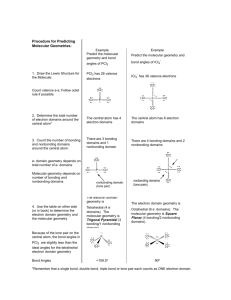
Valence electrons in a covalent bond are called bonding pairs of
advertisement

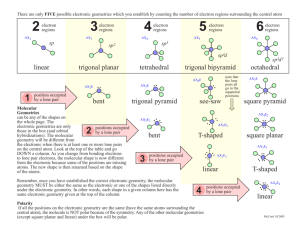
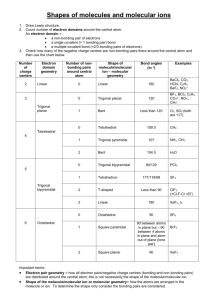
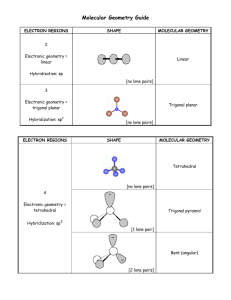
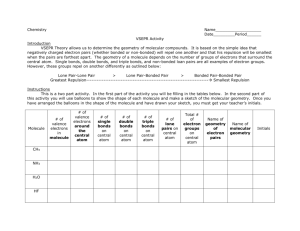
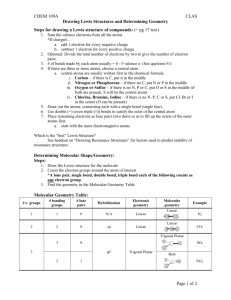
1 2.3. VSEPR continued In order to determine the shapes of molecules we need to consider the arrangement of bonding pairs of electrons and lone pairs of electrons (if present). The repulsion between lone pairs is bigger than between bonding pairs. This means that lone pairs will favour more space. If there are two or more lone pairs, then the lone pairs will be arranged to minimise repulsions between lone pairs. The final shape of the molecule depends on the arrangement of the bonding and lone pairs of electrons – see handout. (table 9.2 p. 351; table 9.3, p. 354) Note If lone pairs are present, the shape of the molecule is not the same as the shape of the electron domains. 2 We can predict the three-dimensional structure or molecular geometry of any main group molecule using the following procedure: 1. Determine molecule. the Lewis structure of the 2. Count the number of electron domains around the central atom and arrange these to minimise repulsion i.e. according to one of the 5 basic shapes. This gives the electron domain geometry. Note that double or triple bonds count as one electron domain because they occupy the same general region of space. 3. From this electron domain geometry, identify the molecular geometry (how the atoms are arranged) by considering the bonded atoms. 3 Example: H2CO 1. Determine the Lewis structure. 2. Total number of electron pairs around the central atom is 4. However, there is one bond, which means the number of electron domains is 3. 3. There are no lone pairs on the central atom, so the electron domain geometry is the same as the molecular geometry. H2CO is therefore trigonal planar. 4 More examples. A. PCl5 1. Determine Lewis structure: Cl Cl Cl Cl P Cl 2. Count number of electron domains around central atom. P is central atom. 5 electron domains, therefore electron domain geometry is trigonal bipyramidal. 5 3. From electron domain geometry, identify molecular geometry by considering bonded atoms. 5 bonding domains, no lone pairs, therefore molecular geometry is also trigonal bipyramidal. Cl Cl P Cl Cl Cl Exercise: H2S