The Solubility Product Constant Interactive (1 of 2)
advertisement

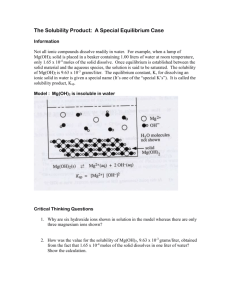
The Solubility Product Constant, Ksp Key Vocabulary Saturated Solution – a solution containing the maximum quantity of a solute at a specific temperature and pressure. Supersaturated Solution – Strong Electrolyte – salt solutions that contain highly soluble salt e.g. NaCl(aq) or MgSO4(aq) Weak Electrolyte – Solubility – Solubility Equilibrium – Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) – Heterogeneous Equilibrium: A Solubility System X-ray technicians give patients barium sulphate suspension prior to x-ray barium sulphate is opaque to x-rays, helping to define body barium sulphate crystals added to water, barium and sulphate ions leave the surface of solid and enter the solution (forward change, dissolving occurs at a greater rate than the reverse change BaSO4(s) Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) As more ions enter the solution, the rate of the reverse change, recrystallisation, increases. Eventually, the rate of recrystallisation becomes equal to the rate of dissolving System is than considered at equilibrium Since reactants and products are in different phases, the reaction is said to have reached heterogeneous equilibrium 1 The Solubility Product Constant when excess solid is present in a saturated solution, we can write the equilibrium constant expression for the dissolution of the solid in the same way that we wrote the equilibrium constant expression for a homogenous equilibrium [ Ba 2 ( aq) ][ SO4 Kc BaSO4( s ) 2 ( aq ) ] the concentration of a solid, however, is itself a constant at a constant temperature, therefore one can combine the term for the concentration of the solid with the equilibrium constant to arrive at a new constant 2 2 ( aq ) c 4( s ) 4 ( aq ) K [ BaSO ] [ Ba ][ SO K sp [ Ba 2 ( aq) ][ SO4 2 ( aq ) ] ] the new constant is called the solubility product constant, Ksp In general, for the dissociation equilibrium equation BC(s) bB+(aq) + cC-(aq) where BC(s) is a slightly soluble salt, and B+(aq) and C-(aq) are aqueous ions Ksp = [B+(aq)]b[C-(aq)]c The Ksp equals the ION PRODUCT of a saturated solution in which dissolved and undissolved solutes are in DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM. For example, Li2CO3(s) Ksp values can be found on p. 802 Table C8 Example 1 Write the balanced chemical equation that represents the dissociation of each compound in water. Then write the corresponding solubility product expression. (a) calcium phosphate (b) barium fluoride 2 Calculating Ksp from Solubility Values Example 2 A chemist finds that the solubility of silver carbonate, Ag2CO3, is 1.3 x 10-4 mol/L at 25ºC. Calculate Ksp for the silver carbonate. Calculating Solubilities from Ksp values Example 3 Calculate the solubility of iron(II) carbonate at 25°C. The Ksp of FeCO3(s) is 3.5 x 10-11 at 25°C 3