Installment Sales Examples
advertisement

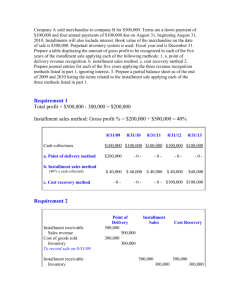
Installment Sales
Example & Homework Problem
Example:
1.
ABC Corp. sold a piece of real estate on January 2, 2009 for $5,000,000. It had
purchased the property in 2002 for $4,500,000 in cash. At that time the land was
worth $450,000 and the remainder was attributed to the building. At the time of
the sale, the carrying value of the building was $3,650,000.
The terms of the sale were as follows:
Downpayment
$ 250,000
Note Receivable
$4,750,000
Interest rate
10%
Length of mortgage
20 years
Annual payment
$ 557,933 due at end of each year
The sale has been consummated, the seller's receivable is not subject to future
subordination, and the seller has no continuing involvement with the property. However,
because the initial investment is inadequate, the seller must use the installment method to
account for this sale.
REQUIRED: Journal entries needed in 2009, 2010.
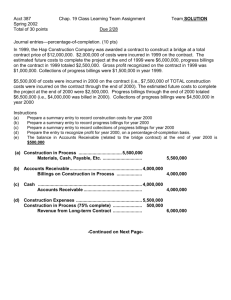
Solution to Installment Accounting Example
1.
1/2/09
Gross profit percentage = 18% [(5,000-3650-450)/5000
or $900,000 deferred gross profit divided by $5,000,000 selling price
Cash
250,000
Notes Receivable
4,750,000
Acc'd Depreciation
400,000
Land
450,000
Building
4,050,000
Deferred gross profit on installment sale of land
900,000
12/28/09 Cash
557,933
Interest revenue
Notes receivable
475,000
82,933
12/31/09 Deferred gross profit {(82,933+250,000)*18%}
Gain on installment sale of land
12/31/10 Cash
59,928
59,928
557,933
Interest Revenue
Note receivable
466,707
91,227
12/31/10 Deferred gross profit (18% * 91,227)
Gain on installment sale of land
YEAR
PAYMENT
DWNPYMT
$
250,000
2009
$557,933
2010
$557,933
2011
$557,933
2012
$557,933
2013
$557,933
2014
$557,933
2015
$557,933
2016
$557,933
2017
$557,933
2018
$557,933
2019
$557,933
2020
$557,933
2021
$557,933
2022
$557,933
2023
$557,933
2024
$557,933
2025
$557,933
2026
$557,933
2027
$557,933
2028
$557,933
$ 11,408,660
10.00%
INTEREST
PRINCIPAL
REVENUE
$475,000
$466,707
$457,584
$447,549
$436,511
$424,369
$411,012
$396,320
$380,159
$362,381
$342,826
$321,315
$297,654
$271,626
$242,995
$211,501
$176,858
$138,750
$96,832
$50,722
$6,408,670
$250,000
$82,933
$91,227
$100,349
$110,384
$121,422
$133,564
$146,921
$161,613
$177,774
$195,552
$215,107
$236,618
$260,279
$286,307
$314,938
$346,432
$381,075
$419,183
$461,101
$507,220
$5,000,000
BALANCE
$ 5,000,000
$4,750,000
$4,667,067
$4,575,840
$4,475,491
$4,365,107
$4,243,685
$4,110,121
$3,963,200
$3,801,587
$3,623,812
$3,428,261
$3,213,154
$2,976,536
$2,716,257
$2,429,949
$2,115,011
$1,768,579
$1,387,504
$968,322
$507,221
$0
16,421
16,421
GROSS
BALANCE
PROFIT
DEFERRED
RECOGNIZED PROFIT
$
900,000
$45,000
$855,000
$14,928
$840,072
$16,421
$823,651
$18,063
$805,588
$19,869
$785,719
$21,856
$763,863
$24,042
$739,822
$26,446
$713,376
$29,090
$684,286
$31,999
$652,286
$35,199
$617,087
$38,719
$578,368
$42,591
$535,776
$46,850
$488,926
$51,535
$437,391
$56,689
$380,702
$62,358
$318,344
$68,594
$249,751
$75,453
$174,298
$82,998
$91,300
$91,300
$0
$900,000
Homework Problem:
2.
RVO Corp. sold a piece of real estate on January 2, 2009 for $10,000,000. It had
purchased the property in 2001 for $6,500,000 in cash. At that time the land was
worth $500,000. At the time of the sale, the carrying value of the building was
$4,500,000.
The terms of the sale were as follows:
Downpayment
$ 500,000
Note Receivable
$ 9,500,000
Interest rate
12%
Length of mortgage
20 years
Annual payment
$ 1,115,866 due at end of each year
The sale has been consummated, the seller's receivable is not subject to future
subordination, and the seller has no continuing involvement with the property. However,
because the initial investment is inadequate, the seller must use the installment method to
account for this sale.
REQUIRED: Journal entries needed in 2009, and 2010