Molecular Geometry & VSEPR Theory
advertisement

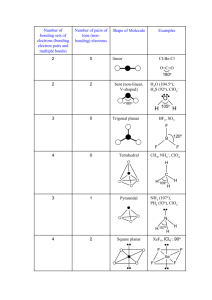
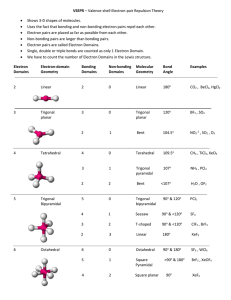
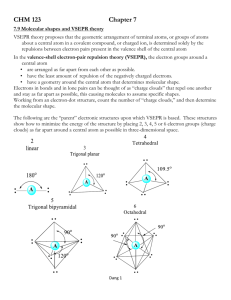
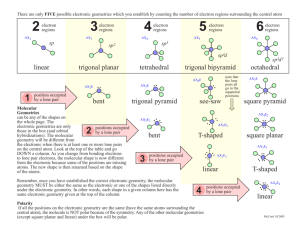
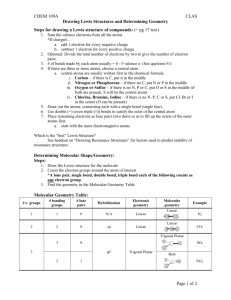
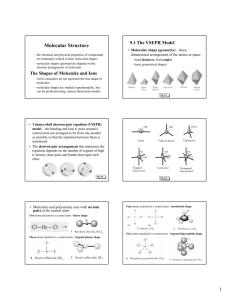
Molecular Geometry Predict with VSEPR Theory Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory - Electron clouds repulse each other - Distribute around a central atom as far apart as possible - 1 electron cloud can be: 1 lone pair 1 single bond 1 double bond 1 triple bond Arrangement of Electron Clouds - 5 basic arrangements around a central atom. 2 clouds linear 3 clouds trigonal planar 4 clouds tetrahedral 5 clouds trigonal bipyramidal 6 clouds octahedral • MOLECULAR GEOMETRIES are named for the positioning of the ATOMS (not including lone pairs) • If all clouds lead to an atom, the molecular and electron cloud geometries are the same. Electron cloud geometry Number Number Molecular of of lone geometry bonding pairs e- pairs Linear 2 0 Linear Trigonal 3 0 Trigonal Planar planar 2 1 Bent or " angular Tetrahedral 4 0 Tetrahedral 3 1 Pyramidal " 2 2 Bent " Bond Angle Example 180o 120o CO2 BF3 180o SO2 109.5o <109.5o CH4 NH3 <109.5o H2O PF5 ClF3 Trigonal bipyramidal 5 0 " 4 1 Trigonal pyramidal See-saw " 3 2 T-shaped 90o 120o 90o <120o 90o " Octahedral 2 3 Linear 180o XeF2 " 6 5 0 1 90o 90o SF6 BrF5 " 4 2 Octahedral Squarepyramidal Squareplanar 90o XeF4 SF4 Factors Affecting Bond Angles - The bond angle decreases as the number of lone pairs on the central atom increases. - Lone pairs take-up more space, so they push-back the chemical bonds. Note: For the trigonal bipyramidal - lone pairs are always placed in equatorial positions. Net Polarity of Molecules NONPOLAR 1. All nonpolar bonds 2. Two or more polar bonds, but they cancel by geometry. Look for: - Outside atoms alike AND no lone pairs on central atom OR - Even number of lone pairs on central atom uniformly distributed in space POLAR (molecule is called a dipole) 1. Only 1 polar bond in the molecule 3. More than 1 polar bond - Outside atoms not all alike AND/OR - Only one lone pair on the central atom OR - 2 or more lone pairs on not evenly distributed in space Net Dipole Moments of Polyatomic Molecules Example: CO2, each C-O dipole is canceled because the molecule is linear. Example: H2O, the H-O dipoles do not cancel because the molecule is bent.