vsepr theory (2015)
advertisement

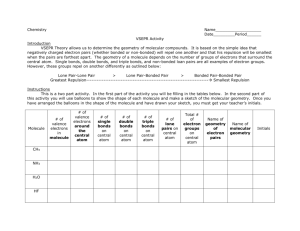
VSEPR Theory – Introduction What Is VSEPR? The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion...theory: is used to PREDICT MOLECULAR ______________ is based on the number of regions of high electron density around a ___________________ atom. can be used to predict structures of molecules or ions that contain only _____________________by minimizing the electrostatic _______________________between the regions of high electron density. can also be used to predict structures of molecules or ions that contain multiple bonds or unpaired electrons. does fail in some cases. What steps need to be followed in order to apply the VSEPR theory? 1. Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule or ion. 2. Count the total number of regions of high electron density (i.e. the number of bonding and non-bonding lone electron pairs) around the central atom. o Double and triple bonds count as ___________ REGION OF HIGH ELECTRON DENSITY. o An unpaired electron counts as ONE REGION OF HIGH ELECTRON DENSITY. o For molecules or ions that have resonance structures, you may use any one of the resonance structures. Some GUIDELINES to follow when applying VSEPR Theory: *Keep in mind that there are some exceptions to the following...these are good “rules of thumb”. 1. Hydrogen only ever forms ___________ bond. 2. Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen and Fluorine always adhere to the _________________ RULE...they are “unable” to expand their octet. *The OCTET RULE “Violators”: 3. Beryllium usually only forms ___________bonds...and yes, beryllium can form covalent bonds even though it is a metal. 4. Boron usually only forms _______________bonds. 5. Non-metals in period three and beyond ________ expand their octet(as a result of “available” ____-orbitals). *(e.g. Sulfur, phosphorus, chlorine , bromine, iodine, xenon...can all have more than 8 electrons in their valence shell.) Bond Pairs Lone Pairs General Formula Molecular Geometry (Name of Shape) Hybridization Electron Domain Geometry Total e- pairs on central atom SHAPES OF MOLECULES: PART 1 Bond Angle e.g. 2 Linear Bel2 3 Trigonal Planar BCl3 SO2 4 Tetrahedral CBr4 NCl3 OF2 Lewis Structure 3-D Shape Sketch Bond Pairs Lone Pairs General Formula Molecular Geometry (Name of Shape) Hybridization Electron Domain Geometry Total e- pairs on central atom SHAPES OF MOLECULES: PART II Bond Angle e.g. PCl5 5 Trigonal Bipyramidal SCl4 ICl3 I3- Lewis Structure 3-D Shape Sketch SF6 6 Octahedral BrF5 XeF4 *Multiple bonding in VSEPR models: Treat DOUBLE and TRIPLE bonds as if they were SINGLE bonds when applying VSEPR theory. Examples: Draw Lewis Structures and predict the shape of the following: a) CO2 d) PO43g) NO3j) methanoic acid, HCOOH b) HCN e) ethene, C2H4 h) CS2 k) methanol, CH3OH 2c) CO3 f) ethyne, C2H2 i) methanal, HCHO l) SO42- m) carbon monoxide, CO n) ozone, O3 *o) benzene ring, C6H6 *m) NO2+ *n) NO2 *o) NO2-