cyme Onosmodium Skunk cabbage inflorescence – a spathe and spadix Pollination syndromes among the phloxes Magnolia – beetle pollinated Honeybee covered with pollen Scotch broom – bee pollinated Honeybee pollinating beebalm – Monarda sp. With visible light with UV light Nectar guides for honeybees Cyrtid fly pollinating a composite Stapelia gigantea – carrion fly pollinated Monarch butterfly pollinating milkweed Brugmansia – moth pollinated Hummingbird pollination Ipomopsis aggregata – hummingbird pollinated Greater double-collared sunbird Proteus – pollinated by perching birds Bat Pollination Box elder – wind pollinated – female left, male right Wild oats – Whole plant Wild oat flower – close up Fruit Types • A fruit may be defined as a matured ovary • There are two basic fruit types – dry or fleshy. These types arise from the development of the pericarp – outer cover of ovary • The pericarp may become dry and these form dry fruits • The pericarp may also become soft, thick and fleshy – and these form fleshy fruits Pome - Apples and Pears Violet flower types