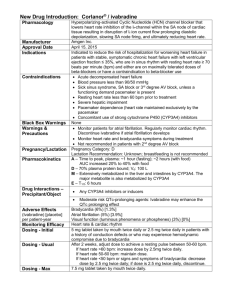
Concomitant therapy-β-blockers
advertisement

Systolic Heart failure treatment with the If inhibitor ivabradine Trial Effects on outcomes of heart rate reduction by ivabradine in patients with congestive heart failure: is there an influence of beta-blocker dose? Swedberg K, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:1938-1945 www.shift-study.com Clinical characteristics of patients by β-blocker status No BB BB <25% of target dose Age, years BB 25% to BB BB <50% of target 50% to <100% ≥100% of dose of target dose target dose 64 61 60 60 58 Resting HR, bpm 84.2 80.6 79.5 79.1 78.9 Systolic BP, mm Hg 121 117 120 122 125 LV EF, % 28.7 28.1 28.9 29.4 29.3 NYHA III or IV, % 58 54 49 50 51 COPD, % 33 11 11 9 5 Asthma, % 11 2 2 2 2 PAD, % 10 6 6 6 5 Hypertension, % 63 55 63 70 73 ACE/ARB, % 90 86 90 92 93 Diuretic, % 86 87 83 83 81 Swedberg K, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:1938-1945 www.shift-study.com Effect of ivabradine on outcomes by β-blocker doses BB category (% of target dose) Placebo Hazard event rate (%) ratio 95 % CI P P P heterogeneity Trend Trend adj** 0.35 0.056 0.135 0.55 0.12 0.19 PEP (CV death, HF hospitalisation) No β-blocker 39.3 0.71 0.55-0.93 BB, 25% 40 0.74 0.59-0.92 BB, 25% to <50% 30.8 0.81 0.68-0.98 BB, 50% to <100% 24.8 0.88 0.72-1.07 BB, ≥100% 20.1 0.99 0.79-1.24 No β-blocker 29 0.62 0.45-0.85 BB, 25% 29 0.68 0.52-0.89 BB, 25% to <50% 22 0.74 0.59-0.93 BB, 50% to <100% 18 0.83 0.65-1.05 BB, ≥100% 14 0.84 0.63-1.11 HF hospitalisation **adjusted for interaction between baseline HR and randomised treatment Swedberg K, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:1938-1945 www.shift-study.com HR reduction according to β-blocker and HR category HR reduction (bpm) from baseline to 28 days with ivabradine* 16 Baseline HR category (bpm) 12 ≥87 8 80 to <87 75 to <80 4 72 to <75 <72 0 No BB BB<25% BB 25-50% BB 50-100% BB ≥100% β-blocker category No impact of BB dose on HR reduction with ivabradine Swedberg K, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:1938-1945 Impact of baseline HR on HR reduction with ivabradine *Placebo corrected www.shift-study.com Conclusion • In patients with systolic HF treated with guidelinerecommended therapies, resting HR remains an important modifiable risk factor in patients treated with β-blockers • When HR ≥70 bpm, reduction of heart rate with ivabradine will provide additional clinical benefits regardless of the ßblocker dose • The magnitude of HR reduction with ivabradine, beyond that achieved by β-blockers, primarily determines subsequent outcome Swedberg K, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:1938-1945 www.shift-study.com