Cell – a basic unit of structure and function in all organisms
advertisement

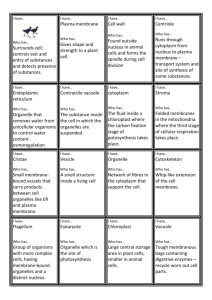
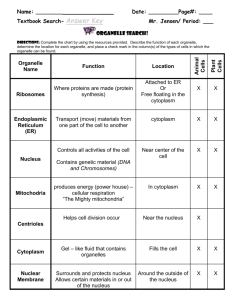
Cell – a basic unit of structure and function in all organisms. Cell theory – states that: all organisms are made up of one or more cells the cell is the basic unit of life all cells come from other cells Eukaryote – an organism whose cells have a nucleus and organelles Multicellular – composed of more than one cell Organelle – structure in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell that can act as a storage site, process energy, move materials, or manufacture substances Prokaryote – a unicellular organism that lacks a true nucleus and membrane organelle Unicellular – composed of only one cell Cell membrane – the semi-permeable membrane that controls what goes in and out of the cell Cytoplasm – Jelly like fluid in the cell. Chemical processes happen in the cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum – organelle in the cytoplasm that moves materials around in a cell and is made up of a complex series of folded membranes; can be rough or smooth Golgi bodies – organelles that package cellular material and transport them within the cell or out of the cell Lysosomes – the organelle that contains enzymes to break down or digest organic compounds and old organelle Mitrochondria – any of the very tiny rod-like structures that process food for energy. Mitochondria produce energy for the cell Nucleus – the part of a cell that controls growth and reproduction. Ribsome – small structure on which cells make their own proteins Vacuole – Sacs inside of the cell used for storage Cell wall – the rigid, outermost layer of a plant cell Chlorophyll – the green pigment in the leaves and stems of plants that is necessary for the production of plant food by photosynthesis Chloroplast – a small oval green bit of protoplasm that contains chlorophyll and is the location of photosynthesis. Nucleolus – a small spherical body in the nucleus of a cell, consisting of protein and RNA. Disease Vocabulary Active immunity: protection against a disease acquired by being infected with the pathogen that causes the disease. Amoebic dysentery: a disease that is caused by a parasite. The protist amoeba that is found in contaminated food and water. Antibiotic: a group of medicines used to kill or slow the growth of bacteria that cause disease. Antibody: a chemical substance made by the body to help destroy an invading pathogen. Antimicrobial product: is a substance that is designed to kill microbes before they enter the body. Carrier: a person with a disease that they can pass on to other organisms. Contagion: an infectious disease that can be transmitted or spread from one organism to another. Disease: is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Epidemic: a disease that spreads over a wide geographic area. Infectious disease: any disease that is caused by a pathogen. Influenza: an acute, commonly epidemic disease, occurring in several forms, caused by numerous rapidly mutating viral strains and characterized by respiratory symptoms. Noninfectious disease: a disease that cannot be spread from one organism to another. Pathogen: a microbe that causes disease in an organism. Polio: an acute viral disease marked by inflammation of nerve cells of the brain stem and spinal cord. Small pox: is an infectious disease unique to humans, caused by either of two virus: variants named Variola major and Variola minor. Vaccine: any preparation used as a preventive inoculation to confer immunity against a specific disease, usually employing an innocuous form of the disease agent, as killed or weakened bacteria or viruses, to stimulate antibody production. Vector: an animal that carries and transmits a disease.