Corlanor
advertisement
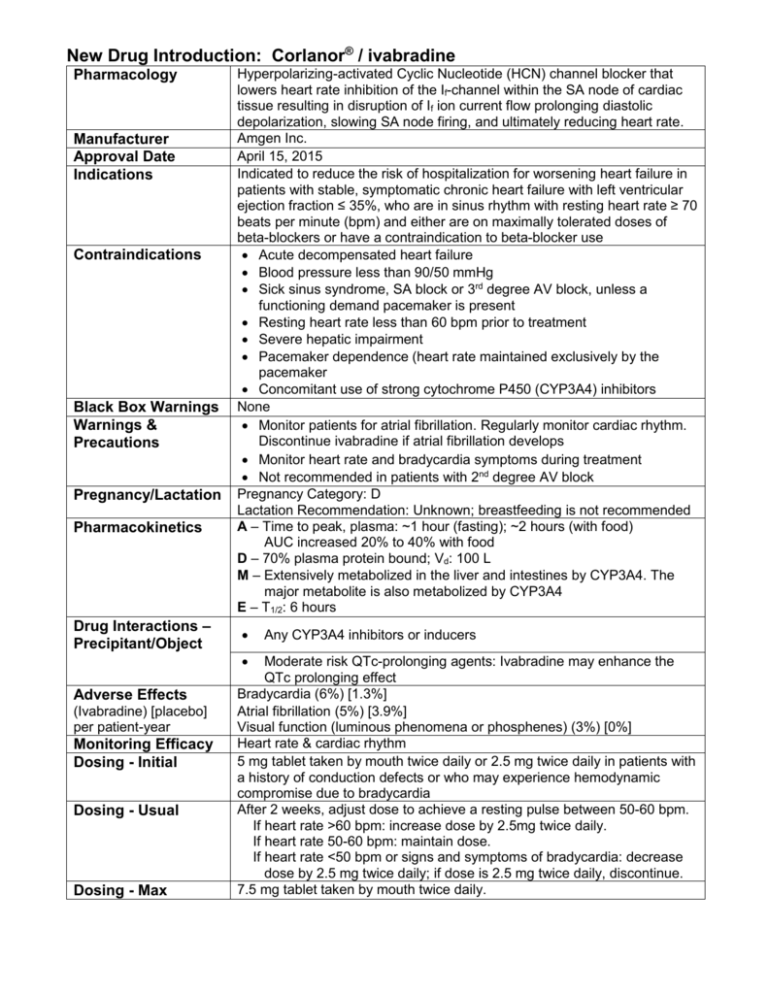
New Drug Introduction: Corlanor® / ivabradine Pharmacology Manufacturer Approval Date Indications Contraindications Black Box Warnings Warnings & Precautions Pregnancy/Lactation Pharmacokinetics Drug Interactions – Precipitant/Object Hyperpolarizing-activated Cyclic Nucleotide (HCN) channel blocker that lowers heart rate inhibition of the If-channel within the SA node of cardiac tissue resulting in disruption of If ion current flow prolonging diastolic depolarization, slowing SA node firing, and ultimately reducing heart rate. Amgen Inc. April 15, 2015 Indicated to reduce the risk of hospitalization for worsening heart failure in patients with stable, symptomatic chronic heart failure with left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 35%, who are in sinus rhythm with resting heart rate ≥ 70 beats per minute (bpm) and either are on maximally tolerated doses of beta-blockers or have a contraindication to beta-blocker use Acute decompensated heart failure Blood pressure less than 90/50 mmHg Sick sinus syndrome, SA block or 3rd degree AV block, unless a functioning demand pacemaker is present Resting heart rate less than 60 bpm prior to treatment Severe hepatic impairment Pacemaker dependence (heart rate maintained exclusively by the pacemaker Concomitant use of strong cytochrome P450 (CYP3A4) inhibitors None Monitor patients for atrial fibrillation. Regularly monitor cardiac rhythm. Discontinue ivabradine if atrial fibrillation develops Monitor heart rate and bradycardia symptoms during treatment Not recommended in patients with 2nd degree AV block Pregnancy Category: D Lactation Recommendation: Unknown; breastfeeding is not recommended A – Time to peak, plasma: ~1 hour (fasting); ~2 hours (with food) AUC increased 20% to 40% with food D – 70% plasma protein bound; Vd: 100 L M – Extensively metabolized in the liver and intestines by CYP3A4. The major metabolite is also metabolized by CYP3A4 E – T1/2: 6 hours Adverse Effects (Ivabradine) [placebo] per patient-year Monitoring Efficacy Dosing - Initial Dosing - Usual Dosing - Max Any CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers Moderate risk QTc-prolonging agents: Ivabradine may enhance the QTc prolonging effect Bradycardia (6%) [1.3%] Atrial fibrillation (5%) [3.9%] Visual function (luminous phenomena or phosphenes) (3%) [0%] Heart rate & cardiac rhythm 5 mg tablet taken by mouth twice daily or 2.5 mg twice daily in patients with a history of conduction defects or who may experience hemodynamic compromise due to bradycardia After 2 weeks, adjust dose to achieve a resting pulse between 50-60 bpm. If heart rate >60 bpm: increase dose by 2.5mg twice daily. If heart rate 50-60 bpm: maintain dose. If heart rate <50 bpm or signs and symptoms of bradycardia: decrease dose by 2.5 mg twice daily; if dose is 2.5 mg twice daily, discontinue. 7.5 mg tablet taken by mouth twice daily. Renal Adjustment Hepatic Adjustment CrCl > 15 mL/min: no dosage adjustment necessary CrCl < 15 mL/min: there are no dosage adjustments provided; use with caution Mild or moderate impairment (Child-Pugh Class A or B): no dosage adjustment necessary Severe impairment (Child-Pugh Class C): use is contraindicated Cost: Source: McKesson- accessed 05/26/2015 Dose(s) Brand – Generic Corlanor® - ivabradine 5mg tablet (scored) 7.5mg tablet $ (30d) $450 $450 Summary Corlanor®, ivabradine, is the first in-class Hyperpolarizing-activated Cyclic Nucleotide (HCN) channel blocker that lowers heart rate, indicated for patients with stable, symptomatic chronic heart failure with left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 35% & resting heart rate ≥ 70 beats per minute. Ivabradine is used for patients who are already on maximum tolerated dose of beta-blockers or are unable to use beta blockers. Unlike beta-blockers, ivabradine reduces heart rate without reducing the heart’s contractility (no negative inotropic effects). Ivabradine has no effect on conduction in the atrioventricular node and therefore, is of no clinical benefit in the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Potential drug interactions are possible with CYP3A4 inhibitors/inducers. Heart rate should be monitored, as bradycardia is the most common adverse effect of ivabradine. References: 1. www.Corlanor.com 2. Corlanor [ivabradine] package insert. Amgen Inc. April. 2015. 3. Ivabradine. UpToDate Drug Information. Accessed through UpToDate. Accessed on May 23, 2015. 4. Swedberg K, et al. SHIFT Study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2012;59:1938-45. Date Prepared: May 30, 2015 Editor: Peter G. Koval, Pharm.D., BCPS Author: Rashmi Patel, Pharm.D. Candidate, UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy