MELASTOMATACEAE
advertisement

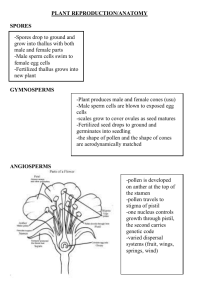
MELASTOMATAC magnoliids monocots MYRTALESMelastomataceae Tibouchina - the best-known ornamental MELASTOMATACEAE (MYRTALES, ROSIDAE unplaced) NUMBERS: 200 Genera, 4000 species GEOGRAPHY: widespread in tropics, most diverse in South America HABITAT: mostly understory trees, heat and moisture requirements vary ROSIDAE CHARACTERS: petals separate, stamens twice the petals in number MYRTALES CHARACTERS: connate carpels, stamens at least twice the petals, tendency to flower parts in fours, internal phloem, hypanthium or inferior ovary APG MYRTALES RECOGNITION CHARACTERS: Myrtales may be recognised by their often flaky bark; opposite leaves with colleters, a t most small stipules and strong intramarginal veins; flowers with petals that are clawed or at least very narrow at the base, a more or less inferior ovary, and a usually nectariferous hypanthium. The sepals are often valvate and the stamens are usually incurved in bud. CHARACTERS DIAGNOSTIC OF FAMILY: Habit woody Leaves opposite, with arcuate secondary ve ins and transverse (ladder-like) tertiary veins Flowers large and showy Androecium with poricidal anthers and appendages (like Ericaceae) Fruit a berry or capsule MELASTOMATACEAE •opposite leaves •2 pair basal secondaries •ladder tertiaries •staminodes or stamen appendages •stamens 2x petals •hypanthium/inferior ovary MELASTOMATACEAE: arcuate basal secondaries, -- including a marginal vein perpendicular tertiaries Miconia calvescens, introduced to Hawaii Monochaetum Mouriri and Memecylon Mouriri Memecylon Origin of poricidal stamens and appendages in melastomes Memecylon Beccarianthus Melastoma Pollen sacs white, connective tissue and appendages shaded Buzz pollination of Melastomataceae https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMvQSx2429U Miconia Miconia Brachyotum Blakea Clidemia hirta, Koster’s Curse Coster's curse growing densely under a young albizia plantation, Hawaii Island, Hawaii