Alstroemeria Flower Dissection: Lab Guide
advertisement

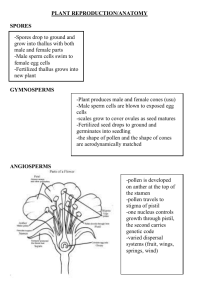
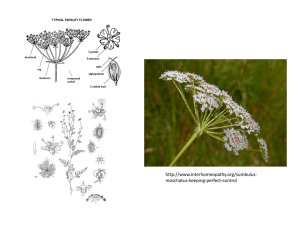
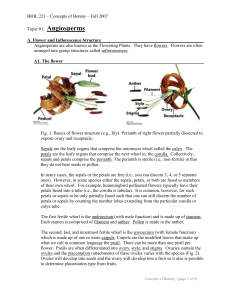
Flower Dissection Alstroemeria Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Monocots Order: Liliales Family: Alstroemeriaceae Genus: Alstroemeria L. Specie Petals, Sepals, or Tepals • The alstroemeria is a type of flower that has tepals, because the petals and sepals are similar. Stamen: Filament, Anther Pistil: Stigma Ovary Pistil Types Ovary Types Staminate: Has only functional stamen Carnation = male Pistiliate: has only functional pistil Perfect: Has both functional stamen and pistil Cotyledon: Embryonic first leaves Features Monocotyledon Dicotyledon Leaf structure Parallel veins Network veins Roots Fibrous roots Tap roots Stem Soft Hard No. of cotyledons 1 2 Number of petals Divisible by 3 Divisible by 4 or 5 Alstroemeria = Monocot Tepals : Petals and Sepals Both the striped petals and the sepals, which are the leaves between the petals, come in an arrangement of three each. The petals and sepals have similar color and texture, so the sepals actually resemble the petals much more closely than they resemble most green leaves. Reproductive Structures Alstreomeria plants contain six undivided stamens, which are the male reproductive stalks extending from the center of the flower. The ovaries of the flower have three carpels and are known as inferior, because they are fused to the base floral structure. Leaves Alstroemeria plants are like grasses, irises and lilies in that veins go up to the leaves but do not branch across. These leaves are actually upside down because they twist as they extend from the stem. This feature is known as being resupinate. For a closer look http://www.microscopyuk.org.uk/mag/indexmag.html?http:/ /www.microscopyuk.org.uk/mag/artoct08/bj-peru.html Begin your lab