summary
advertisement

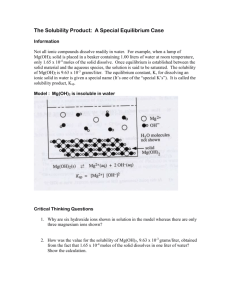
Unit 2 Summery Solids and Liquids Intermolecular Forces (Weakest to Strong) o London Dispersion – non-polar/non-polar o Dipole-Dipole – polar/polar o Hydrogen Bond – ultra polar/ultra polar H with N,O,F o Covalent Bond – non-metal/non-metal Cubic Crystal Structures o Simple Cubic (1 atom) V = e3 = 8r3 o Body-Centered Cubic (2 atoms) o 4r = V = e3 =(4r/ e )3 Face-Centered Cubic (4 atoms) V = e3 = (4r/ )3 o Density = m/v = g/e3 Phase Changes o Matter exists as solids, liquids, or gases o Matter changes between these three phases based on temperature or atmospheric pressure o Phase Diagrams – show which state matter exist at certain temp and pressure Triple Point (T) – all three phases are at equilibrium Critical Point (C) – highest temp of pressure where a distinct gas and liquid phase can exist Supercritical Fluid (SCF) – liquid and gas phases are indistinguishable Solubility The amount of substance that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature (g/L) Some Simple Solubility Rules o NO3- is always soluble o C2H3O2- is always soluble o See Appendix A-8 for full solubility rules Equilibrium ( aA + bB cC + dD ) Occurs when opposing reactions proceed at equal rates with constant concentrations KC = equilibrium constant o KC = [(C)c(D)d]/[(A)a(B)b] o No Solids and Liquids included in equation Q = Reaction Quotient o Q = [(C)c(D)d]/[(A)a(B)b] o When not at equilibrium o Q < K Shift Right, Q > K Shift Left, Q = K Equilibrium Established o No solids or liquids included in equation KP = KC(RT)-n KSP = solubility product constant, this indicates how soluble a solid is in water o KSP = (C)c(D)d o Reactants are Solids so they are not included in the equation LeChâtlier’s Principle – A system in equilibrium, when disturbed, will shift to the extent necessary to restore equilibrium o N2 + 3H2 2NH3 + 94K Disturbance add N2: reactant is increased so product is increased, shift right Disturbance increase temp: tries to lower temp, lower products, shift left Disturbance increase pressure: will favor side with fewer moles, fewer moles on product side, increase products, shift right Disturbance add catalyst: reaction goes faster but no change to each side, no shift Predicting Formation of precipitates based on Ksp o Knet = Ksp x Kf Kf = formation constant o Used in reactions with complex ions o Lower Ksp means it’s less soluble. The combination with a complex ion makes it more soluble (the Kf value cancels out the Ksp value). Solutions Concentration Units o Cmolar = nsolute/Vsolution o Cmolal = nsolute /msolvent (kg) o Mass Percent = msolute /msolution o Mole Fraction = nsolute /nsolution o Volume Fraction = Vsolute /Vsolution o Parts Per Million (PPM) = msolute (mg) / msolvent (kg) ≈ msolute (mg) / msolution (kg) Henry’s Law o Sg = kHPg o The solubility of gas increases in direct proportion to the partial pressure above the solution Colligative Properties o Boiling Point Elevation: Tb = iCmolalKb i = Van’t Hoff Factor – when dissolved , # of particles the molecule breaks into (Ex. NaCl = 2) Kb = Boiling point elevation constant Ions make it harder for water molecules to vaporize, thus requiring more energy to boil o Freezing Point Depression: Tf = iCmolalKf Kf = freezing point depression constant Ions make it harder for water molecules to form an orderly crystalline structure Raoult’s Law (Vapor Pressure) o PA = XAPOA o PA = solution vapor pressure o XA = mole fraction of solvent (nsolvent/nsolution) o POA = solvent vapor pressure o Adding a non-volatile solute to a solution will lower the vapor pressure, thus raising the boiling point Osmosis o V = nRT o = nRT/V = CmolarRT = osmotic pressure R = 8.314 Pascals (Pa) = 0.08206 atm o Pressure required to prevent osmosis by a solvent toward a solution with a higher solute concentration