Predicting Molecular Geometry: PCl3 and ICl4 Examples
advertisement
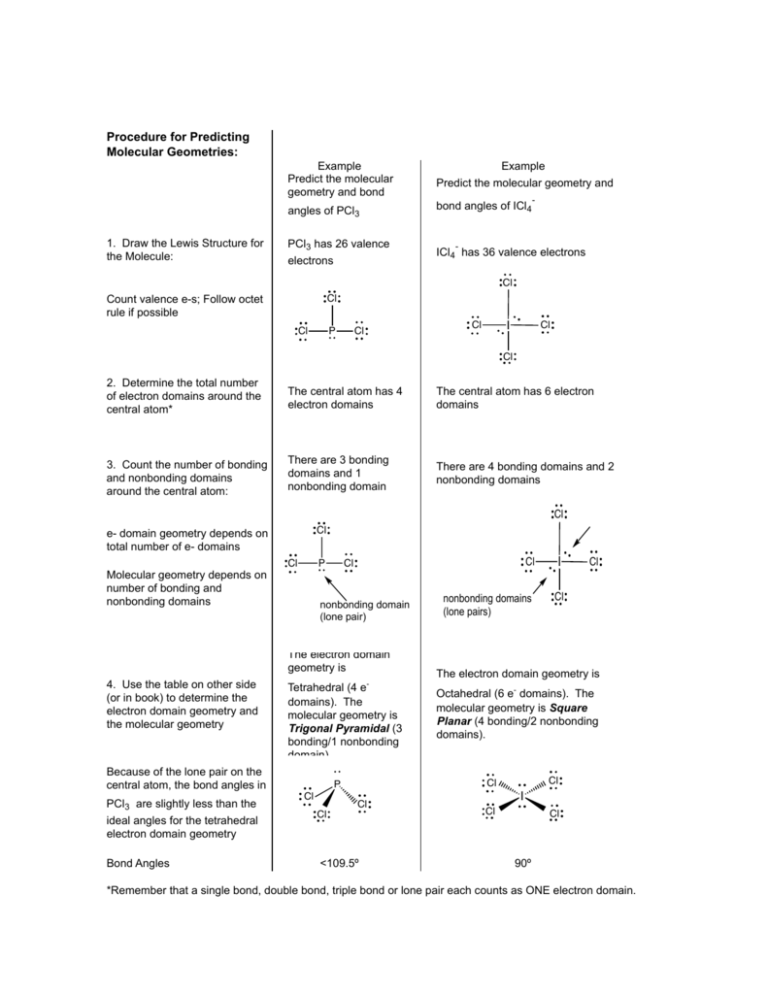
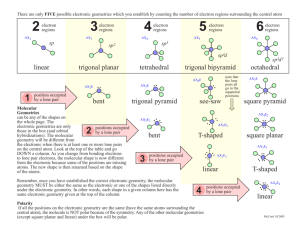
Procedure for Predicting Molecular Geometries: 1. Draw the Lewis Structure for the Molecule: Example Predict the molecular geometry and bond Predict the molecular geometry and angles of PCl3 bond angles of ICl4 PCl3 has 26 valence electrons Example - - ICl4 has 36 valence electrons Cl Count valence e-s; Follow octet rule if possible Cl Cl P Cl I Cl Cl Cl 2. Determine the total number of electron domains around the central atom* The central atom has 4 electron domains The central atom has 6 electron domains 3. Count the number of bonding and nonbonding domains around the central atom: There are 3 bonding domains and 1 nonbonding domain There are 4 bonding domains and 2 nonbonding domains Cl Cl e- domain geometry depends on total number of e- domains Molecular geometry depends on number of bonding and nonbonding domains Cl P nonbonding domain (lone pair) The electron domain geometry is 4. Use the table on other side (or in book) to determine the electron domain geometry and the molecular geometry Tetrahedral (4 edomains). The molecular geometry is Trigonal Pyramidal (3 bonding/1 nonbonding domain). Because of the lone pair on the central atom, the bond angles in PCl3 are slightly less than the ideal angles for the tetrahedral electron domain geometry Bond Angles Cl I nonbonding domains (lone pairs) Cl Cl <109.5º Cl The electron domain geometry is Octahedral (6 e- domains). The molecular geometry is Square Planar (4 bonding/2 nonbonding domains). Cl Cl P Cl Cl Cl I Cl Cl 90º *Remember that a single bond, double bond, triple bond or lone pair each counts as ONE electron domain.