ATOMIC PHYSICS WORKSHEET
advertisement

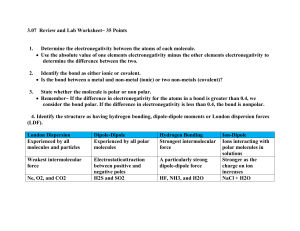
CHAPTER 18: ELECTRONEGATIVITY AND POLARITY CLASSNOTES NON-POLAR VERSUS POLAR MOLECULES Atoms can share electrons evenly or unevenly. Atoms that share electrons evenly form covalent molecules. Atoms that share electrons unevenly form polar molecules. POLAR MOLECULES Because electrons in polar molecules are distributed unevenly, polar molecules have partial positive (+) regions and partial negative (-) regions. Polar molecules are sometimes called dipoles because, like magnets, they form two opposite poles. THE WATER MOLECULE Water is a typical example of a polar molecule. The central oxygen atom holds valence electrons closer to itself than the hydrogen atoms. This creates a partial negative charge around the oxygen and partial positive charge around the hydrogen atoms within the molecule. THE WATER MOLECULE + = partial positive charge - = partial negative charge ELECTRONEGATIVITY Some elements attract and hold on to electrons better than others. Electronegativity measures the affinity that particular atoms have for electrons. ELECTRONEGATIVITY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Electronegativity values range from 0.7 (cesium) to 4.0 (fluorine). In general, electronegativity increases from the lower left-hand corner of the periodic table (large alkali metals) to the upper righthand corner of the periodic table (small halogen gases). ELECTRONEGATIVITY TRENDS CHEMICAL BONDS In general, there are three types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and polar. Ionic bonds form when electrons completely transfer from metal atoms to non-metal atoms. Covalent bonds form when atoms share their electrons evenly. Polar bonds form when atoms share their electrons unevenly. ELECTRONEGATIVITY TABLES Electronegativity tables predict the types of bonds formed between atoms. Example 7. A fluorine and a hydrogen atom combine and form hydrogen fluoride. According to electronegativity values, what type of compound is hydrogen fluoride? (A) covalent (B) polar (C) ionic 7A. (B) polar. Fluorine has a 4.0 electronegativity and hydrogen has a 2.1 electronegativity. The difference between these electronegativity values is: 4.0 – 2.1 = 1.9. This means hydrogen fluoride is a polar molecule.



![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-300x300.png)